|
Stripe (pattern)
A stripe is a line or band that differs in color or tone from an adjacent area. Stripes are a group of such lines. Usage and appearance As a pattern (more than one stripe together), stripes are commonly seen in nature, food, emblems, clothing, and elsewhere. Two-toned stripes inherently draw one's attention, and as such are used to signal hazards. They are used in road signs, barricade tape, and thresholds. In nature, as with the zebra, stripes may have developed through natural selection to produce motion dazzle. Stripes may give appeal to certain sweets like the candy cane. For hundreds of years, stripes have been used in clothing. Striped clothing has frequently had negative symbolism in Western cultures. Historian Michel Pastoureau explores the cultural history of these design decisions in the book, '' The Devil's Cloth.'' See also * Square tiling *Sussi cloth * The Devil's Cloth * Argyle (pattern) * Racing flags * Flannel * Gingham * Madras (cloth) * Plaid (pattern) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
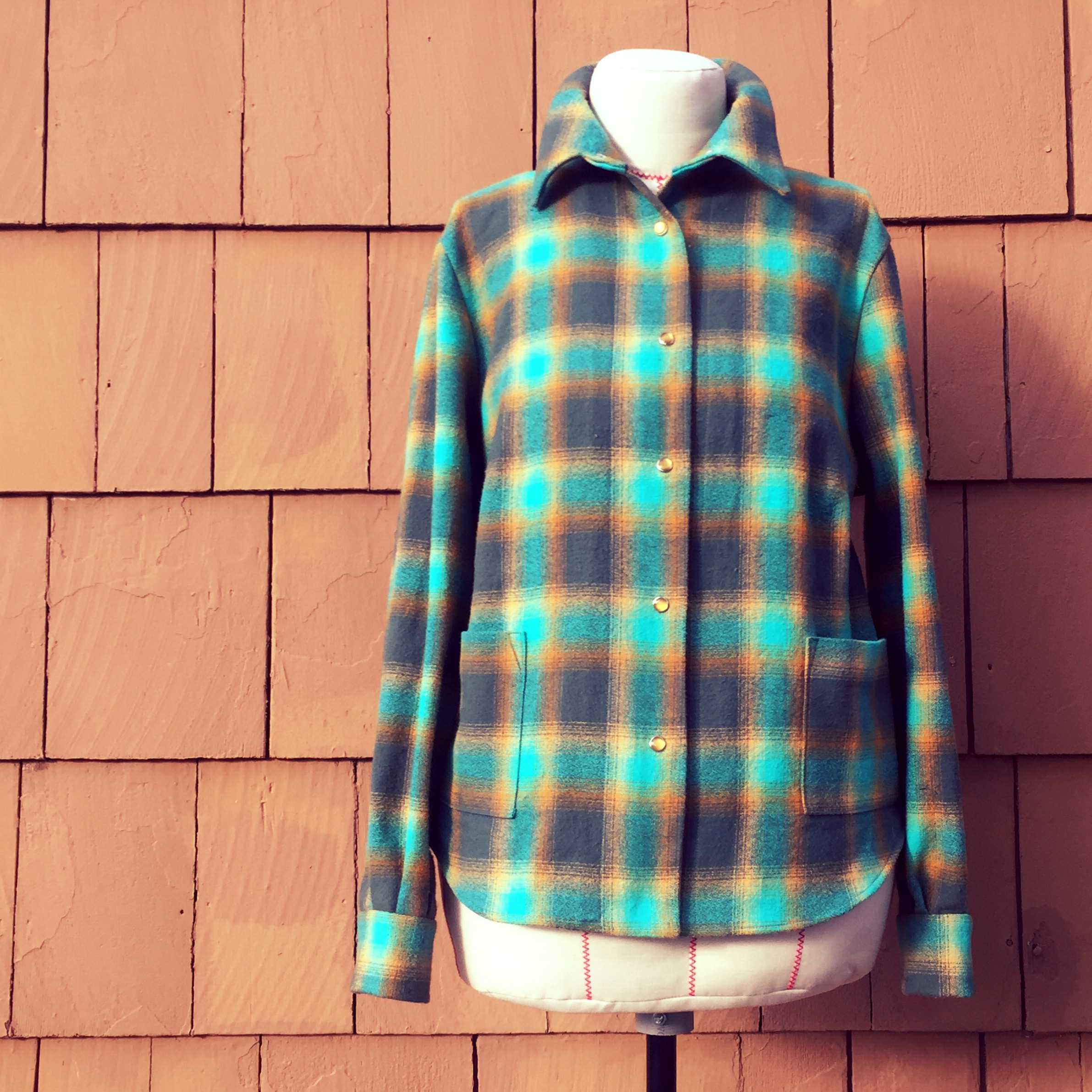
Flannel
Flannel is a soft woven fabric, of various fineness. Flannel was originally made from carded wool or worsted yarn, but is now often made from either wool, cotton, or synthetic fiber. Flannel is commonly used to make tartan clothing, blankets, bed sheets, and sleepwear. Flannel may be brushed to create extra softness or remain unbrushed. Brushing is a mechanical process wherein a fine metal brush rubs the fabric to raise fine fibres from the loosely spun yarns to form a nap on one or both sides. If the flannel is not napped, it gains its softness through the loosely spun yarn in its woven form. The term "flannel shirt" is often mistakenly used to refer to any shirt with a plaid or tartan pattern. However, 'flannel' refers simply to the fabric, and not all flannel shirts are plaid. History The origin of the word is uncertain, but a Welsh origin has been suggested as fabric similar to flannel can be traced back to Wales, where it was well known as early as the 16th century. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
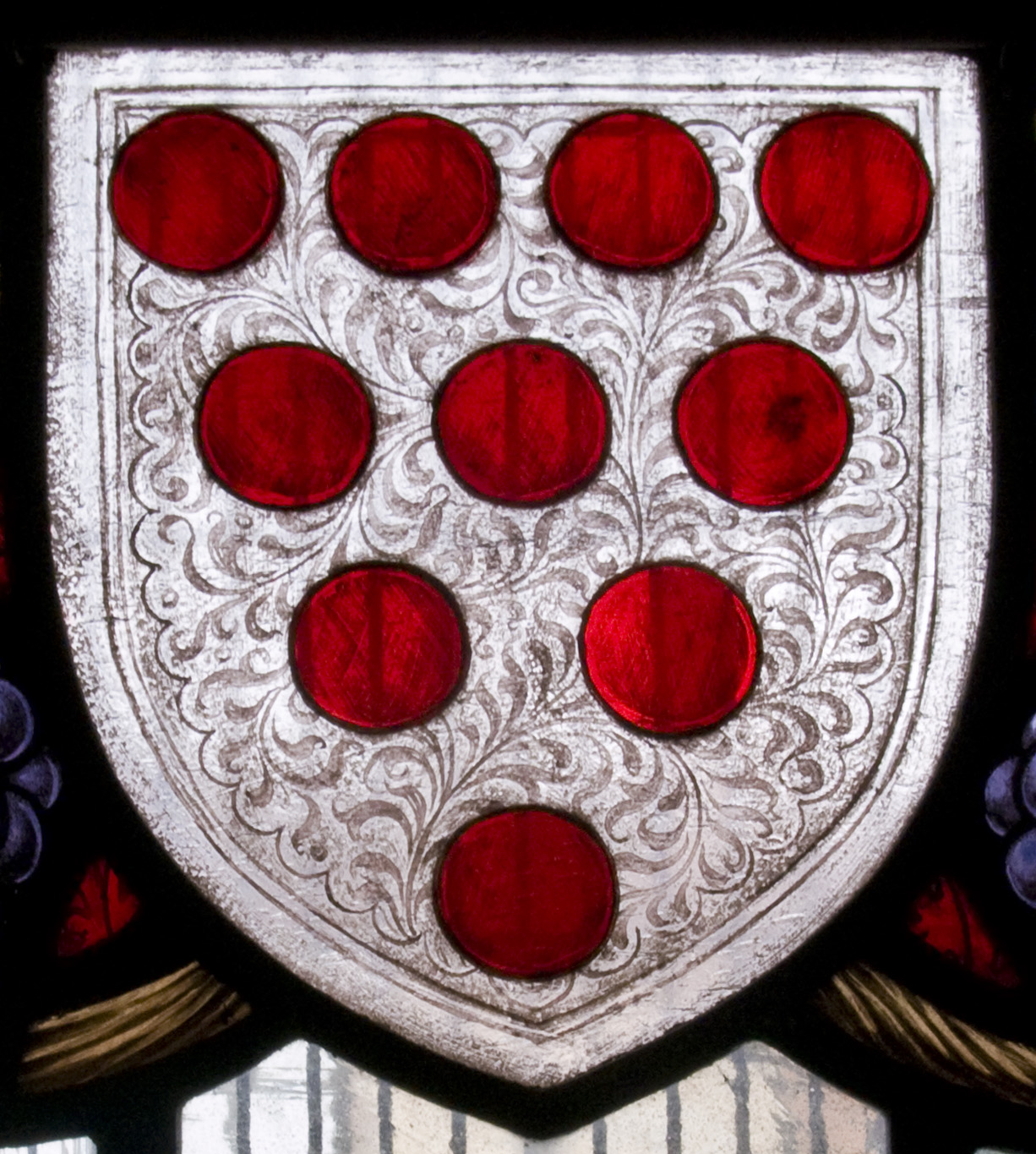
Diapering
