|
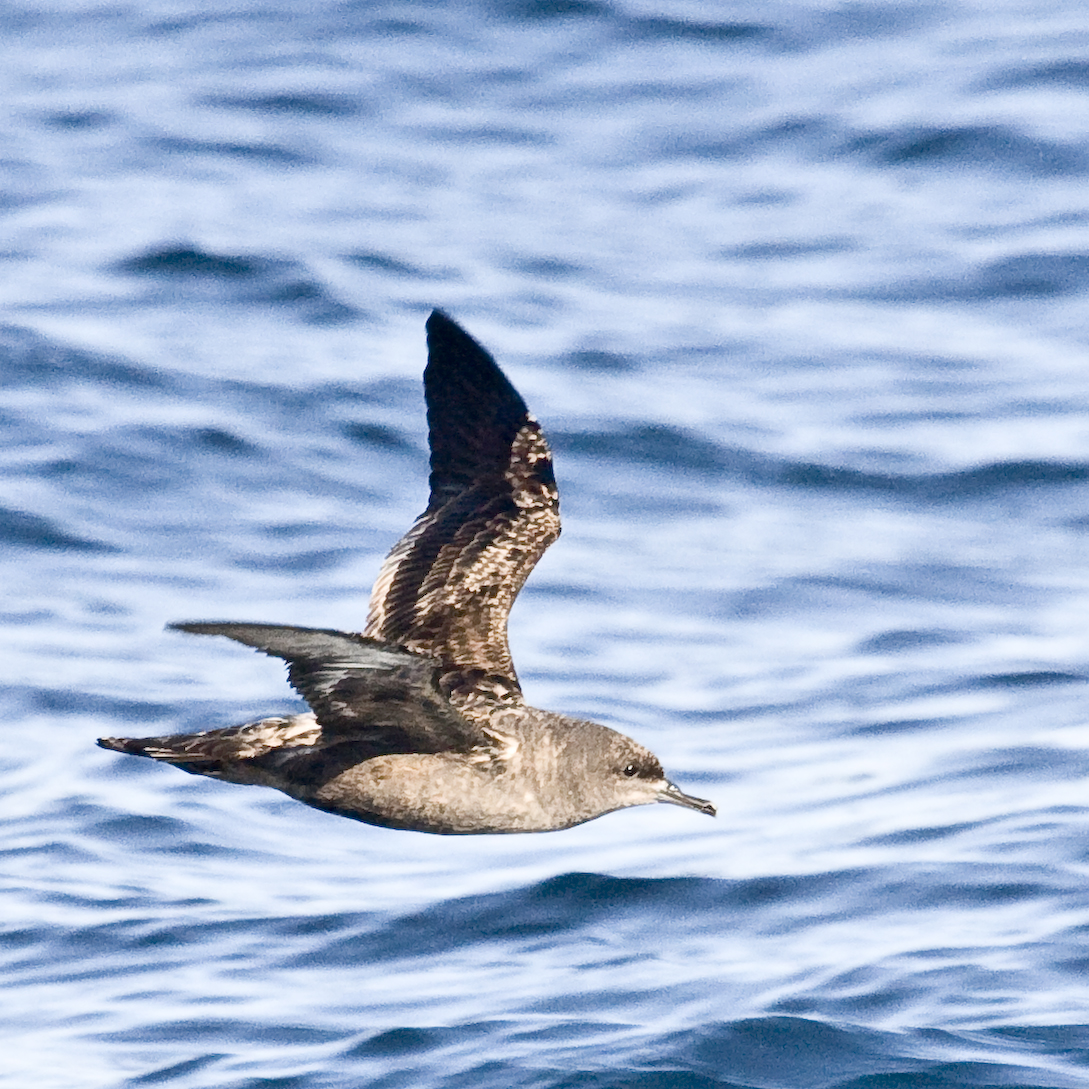
Subantarctic Snipe
The Subantarctic snipe (''Coenocorypha aucklandica'') is a species of snipe endemic to New Zealand's subantarctic islands. The Maori call it "Tutukiwi". The nominate race ''C. a. aucklandica'' (Auckland snipe) is found on the Auckland Islands (excluding the main island). Other subspecies include ''C. a. meinertzhagenae'' (Antipodes snipe) from the Antipodes Islands, and ''C. a. perseverance'' (Campbell snipe) from Campbell Island. The former subspecies from the Snares Islands has been separated as a full species, the Snares snipe (''C. huegeli''), as have the extinct South Island (''C. iredalei'') and North Island snipes (''C. barrierensis''). Description The Subantarctic snipe is a small wading bird with adults growing to about in length. It has cryptic brown plumage, sturdy legs and a slender beak about long. The head is striped in black and reddish brown and the body is brown, mottled with black and reddish brown. Distribution The Subantarctic snipe is endemic to certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Robert Gray
George Robert Gray FRS (8 July 1808 – 6 May 1872) was an English zoologist and author, and head of the ornithological section of the British Museum, now the Natural History Museum, in London for forty-one years. He was the younger brother of the zoologist John Edward Gray and the son of the botanist Samuel Frederick Gray. George Gray's most important publication was his ''Genera of Birds'' (1844–49), illustrated by David William Mitchell and Joseph Wolf, which included 46,000 references. Biography He was born in Little Chelsea, London, to Samuel Frederick Gray, naturalist and pharmacologist, and Elizabeth (née Forfeit), his wife. He was educated at Merchant Taylor's School. Gray started at the British Museum as Assistant Keeper of the Zoology Branch in 1831. He began by cataloguing insects, and published an ''Entomology of Australia'' (1833) and contributed the entomogical section to an English edition of Georges Cuvier's ''Animal Kingdom''. Gray described many spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island Snipe
The South Island snipe (''Coenocorypha iredalei''), also known as the Stewart Island snipe or tutukiwi in Māori, is an extinct species of bird in the sandpiper family Scolopacidae that was endemic to New Zealand. Taxonomy and etymology Determination of the taxonomy of ''Coenocorypha'' snipe has been hindered by lack of material, erroneous locality data, misidentified specimens and confused nomenclature.Higgins & Davies (1996). The South Island snipe was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the Subantarctic snipe (''Coenocorypha aucklandica''), but has since been elevated to a full species, with fossil material from the South Island referred to it.Baker ''et al''. (2009). The specific epithet honours ornithologist Tom Iredale. The Māori name, "tutukiwi", which may be applied to other ''Coenocorypha'' snipes, alludes to the bird's fancied resemblance to a miniature kiwi.Oliver (2005). Distribution and extinction The South Island snipe is extinct. Its prehistoric distributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Described In 1845
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the Common ostrich, ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenocorypha
The austral snipes, also known as the New Zealand snipes or tutukiwi, are a genus, ''Coenocorypha'', of tiny birds in the sandpiper family (biology), family, which are now only found on New Zealand outlying islands, New Zealand's outlying islands. There are currently three living species and six known extinct species, with the Subantarctic snipe having three subspecies, including the Campbell Island snipe discovered as recently as 1997. The genus was once distributed from Fiji, New Caledonia and Norfolk Island, across New Zealand and southwards into New Zealand's subantarctic islands, but predation by introduced species, especially rats, has drastically reduced their range. Taxonomy and range The relationship between ''Coenocorypha'' snipe and the snipes of the genus ''Gallinago'' is uncertain. ''Coenocorypha'' is sometimes thought to be a relict taxon of an ancient lineage;Tennyson, A., & Martinson, P. (2006). ''Extinct Birds of New Zealand''. Te Papa Press, Wellington . however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of New Zealand
Many of New Zealand's birds are endemic to the country, that is, they are not found in any other country. Approximately 71% of the bird species breeding in New Zealand before humans arrived are widely accepted as being endemic. There is also a smaller group of species are not fully endemic, but are breeding endemic, in that they breed only in New Zealand, but migrate or range elsewhere. Population status symbols are those of the Red List published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.''The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species''. Version 2017-1 . Accessed 23 May 2017 The symbols and their meanings, in increasing order of peril, are: = least concern = near threatened = vulnerable = endangered = critically endangered = extinct Endemic Bird Areas BirdLife International has defined the following Endemic Bird Areas (EBAs) in New Zealand: * Auckland Islands * Chatham Islands * North Island of New Zealand * South Island of New Zealand In addition the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
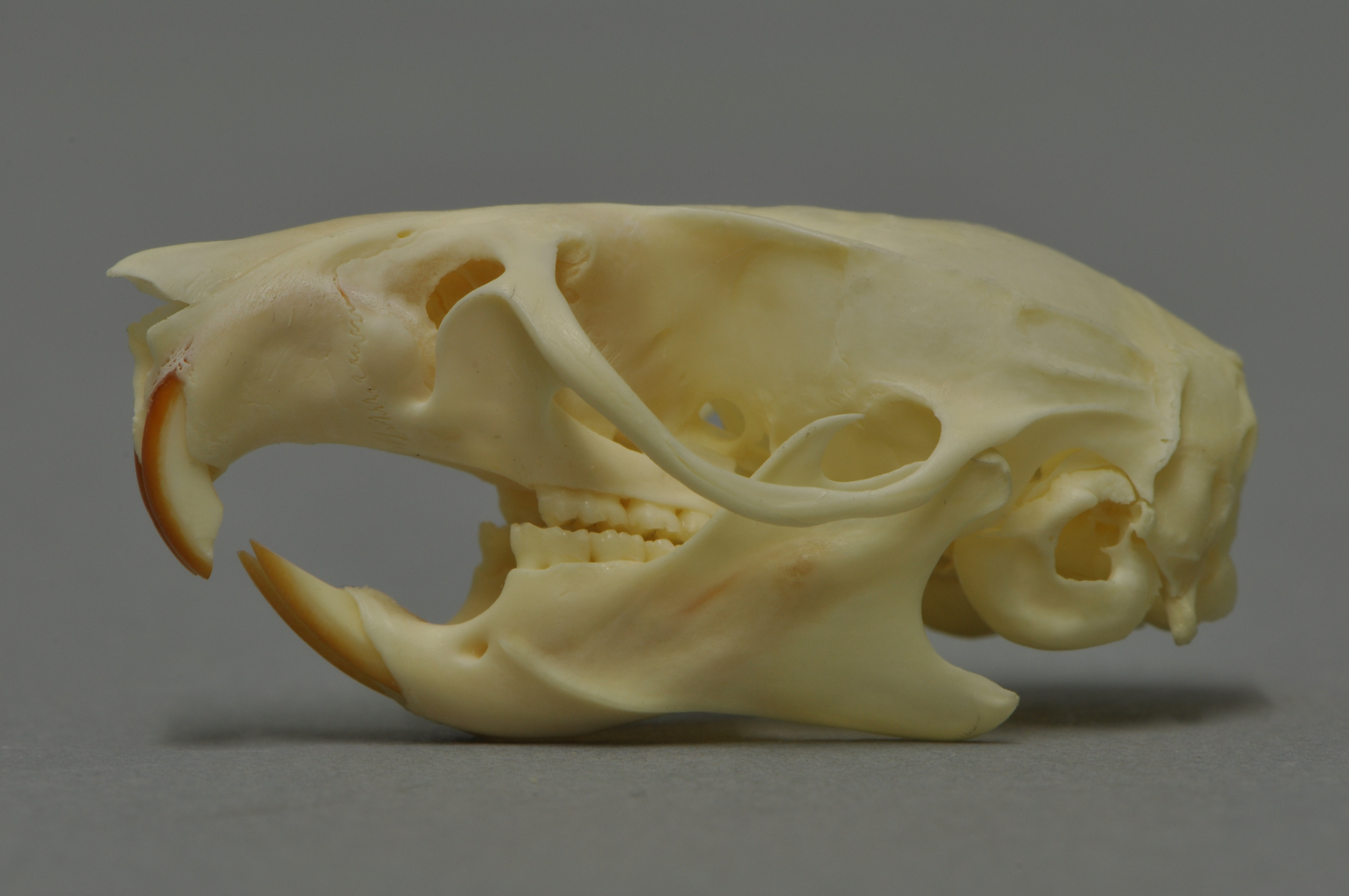
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is long, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big South Cape Island
Big South Cape Island or Taukihepa is an offshore island of New Zealand to the west of the southern tip of Stewart Island / Rakiura. The island has no permanent inhabitants but muttonbirders visit the island to catch the sooty shearwater, known in New Zealand as a "muttonbird". Māori named the island "Taukihepa" and Europeans, who arrived later, called it "Big South Cape". The island was given dual names in 2001 as part of a Treaty of Waitangi settlement with Ngāi Tahu. The island is the largest of a group of islands off the southwestern coast of Stewart Island / Rakiura, from which it is separated by a wide channel. Surrounding smaller islands include Poutama Island to the south, Putauhina Island and the Putauhina Nuggets to the northwest, and Solomon Island to the north. The island rises to a height of at its centre, and numerous small streams run to the coast. Named features on the island include two inlets – Murderers Cove in the central east coast and Puwai Bay in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weka
The weka, also known as the Māori hen or woodhen (''Gallirallus australis'') is a flightless bird species of the rail family. It is endemic to New Zealand. It is the only extant member of the genus ''Gallirallus''. Four subspecies are recognized but only two (northern/southern) are supported by genetic evidence. The weka are sturdy brown birds, about the size of a chicken. As omnivores, they feed mainly on invertebrates and fruit. Weka usually lay eggs between August and January; both sexes help to incubate. Description Weka are large rails. They are predominantly rich brown mottled with black and grey; the brown shade varies from pale to dark depending on subspecies. The male is the larger sex at in length and in weight. Females measure in length and weigh . The reduced wingspan ranges from . The relatively large, reddish-brown beak is about long, stout and tapered, and used as a weapon. The pointed tail is near-constantly being flicked, a sign of unease characteristic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle and mimicry. Crypsis can involve visual, olfactory (with pheromones) or auditory concealment. When it is visual, the term cryptic coloration, effectively a synonym for animal camouflage, is sometimes used, but many different methods of camouflage are employed by animals or plants. Overview There is a strong evolutionary pressure for animals to blend into their environment or conceal their shape, for prey animals to avoid predators and for predators to be able to avoid detection by prey. Exceptions include large herbivores without natural enemies, brilliantly colored birds that rely on flight to escape predators, and venomous or otherwise powerfully armed animals with warning coloration. Cryptic animals include the tawny frogmouth (feather pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island Snipe
The North Island snipe (''Coenocorypha barrierensis''), also known as the little barrier snipe or tutukiwi, is an extinct species of bird in the sandpiper family, Scolopacidae, that was endemic to New Zealand. Taxonomy and etymology Examination of the taxonomy of ''Coenocorypha'' snipe has been hindered by lack of material, erroneous locality data, misidentified specimens and confused nomenclature.Higgins & Davies (1996). The North Island snipe was described in 1955 by Walter Oliver as a subspecies of the Subantarctic snipe (''Coenocorypha aucklandica''), but has since been elevated to a full species, with fossil material from the North Island referred to it.Baker ''et al''. (2009). The specific epithet and older common name refer to the type locality. Distribution and extinction The North Island snipe is extinct. Its prehistoric distribution comprised the North Island where subfossil remains have been found in several places. It became extinct on the mainland of North Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_with_its_prey.jpg)