|
Succinic Semialdehyde Reductase
Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AKR7A2'' gene. Function Aldo-keto reductases, such as AKR7A2, are involved in the detoxification of aldehydes and ketone In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double b ...s. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> References External links * * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * EC 1.1.1 Gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde Reductase
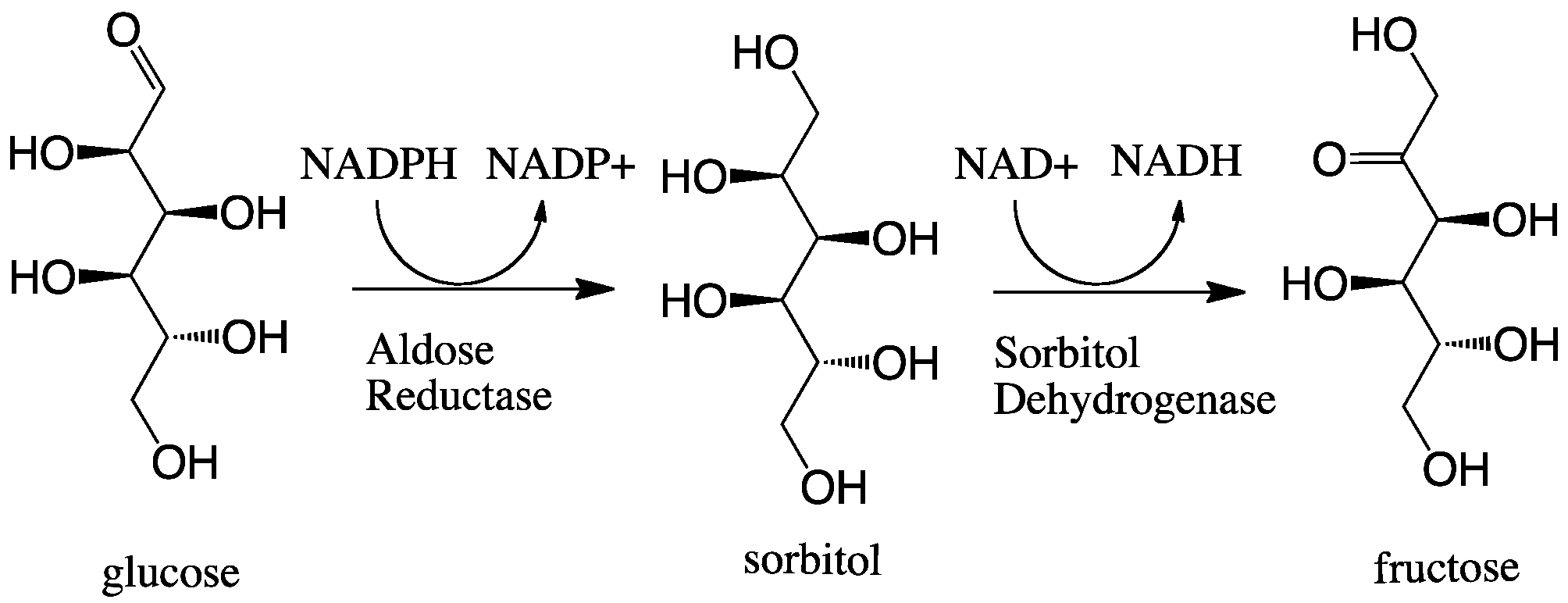
In enzymology, aldose reductase (or aldehyde reductase) () is a cytosolic NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reduction of a variety of aldehydes and carbonyls, including monosaccharides. It is primarily known for catalyzing the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. Reactions Aldose reductase catalyzes the NADPH-dependent conversion of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. The second and last step in the pathway is catalyzed by sorbitol dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the NAD-linked oxidation of sorbitol to fructose. Thus, the polyol pathway results in conversion of glucose to fructose with stoichiometric utilization of NADPH and production of NADH. ;glucose + NADPH + H+ \rightleftharpoons sorbitol + NADP+ Galactose is also a substrate for the polyol pathway, but the corresponding keto sugar is not produced because sorbitol dehydrogenase is incapable of oxidizing galactitol. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus '' Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldo-keto Reductase
The aldo-keto reductase family is a family of proteins that are subdivided into 16 categories; these include a number of related monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases, such as aldehyde reductase, aldose reductase, prostaglandin F synthase, xylose reductase, rho crystallin, and many others. Structure All possess a similar structure, with a beta-alpha-beta fold characteristic of nucleotide binding proteins. The fold comprises a parallel beta-8/alpha-8-barrel, which contains a novel NADP-binding motif. The binding site is located in a large, deep, elliptical pocket in the C-terminal end of the beta sheet, the substrate being bound in an extended conformation. The hydrophobic nature of the pocket favours aromatic and apolar substrates over highly polar ones. Binding of the NADPH coenzyme causes a massive conformational change, reorienting a loop, effectively locking the coenzyme in place. This binding is more similar to FAD- than to NAD(P)-binding oxidoreductases. Examples So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detoxification
Detoxification or detoxication (detox for short) is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. Additionally, it can refer to the period of drug withdrawal during which an organism returns to homeostasis after long-term use of an addictive substance. In medicine, detoxification can be achieved by decontamination of poison ingestion and the use of antidotes as well as techniques such as dialysis and (in a limited number of cases) chelation therapy. Many alternative medicine practitioners promote various types of detoxification such as detoxification diets. Scientists have described these as a "waste of time and money". Sense About Science, a UK-based charitable trust, determined that most such dietary "detox" claims lack any supporting evidence. The liver and kidney are naturally capable of detox, as are intracellular (specifically, inner membrane of mitochondria or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile aldehydes have pungent odors. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |