|
Stub (electronics)
In microwave and radio-frequency engineering, a stub or resonant stub is a length of transmission line or waveguide that is connected at one end only. The free end of the stub is either left open-circuit, or short-circuited (as is always the case for waveguides). Neglecting transmission line losses, the input impedance of the stub is purely reactive; either capacitive or inductive, depending on the electrical length of the stub, and on whether it is open or short circuit. Stubs may thus function as capacitors, inductors and resonant circuits at radio frequencies. The behaviour of stubs is due to standing waves along their length. Their reactive properties are determined by their physical length in relation to the wavelength of the radio waves. Therefore, stubs are most commonly used in UHF or microwave circuits in which the wavelengths are short enough that the stub is conveniently small. They are often used to replace discrete capacitors and inductors, because at UHF and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
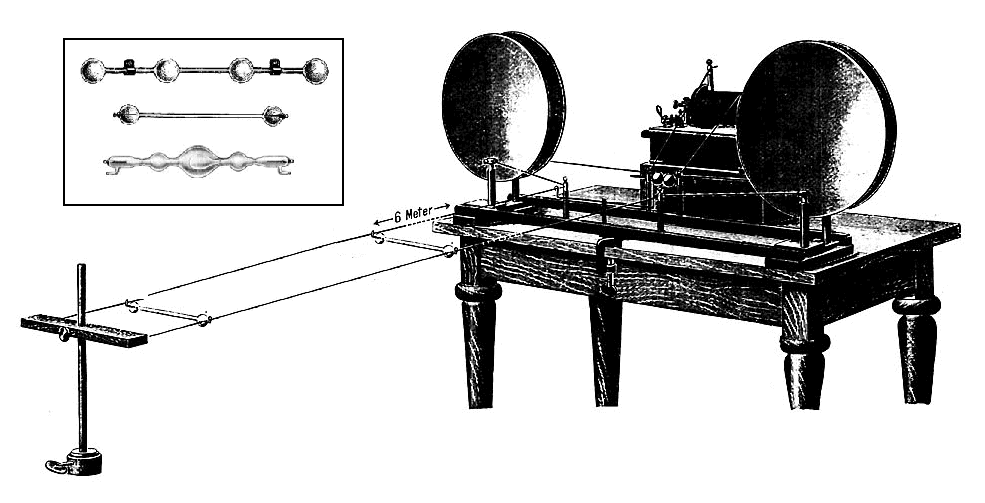
Resonant Stubs In UHF Transceiver 1938
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and reson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumped Component
The lumped-element model (also called lumped-parameter model, or lumped-component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems, such as electrical circuits, into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc. This may be contrasted to distributed parameter systems or models in which the behaviour is distributed spatially and cannot be considered as localized into discrete entities. Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters. Electrical systems Lumped-matter disci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflections Of Signals On Conducting Lines
A signal travelling along an electrical transmission line will be partly, or wholly, reflected back in the opposite direction when the travelling signal encounters a discontinuity in the characteristic impedance of the line, or if the far end of the line is not terminated in its characteristic impedance. This can happen, for instance, if two lengths of dissimilar transmission lines are joined. This article is about signal reflections on electrically conducting lines. Such lines are loosely referred to as copper lines, and indeed, in telecommunications are generally made from copper, but other metals are used, notably aluminium in power lines. Although this article is limited to describing reflections on conducting lines, this is essentially the same phenomenon as optical reflections in fibre-optic lines and microwave reflections in waveguides. Reflections cause several undesirable effects, including modifying frequency responses, causing overload power in transmitters and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Chart
The Smith chart, invented by Phillip H. Smith (1905–1987) and independently by Mizuhashi Tosaku, is a graphical calculator or nomogram designed for electrical and electronics engineers specializing in radio frequency (RF) engineering to assist in solving problems with transmission lines and matching circuits. The Smith chart can be used to simultaneously display multiple parameters including impedances, admittances, reflection coefficients, S_\, scattering parameters, noise figure circles, constant gain contours and regions for unconditional stability, including mechanical vibrations analysis. The Smith chart is most frequently used at or within the unity radius region. However, the remainder is still mathematically relevant, being used, for example, in oscillator design and stability analysis. While the use of paper Smith charts for solving the complex mathematics involved in matching problems has been largely replaced by software based methods, the Smith chart is still a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Waveguide
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light guides, and liquid waveguides. Optical waveguides are used as components in integrated optical circuits or as the transmission medium in local and long-haul optical communication systems. Optical waveguides can be classified according to their geometry (planar, strip, or fiber waveguides), mode structure (single-mode, multi-mode), refractive index distribution (step or gradient index), and material (glass, polymer, semiconductor). Total internal reflection The basic principles behind optical waveguides can be described using the concepts of geometrical or ray optics, as illustrated in the diagram. Light passing into a medium with higher refractive index bends toward the normal by the process of refraction (Figure a.). Take, for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities decrease according to the inverse square law as they expand into three-dimensional space. There are different types of waveguides for different types of waves. The original and most common meaningInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)/ref> is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves. Dielectric waveguides are used at higher radio frequencies, and transparent dielectric waveguides and optical fibers serve as waveguides f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of planar transmission line. Description A stripline circuit uses a flat strip of metal which is sandwiched between two parallel ground planes. The insulating material of the substrate forms a dielectric. The width of the strip, the thickness of the substrate and the relative permittivity of the substrate determine the characteristic impedance of the strip which is a transmission line. As shown in the diagram, the central conductor need not be equally spaced between the ground planes. In the general case, the dielectric material may be different above and below the central conductor. To prevent the propagation of unwanted modes, the two ground planes must be shorted together. This is commonly achieved by a row of vias running parallel to the strip on each side. Like coaxial cable, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ) is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term ''coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer data busses, cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a transmission line. Coaxial cable was used in the first (1858) and followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecher Lines
In electronics, a Lecher line or Lecher wires is a pair of parallel wires or rods that were used to measure the wavelength of radio waves, mainly at VHF, UHF and microwave frequencies. They form a short length of balanced transmission line (a resonant stub). When attached to a source of radio-frequency power such as a radio transmitter, the radio waves form standing waves along their length. By sliding a conductive bar that bridges the two wires along their length, the length of the waves can be physically measured. Austrian physicist Ernst Lecher, improving on techniques used by Oliver Lodge and Heinrich Hertz, developed this method of measuring wavelength around 1888. Lecher lines were used as frequency measuring devices until frequency counters became available after World War 2. They were also used as components, often called " resonant stubs", in VHF, UHF and microwave radio equipment such as transmitters, radar sets, and television sets, serving as tank circuits, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladder Line
Twin-lead cable is a two-conductor flat cable used as a balanced transmission line to carry radio frequency (RF) signals. It is constructed of two stranded or solid copper or copper-clad steel wires, held a precise distance apart by a plastic (usually polyethylene) ribbon. The uniform spacing of the wires is the key to the cable's function as a transmission line; any abrupt changes in spacing would reflect some of the signal back toward the source. The plastic also covers and insulates the wires. It is available with several different values of characteristic impedance, the most common type is 300 ohm. Twin lead is mainly used as an antenna feedline at shortwave and VHF frequencies, to connect radio receivers and transmitters to their antennas. It can have significantly lower signal loss than miniature flexible coaxial cable, the main alternative type of feedline at these frequencies; for example, type RG-58 coaxial cable loses 6.6 dB per 100 m at 30 MHz, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillation, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave or a triangle wave. Oscillation, Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current (AC) signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices ranging from simplest clock generators to digital instruments (like calculators) and complex computers and peripherals etc. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by Transmitter, radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A Low-frequency oscillation, low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |