|
Stereotactic Surgery
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc. In theory, any organ system inside the body can be subjected to stereotactic surgery. However, difficulties in setting up a reliable frame of reference (such as bone landmarks, which bear a constant spatial relation to soft tissues) mean that its applications have been, traditionally and until recently, limited to brain surgery. Besides the brain, biopsy and surgery of the breast are done routinely to locate, sample (biopsy), and remove tissue. Plain X-ray images (radiographic mammography), computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to guide the procedure. Another accepted form of "stereotactic" is "stereotaxic". The word roots are '' stereo-'', a pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotaxy
Stereotaxy (from '' stereo'' meaning "solidity", and ''tactile'' meaning "touch") refers to any technique that involves the recording and reproduction of three-dimensional haptic information or creating an illusion of depth to the sense of touch within an otherwise-flat surface. Unlike the current trend in haptic technology to provide haptic perception of simulated, virtual objects within an augmented-reality (that is, within a mostly-realistic) setting, stereohapty, which, when applied as a field of study, is known as stereohaptics or stereotactics, stereotaxy aims to provide an illusion of three-dimensional depth to the sense of touch by the human body. This resembles how stereoscopy, its visual counterpart, is meant to provide a visual illusion of depth to otherwise-flat images (such as 3-D films), a process known as stereopsis. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
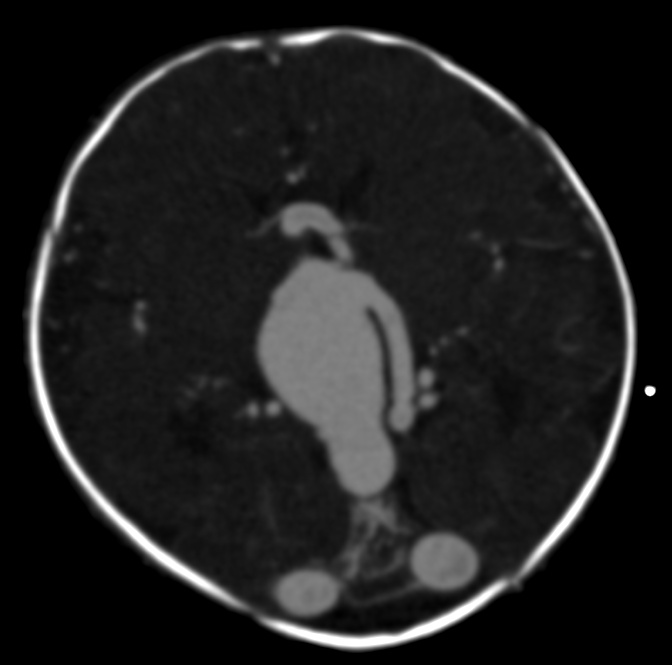
Image-guided Surgery
Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems use cameras, ultrasonic, electromagnetic or a combination or fields to capture and relay the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's precise movements in relation to the patient, to computer monitors in the operating room or to augmented reality headsets (augmented reality surgical navigation technology). This is generally performed in real-time though there may be delays of seconds or minutes depending on the modality and application. Image-guided surgery helps surgeons perform safer and less invasive procedures and has become a recognized standard of care in managing disorders including cranial, otorhinolaryngology, spine, orthopedic, and cardiovascular. Benefits The benefits of Image-guided surgery include greater control of the surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, or trifacial neuralgia is a long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is a form of neuropathic pain. There are two main types: typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The typical form results in episodes of severe, sudden, shock-like pain in one side of the face that lasts for seconds to a few minutes. Groups of these episodes can occur over a few hours. The atypical form results in a constant burning pain that is less severe. Episodes may be triggered by any touch to the face. Both forms may occur in the same person. It is regarded as one of the most painful disorders known to medicine, and often results in depression. The exact cause is unknown, but believed to involve loss of the myelin of the trigeminal nerve. This might occur due to compression from a blood vessel as the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be |
Vestibular Schwannoma
A vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve that passes from the inner ear to the brain. The tumor originates when Schwann cells that form the insulating myelin sheath on the nerve malfunction. Normally, Schwann cells function beneficially to protect the nerves which transmit balance and sound information to the brain. However, sometimes a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene, NF2, located on chromosome 22, results in abnormal production of the cell protein named ''Merlin'', and Schwann cells multiply to form a tumor. The tumor originates mostly on the vestibular division of the nerve rather than the cochlear division, but hearing as well as balance will be affected as the tumor enlarges. The great majority of these VSs (95%) are unilateral, in one ear only. They are called "sporadic" (i.e., by-chance, non-hereditary). Although non-cancerous, they can do harm or even become life-threatening if they gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (cerebral AVM, CAVM, cAVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain—specifically, an arteriovenous malformation in the cerebrum. Signs and symptoms The most frequently observed problems, related to an AVM, are headaches and seizures, cranial nerve deficits, backaches, neckaches and eventual nausea, as the coagulated blood makes its way down to be dissolved in the individual's spinal fluid. It is supposed that 15% of the population, at detection, have no symptoms at all. Other common symptoms are a pulsing noise in the head, progressive weakness and numbness and vision changes as well as debilitating, excruciating pain. In serious cases, the blood vessels rupture and there is bleeding within the brain (intracranial hemorrhage). Nevertheless, in more than half of patients with AVM, hemorrhage is the first symptom. Symptoms due to bleeding include loss of consciousness, sudden and severe headache, nausea, vomiting, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur. Risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation such as during radiation therapy, a family history of the condition, and neurofibromatosis type 2. As of 2014 they do not appear to be related to cell phone use. They appear to be able to form from a number of different types of cells including arachnoid cells. Diagnosis is typically by medical imaging. If there are no symptoms, periodic observation may be all that is required. Most cases that result in symptoms can be cured by surgery. Following complete removal fewer than 20% recur. If surgery is not possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They can either start from normal brain cells or develop from an existing low-grade astrocytoma. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Brain Radiotherapy
Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) is a palliative option for patients with brain metastases that alleviates symptoms, decreases the use of corticosteroids needed to control tumor-associated edema, and potentially improves overall survival. Usage Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) has been reported to increase the risk of cognitive decline. WBRT is sometimes used along with stereotactic radiosurgery Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, inje ... (SRS) or surgery, and while these can improve survival for some patients with single brain metastasis, a 2021 systematic review of the literature found inconsistent results for overall survival. References {{Reflist Chemotherapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Scientific Vocabulary
International scientific vocabulary (ISV) comprises scientific and specialized words whose language of origin may or may not be certain, but which are in current use in several modern languages (that is, translingually, whether in naturalized, loanword, or calque forms). The name "international scientific vocabulary" was first used by Philip Gove in '' Webster's Third New International Dictionary'' (1961). As noted by David Crystal, science is an especially productive field for new coinages. It is also especially predisposed to immediate translingual sharing of words owing to its very nature: scientists working in many countries and languages, reading each other's latest articles in scientific journals (via foreign language skills, translation help, or both), and eager to apply any reported advances to their own context. Instances According to ''Webster's Third'', "some ISV words (like haploid) have been created by taking a word with a rather general and simple meaning from o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Latin
New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy and international scientific vocabulary, draws extensively from New Latin vocabulary, often in the form of classical or neoclassical compounds. New Latin includes extensive new word formation. As a language for full expression in prose or poetry, however, it is often distinguished from its successor, Contemporary Latin. Extent Classicists use the term "Neo-Latin" to describe the Latin that developed in Renaissance Italy as a result of renewed interest in classical civilization in the 14th and 15th centuries. Neo-Latin also describes the use of the Latin language for any purpose, scientific or literary, during and after the Renaissance. The beginning of the period cannot be precisely identified; however, the spread of secular educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |