|
Steam Chest
__NOTOC__ This article is a glossary of the main components found on a typical steam locomotive. The diagram, which is not to scale, is a composite of various designs in the late steam era. Some components shown are not the same, or are not present, on some locomotives – for example, on smaller or articulated types. Conversely, some locomotives have components not listed here. Details of the components See also * Glossary of boiler terms * Glossary of rail transport terms * Horsepower#Drawbar horsepower * Power classification * Tractive effort References Further reading * * * External linksList of US–UK terminology– Railway Technical Website {{Steam engine configurations Glossaries of rail transport Steam locomotive components __NOTOC__ This article is a glossary of the main components found on a typical steam locomotive. The diagram, which is not to scale, is a composite of various designs in the late steam era. Some components shown are not the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
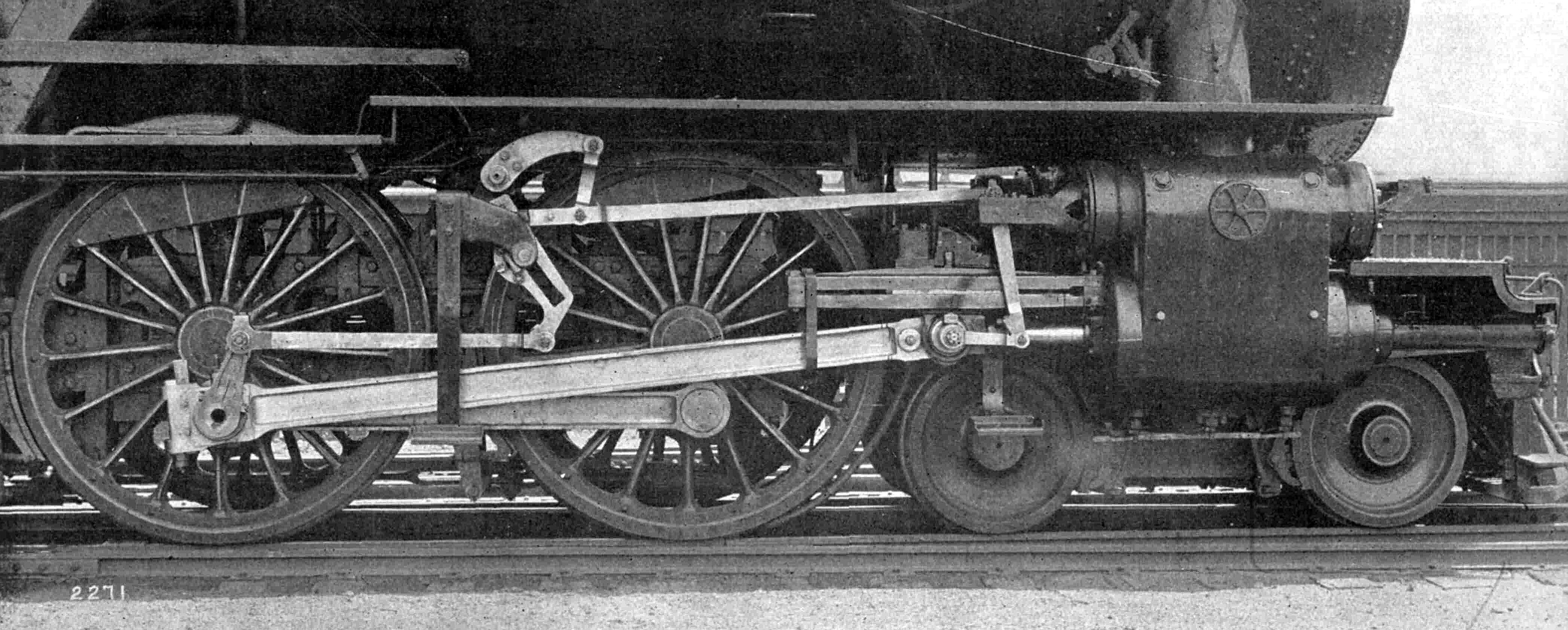
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastpipe
The blastpipe is part of the exhaust system of a steam locomotive that discharges exhaust steam from the cylinders into the smokebox beneath the chimney in order to increase the draught through the fire. History The primacy of discovery of the effect of directing the exhaust steam up the chimney as a means of providing draft through the fire is the matter of some controversy, Ahrons (1927) devoting significant attention to this matter. The exhaust from the cylinders on the first steam locomotive – built by Richard Trevithick – was directed up the chimney, and he noted its effect on increasing the draft through the fire at the time. At Wylam, Timothy Hackworth also employed a blastpipe on his earliest locomotives, but it is not clear whether this was an independent discovery or a copy of Trevithick's design. Shortly after Hackworth, George Stephenson also employed the same method, and again it is not clear whether that was an independent discovery or a copy of one of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
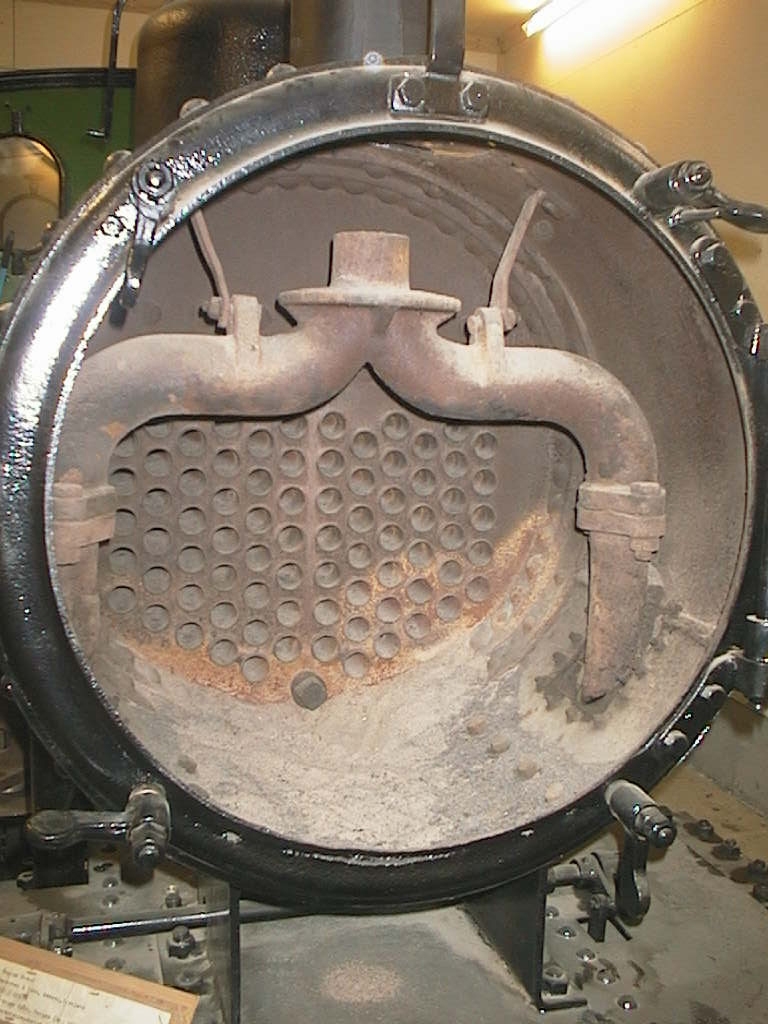
Smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney (or funnel). Early locomotives had no smokebox and relied on a long chimney to provide natural draught for the fire but smokeboxes were soon included in the design for two specific reasons. Firstly and most importantly, the blast of exhaust steam from the cylinders, when directed upwards through an airtight smokebox with an appropriate design of exhaust nozzle, effectively draws hot gases through the boiler tubes and flues and, consequently, fresh combustion air into the firebox. Secondly, the smokebox provides a convenient collection point for ash and cinders ("char") drawn through the boiler tubes, which can be easily cleaned out at the end of a working day. Without a smokebox, all char must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Brake
The vacuum brake is a braking system employed on trains and introduced in the mid-1860s. A variant, the automatic vacuum brake system, became almost universal in British train equipment and in countries influenced by British practice. Vacuum brakes also enjoyed a brief period of adoption in the United States, primarily on narrow-gauge railroads. Their limitations caused them to be progressively superseded by compressed air systems starting in the United Kingdom from the 1970s onward. The vacuum brake system is now obsolete; it is not in large-scale usage anywhere in the world, other than in South Africa, largely supplanted by air brakes. Introduction In the earliest days of railways, trains were slowed or stopped by the application of manually applied brakes on the locomotive and in brake vehicles through the train, and later by steam power brakes on locomotives. This was clearly unsatisfactory, given the slow and unreliable response times (each brake being separately applied by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon
Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon was a Swiss engineering company based in the Zürich district of Oerlikon known for the early development of electric locomotives. It was founded in 1876 by the industrialist Peter Emil Huber-Werdmüller, and occupied a large site immediately to the west of Oerlikon railway station. In 1906 the armaments business was demerged to form ', which evolved into the technology company OC Oerlikon and the armaments company Rheinmetall Air Defence (formerly ''Oerlikon Contraves''). In 1967 Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon was taken over by Brown, Boveri & Cie, which in 1988 merged with ASEA to form ABB Group. The site of the company's works has been redeveloped, including the innovative public MFO-Park The MFO-Park is a public park in the Oerlikon quarter of the Swiss city of Zürich. The area to the north of Zürich Oerlikon railway station was once home to the extensive works of ''Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon'' (MFO), as site that has now been .... In the seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunze-Knorr Brake
The Kunze-Knorr brake (''Kunze-Knorr-Bremse'' or ''KK-Bremse'') is an automatic compressed-air brake for goods, passenger and express trains. It was the first graduated brake for goods trains in Europe. When it was introduced after the First World War, goods train brakes switched from hand operation to compressed-air in various European countries. The Deutsche Reichsbahn alone put the cost of equipping German goods wagons with Kunze-Knorr brakes between 1918 and 1927 at 478.4 million Reichsmarks. The operating cost savings from faster goods services and having fewer brakemen was assessed by the Reichsbahn at almost 96.3 million Reichsmark annually. Inventors The Kunze-Knorr brake brought together the ideas of Prussian senior surveyor, Bruno Kunze (1854–1935), and preparatory work by the founder of Knorr-Bremse, Georg Knorr (1859–1911). It was the first, continuous, compressed-air brake that, even on long goods trains, enabled the brake force not only to be applied gradually, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Air Brake
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted. The Westinghouse system uses air pressure to charge air reservoirs (tanks) on each car. Full air pressure causes each car to release the brakes. A subsequent reduction or loss of air pressure causes each car to apply its brakes, using the compressed air stored in its reservoirs. Overview Straight air brake In the air brake's simplest form, called the ''straight air system'', compressed air pushes on a piston in a cylinder. The piston is connected through mechanical linkage to brake shoes that can rub on the train wheels, using the resulting friction to slow the train. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Dome
The steam dome is a vessel fitted to the top of the boiler of a steam engine. It contains the opening to the main steam pipe and its purpose is to allow this opening to be kept well above the water level in the boiler. This arrangement acts as a simple steam separator and minimises the risk that water will be carried over to the cylinders where it might cause a hydraulic lock, also known as priming. A steam dome should not be confused with a sand dome. Railway locomotives The first locomotive with a deliberate dome added to the boiler barrel was Stephenson's 'Phoenix' an 0-2-2 for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in 1830. Many other locomotives built from the late 1830s instead used either the 'haycock' boiler, where the firebox outer casing was raised high above the main part of the boiler, forming a steam dome, or Gooch's development of this where the semi-cylindrical firebox wrapper was raised above the boiler barrel. The most vigorous boiling in a locomotive boile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snifting Valve
A snifting valve (sometimes snifter valve) is an automatic anti-vacuum valve used in a steam locomotive when coasting. The word ''Snift'' imitates the sound made by the valve. Overview When the driver shuts off the steam to the cylinders of a steam locomotive while it is in motion, the moving pistons could create a partial vacuum in the cylinders. This would give rise to two problems. Firstly, the pumping action would absorb energy and prevent the engine from coasting freely. Secondly, when the exhaust valve opened, soot and cinders from the smokebox could be sucked down the exhaust pipe and into the valve chest or cylinder, causing damage. (The exhaust is open to the smokebox because in normal running the exhaust steam is sent through the blastpipe to draw the fire and eject the combustion products from the chimney.) These problems are avoided by using snifting valves to allow air to be drawn into the cylinder. On railways which did not use snifting valves, drivers were instr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_vacuum_brake_1.jpg)