Diaper is any of a wide range of decorative patterns used in a variety of works of art, such as stained glass, heraldic shields, architecture, and silverwork. Its chief use is in the enlivening of plain surfaces. Etymology For the full etymology, see "". The Oxford dictionary gives the Greek ''dia'' for "cross" as in "diamond" or "diagonal"; and ''aspros'', Greek for "white". A white diamond or white cloth is used on the diagonal, hence the diagonal lattice or reticulation in patterning. In art In architecture and other decorative arts, diaper is applied as a decorative treatment of a surface with a repeat pattern of squares (chequers), rectangles, or lozenges. Diaper was particularly used in mediaeval stained glass to increase the vividness of a coloured pane, for example the field in a shield of arms. A stone wall may be decorated with such a pattern sculpted in relief; in brickwork the effect may be achieved by using bricks of different colours, or by allowing certain bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
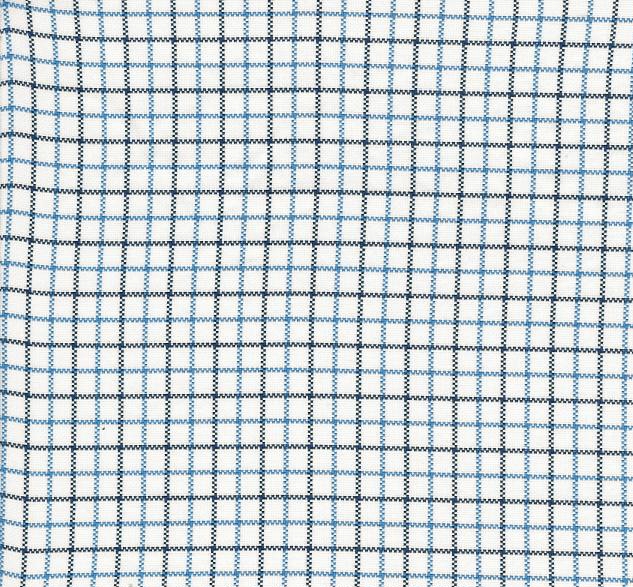
Tattersall (cloth)
Tattersall is a style of check or plaid pattern woven into cloth. The pattern is composed of regularly-spaced thin, even vertical warp stripes, repeated horizontally in the weft, thereby forming squares. The stripes are usually in two alternating colours, generally darker on a light ground. The cloth pattern takes its name from Tattersall's horse market, which was started in London in 1766. During the 18th century at Tattersall's horse market blankets with this checked pattern were sold for use on horses. Today tattersall is a common pattern, often woven in cotton, particularly in flannel, used for shirts or waistcoats. Tattersall shirts, along with gingham, are often worn in country attire, for example in combination with tweed suits and jackets. Traditional waistcoats of this cloth are often used by horse riders in formal riding attire, and adorned with a stock tie. See also * British country clothing British country clothing or English country clothing is the traditional a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartan
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns. Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both warp (weaving), warp and Warp and woof, weft at right angles to each other. The weft is woven in a simple twill, two over—two under the warp, advancing one thread at each pass. This pattern forms visible diagonal lines where different colours cross, which give the appearance of new colours blended from the original ones. The resulting blocks of colour repeat vertically and horizontally in a distinctive pattern of squares and lines known as a ''sett''. Tartan is often called "plaid" (particularly in North America), because in Scotland, a ''Full plaid, plaid'' is a large piece of tartan cloth, wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polka Dot
Red polka dots on a yellow background Girl wearing polka dot dress Polish ceramics German ceramics Polka dot is a pattern consisting of an array of large filled circles of the same size. Polka dots are commonly seen on children's clothing, toys, furniture, ceramics, and Central European folk art, but they appear in a wide array of contexts. The pattern rarely appears in formal contexts, and is generally confined to more playful attire such as bathing suits and lingerie. Occasionally, white-on-black small dots appear on more formal clothing. Etymology It is likely that the term originated because of the popularity of the polka dance around the same time the pattern became fashionable, just as many other products and fashions of the era also adopted the "polka" name. Usage In 1962, DC Comics introduced Polka-Dot Man with irregularly-sized and differently coloured dots. Since 1975, a red-on-white Polka-dotted jersey is awarded to the leader in the Mountain stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaid (pattern)
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Scotland, as Scottish kilts almost always have tartan patterns. Tartan is made with alternating bands of coloured (pre-dyed) threads woven as both warp and weft at right angles to each other. The weft is woven in a simple twill, two over—two under the warp, advancing one thread at each pass. This pattern forms visible diagonal lines where different colours cross, which give the appearance of new colours blended from the original ones. The resulting blocks of colour repeat vertically and horizontally in a distinctive pattern of squares and lines known as a ''sett''. Tartan is often called "plaid" (particularly in North America), because in Scotland, a '' plaid'' is a large piece of tartan cloth, worn as a type of kilt or large shawl. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras (cloth)
Madras is a lightweight cotton fabric with typically patterned texture and tartan design, used primarily for summer clothing such as pants, shorts, lungi, dresses, and jackets. The fabric takes its name from the former name of the city of Chennai in south India. Madras today is sewing them back together to form a mixed pattern of various plaids. Definition Authentic Madras comes from Chennai (Madras); both sides of the cloth must bear the same pattern; it must be handwoven (evidenced by the small flaws in the fabric). Most popular in the 1960s. Cotton madras is woven from a fragile, short-staple cotton fiber that cannot be combed, only carded. This results in bumps known as slubs which are thick spots in the yarn that give madras its unique texture. The cotton is hand-dyed after being spun into yarn, woven, and finished in some 200 small villages in the Madras area. History By the 1500s madras cotton had morphed into something more elegant, printed with floral patterns o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingham
Gingham, also called Vichy check, is a medium-weight balanced plain-woven fabric typically with striped, check or plaid duotone patterns, in bright colour and in white made from dyed cotton or cotton-blend yarns. It is made of carded, medium or fine yarns. History The name may originate . Alternatively, it is speculated that the fabric now known as ''gingham'' may have been made at Guingamp, a town in Brittany, France, and that the fabric may be named after the town. Some sources say that the name came into English via Dutch. When originally imported into Europe in the 17th century, gingham was a striped fabric, though now it is distinguished by its checkered pattern. From the mid-18th century, when it was being produced in the mills of Manchester, England, it started to be woven into checked or plaid patterns (often blue and white). Checked gingham became more common over time, though striped gingham was still available in the late Victorian period. The equivalent in the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
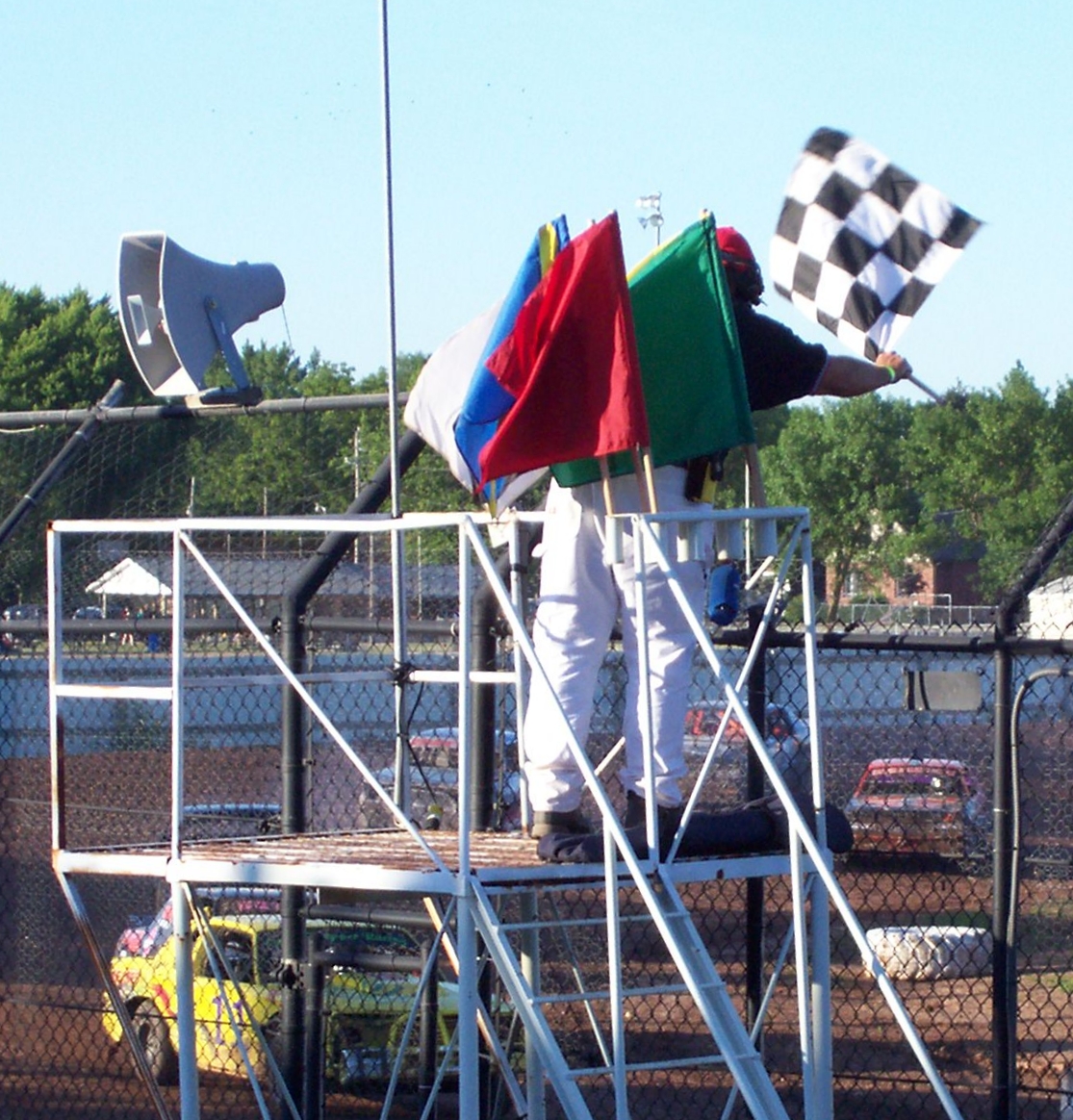
Racing Flags
Racing flags are traditionally used in auto racing and similar motorsports to indicate track condition and to communicate important messages to drivers. Typically, the starter, sometimes the grand marshal of a race, waves the flags atop a flag stand near the start/finish line. Track marshals are also stationed at observation posts along the race track in order to communicate both local and course-wide conditions to drivers. Alternatively, some race tracks employ lights to supplement the primary flag at the start/finish line. Summary While there is no universal system of racing flags across all of motorsports, most series have standardized them, with some flags carrying over between series. For example, the chequered flag is commonly used across all of motorsport to signify the end of a session (practice, qualifying, or race), while the penalty flags differ from series to series. FIA-sanctioned championship flags are the most commonly used internationally (outside of North Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyle (pattern)
An argyle (, occasionally spelled argyll) pattern is made of diamonds or lozenges. The word is sometimes used to refer to an individual diamond in the design, but more commonly refers to the overall pattern. Most argyle contains layers of overlapping motifs, adding a sense of three-dimensionality, movement, and texture. Typically, there is an overlay of intercrossing diagonal lines on solid diamonds. History The argyle pattern derives from the tartan of Clan Campbell of Argyll in western Scotland, used for kilts and plaids, and from the patterned socks worn by Scottish Highlanders since at least the 17th century. These were generally known as "tartan hose". 20th century Argyle knitwear became fashionable in Great Britain and then in the United States after the First World War of 1914–1918. Pringle of Scotland popularised the design, helped by its identification with the Duke of Windsor. Pringle's website says that "the iconic Pringle argyle design was developed" in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |