|
Substantive Adjective
A nominalized adjective is an adjective that has undergone nominalization, and is thus used as a noun. In ''the rich and the poor'', the adjectives ''rich'' and ''poor'' function as nouns denoting people who are rich and poor respectively. In English The most common appearance of the nominalized adjective in English is when an adjective is used to indicate a collective group. This happens in the case where a phrase such as ''the poor people'' becomes ''the poor''. The adjective ''poor'' is nominalized, and the noun ''people'' disappears. Other adjectives commonly used in this way include ''rich'', ''wealthy'', ''homeless'', ''disabled'', ''blind'', ''deaf'', etc., as well as certain demonyms such as ''English'', ''Welsh'', ''Irish'', ''French'', ''Dutch''. Another case is when an adjective is used to denote a single object with the property, as in "you take the long route, and I'll take the ''short''". Here ''the short'' stands for "the short route". A much more common alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that generally grammatical modifier, modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the main part of speech, parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with Noun, nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as Determiner (class), determiners. Here are some examples: * That's a funny idea. (attributive) * That idea is funny. (predicate (grammar), predicative) * * The good, the bad, and the funny. (substantive adjective, substantive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of grc, ἐπίθετον ὄνομα, epítheton ónoma, additional noun (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of singular or plural, both of which are cited by using the hash sign (#) or by the numero signs "No." and "Nos." respectively. Some languages also have a dual, trial and paucal number or other arrangements. The count distinctions typically, but not always, correspond to the actual count of the referents of the marked noun or pronoun. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Class (linguistics)
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particular t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Noun
Empty may refer to: Music Albums * ''Empty'' (God Lives Underwater album) or the title song, 1995 * ''Empty'' (Nils Frahm album), 2020 * ''Empty'' (Tait album) or the title song, 2001 Songs * "Empty" (The Click Five song), 2007 * "Empty" (Garbage song), 2016 * "Empty", by Bebe Rexha from ''Better Mistakes'', 2021 * "Empty", by Belmont from '' Belmont'', 2018 * "Empty", by Blair St. Clair from ''Identity'', 2020 * "Empty", by Boyinaband featuring Jaiden Animations, 2018 * "Empty", by Cooliecut, Kin$oul, Craig Xen, and Ski Mask the Slump God from ''Members Only, Vol. 4'', 2019 * "Empty", by the Cranberries from ''No Need to Argue'', 1994 * "Empty", by Harry Chapin from '' Heads & Tales'', 1972 * "Empty", by Juice Wrld from ''Death Race for Love'', 2019 * "Empty", by King Gizzard & the Lizard Wizard from ''I'm in Your Mind Fuzz'', 2014 * "Empty", by Metric from ''Live It Out'', 2005 * "Empty", by Neurosis from ''Souls at Zero'', 1992 * "Empty", by Olivia O'Brien, 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram Of A Noun Phrase With Both The Noun And The Adjective
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Nouns
In linguistics, a count noun (also countable noun) is a noun that can be modified by a quantity and that occurs in both singular and plural forms, and that can co-occur with quantificational determiners like ''every'', ''each'', ''several'', etc. A mass noun has none of these properties: It cannot be modified by a number, cannot occur in plural, and cannot co-occur with quantificational determiners. Examples Below are examples of all the properties of count nouns holding for the count noun ''chair'', but not for the mass noun ''furniture''. * Occurrence in plural. : There is a chair in the room. (correct) : There are chairs in the room. (correct) : There is chair in the room. (incorrect) : There is a furniture in the room. (incorrect) : There are furnitures in the room. (incorrect) : There is furniture in the room. (correct) * Co-occurrence with count determiners : Every chair is man-made. : There are several chairs in the room. : Every furniture is man-made. (incorrect) : Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definite
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical definite noun phrase picks out a unique, familiar, specific referent such as ''the sun'' or ''Australia'', as opposed to indefinite examples like ''an idea'' or ''some fish''. There is considerable variation in the expression of definiteness across languages, and some languages such as Japanese do not generally mark it so that the same expression could be definite in some contexts and indefinite in others. In other languages, such as English, it is usually marked by the selection of determiner (e.g., ''the'' vs ''a''). In still other languages, such as Danish, definiteness is marked morphologically. Definiteness as a grammatical category There are times when a grammatically marked definite NP is not in fact identifiable. For example, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Item
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words ( catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also sometimes used. Types Common types of lexical items/chunks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and Official language, official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italy, Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots language, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic languages, North Germanic group, such as Danish lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Poor Rich
''The Poor Rich'' is a 1934 American pre-Code comedy film directed by Edward Sedgwick and written by Ebba Havez and Dale Van Every. The film stars Edward Everett Horton, Edna May Oliver, Andy Devine, Leila Hyams, Grant Mitchell and Thelma Todd. The film was released on February 26, 1934, by Universal Pictures. Plot A once wealthy American dynasty, the Spottiswoods, envision their financial salvation in marrying into money via an upcoming visit from the British (and actually wealthy) Fetherstones. To play the part, the Spottiswoods must quickly rehabilitate their estate to have a veneer of class and enlist a cadre of quirky workers to act as their domestic servants. Hijinks ensue. Cast *Edward Everett Horton as Albert Stuyvesant Spottiswood *Edna May Oliver as Harriet Spottiswood *Andy Devine as Andy *Leila Hyams as Grace Hunter * Grant Mitchell as Tom Hopkins *Thelma Todd as Gwendolyn Fetherstone * Una O'Connor as Lady Fetherstone *E. E. Clive as Lord Fetherstone *John Miljan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Determiner Phrase
In linguistics, a determiner phrase (DP) is a type of phrase headed by a determiner such as ''many''. Controversially, many approaches, take a phrase like ''not very many apples'' to be a DP, headed, in this case, by the determiner ''many''. This is called the DP analysis or the DP hypothesis. Others reject this analysis in favor of the more traditional NP (noun phrase or nominal phrase) analysis where ''apples'' would be the head of the phrase in which the DP ''not very many'' is merely a dependent. Thus, there are competing analyses concerning heads and dependents in nominal groups. The DP analysis developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and it is the majority view in generative grammar today. In the example determiner phrases below, the determiners are in boldface: * a little dog, the little dogs (indefinite or definite articles) * my little dog, your little dogs (possessives) * this little dog, those little dogs (demonstratives) * every little dog, each little dog, no dog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
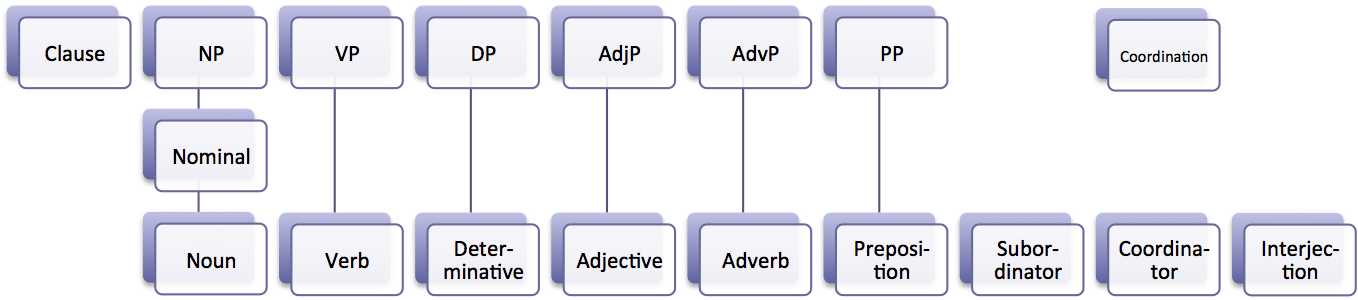
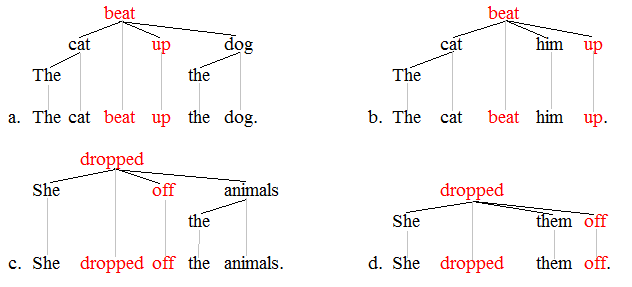
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |