|
Spires
The Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) is a database management system developed by Stanford University. It is used by universities, colleges and research institutions. The first website in North America was created to allow remote users access to its database. History SPIRES was originally developed at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) in 1969, from a design based on a 1967 information study of physicists at SLAC. The system was designed as a physics database management system (DBMS) to deal with high-energy-physics preprints. Written in PL/I, SPIRES ran on an IBM System/360. In the early 1970s, an evaluation of this system resulted in the decision to implement a new system for use by faculty, staff and students at Stanford University. SPIRES was renamed the Stanford Public Information Retrieval System. The new development took place under a National Science Foundation grant headed by Edwin B. Parker, principal investigator. SPIRES joined force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
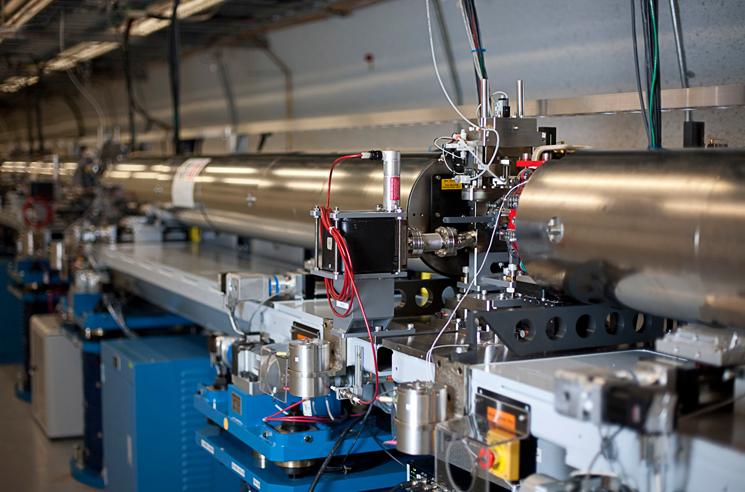
Stanford Linear Accelerator Center
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and located in Menlo Park, California. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 and shut down in the 2000s, that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, the facility is located on of Stanford University-owned land on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and located in Menlo Park, California. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 and shut down in the 2000s, that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, the facility is located on of Stanford University-owned land on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PL360
PL360 (or PL/360) is a system programming language designed by Niklaus Wirth and written by Wirth, Joseph W. Wells Jr., and Edwin Satterthwaite Jr. for the IBM System/360 computer at Stanford University. A description of PL360 was published in early 1968, although the implementation was probably completed before Wirth left Stanford in 1967. Description PL/360 is a one pass compiler with a syntax similar to ALGOL that provides facilities for specifying exact machine code (language) instructions and registers similar to assembly language, but also provides features commonly found in high-level programming languages, such as complex arithmetic expressions and control structures. Wirth used PL360 to create ALGOL W. Data types are: * Byte or character – 1 byte * Short integer – 2 bytes, interpreted as an integer in two's complement binary notation * Integer or logical – 4 bytes, interpreted as an integer in two's complement binary notation * Real – 4 bytes, interpreted as a base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System Logo
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneurialism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For High Energy Physics
State Research Center – Institute for High Energy Physics (IHEP) is a research organisation in Protvino (near Moscow, Moscow Oblast), Russia. It was established in 1963. The institute is known for the particle accelerator U-70 (synchrotron), U-70 synchrotron launched in 1967 with the maximum proton energy of 70 GeV, which had the largest proton energy in the world for five years. The first director of the institute from 1963 to 1974 was Anatoly Logunov. From 1974 to 1993 professor Lev Solovyov (Russian: Лев Дмитриевич Соловьев) served as the director of the institute. A professor, Nikolai E. Tyurin has been the director of the institute since 2003. In 1978, a scientist of the institute, Anatoli Bugorski, was irradiated by an extreme dose of proton beam. His demise was deemed inevitable as the doctors believed he had received a dosage far in excess of what could be considered fatal. However, he survived the accident and continued to work in the institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |