|
Spin Flip
A black hole spin-flip occurs when the spin axis of a rotating black hole undergoes a sudden change in orientation due to absorption of a second (smaller) black hole. Spin-flips are believed to be a consequence of galaxy mergers, when two supermassive black holes form a bound pair at the center of the merged galaxy and coalesce after emitting gravitational waves. Spin-flips are significant astrophysically since a number of physical processes are associated with black hole spins; for instance, jets in active galaxies are believed to be launched parallel to the spin axes of supermassive black holes. A change in the rotation axis of a black hole due to a spin-flip would therefore result in a change in the direction of the jet. Physics of spin-flips A spin-flip is a late stage in the evolution of a binary black hole. The binary consists of two black holes, with masses M_1 and M_2, that revolve around their common center of mass. The total angular momentum J of the binary sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics of orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Galaxies
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wavelengths between 10 MHz and 100 GHz. The radio emission is due to the synchrotron process. The observed structure in radio emission is determined by the interaction between twin jets and the external medium, modified by the effects of relativistic beaming. The host galaxies are almost exclusively large elliptical galaxies. ''Radio-loud'' active galaxies can be detected at large distances, making them valuable tools for observational cosmology. Recently, much work has been done on the effects of these objects on the intergalactic medium, particularly in galaxy groups and clusters. Alcyoneus is a low-excitation radio galaxy, identified as having the largest radio lobes found, with lobed structures spanning 5 megaparsecs (16×10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-shaped Radio Galaxy
X-shaped (or "winged") radio galaxies are a class of extragalactic radio source that exhibit two, low-surface-brightness radio lobes (the "wings") oriented at an angle to the active, or high-surface-brightness, lobes. Both sets of lobes pass symmetrically through the center of the elliptical galaxy that is the source of the lobes, giving the radio galaxy an X-shaped morphology as seen on radio maps (see figure). X-shaped sources were first described by J. P. Leahy and P. Parma in 1992, who presented a list of 11 such objects. The X-shaped galaxies have received much attention following the suggestion in 2002 that they might be the sites of spin-flips associated with the recent coalescence of two supermassive black holes. Properties X-shaped galaxies are a sub-class of Fanaroff-Riley Type II (FRII) radio galaxies. FRII objects exhibit a pair of large (kiloparsec) scale radio lobes that straddle the parent elliptical galaxy; the lobes are believed to consist of plasma ejected fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Galaxy
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wavelengths between 10 MHz and 100 GHz. The radio emission is due to the synchrotron process. The observed structure in radio emission is determined by the interaction between twin jets and the external medium, modified by the effects of relativistic beaming. The host galaxies are almost exclusively large elliptical galaxies. ''Radio-loud'' active galaxies can be detected at large distances, making them valuable tools for observational cosmology. Recently, much work has been done on the effects of these objects on the intergalactic medium, particularly in galaxy groups and clusters. Alcyoneus is a low-excitation radio galaxy, identified as having the largest radio lobes found, with lobed structures spanning 5 megaparsecs (16×1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
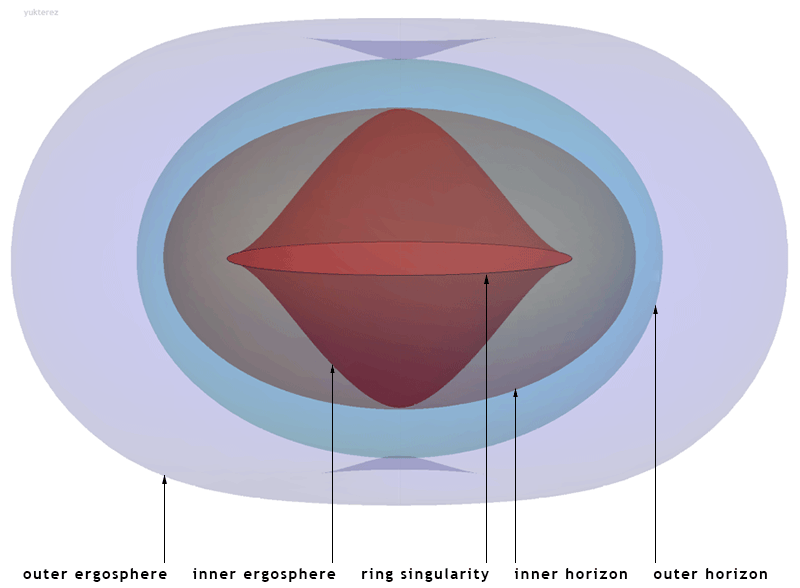
Kerr Black Hole
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of general relativity; these equations are highly non-linear, which makes exact solutions very difficult to find. Overview The Kerr metric is a generalization to a rotating body of the Schwarzschild metric, discovered by Karl Schwarzschild in 1915, which described the geometry of spacetime around an uncharged, spherically symmetric, and non-rotating body. The corresponding solution for a ''charged'', spherical, non-rotating body, the Reissner–Nordström metric, was discovered soon afterwards (1916–1918). However, the exact solution for an uncharged, ''rotating'' black hole, the Kerr metric, remained unsolved until 1963, when it was discovered by Roy Kerr.Melia, Fulvio (2009). "Cracking the Einstein code: relativity and the birth of black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Radiation
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as waves similar to electromagnetic waves but the gravitational equivalent. Gravitational waves were later predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Later he refused to accept gravitational waves. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously (at infinite speed)showing one of the ways the methods of Newtonian physics are unable to explain phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosalba Perna
Rosalba Perna is an Italian and American theoretical astrophysicist whose research concerns high-energy cosmic sources including gamma-ray bursts and neutron star mergers. She has also studied exoplanets and the growth of supermassive black holes. She is professor of physics and astronomy at Stony Brook University. Education and career Perna earned a laurea at the University of Salerno in 1993, with a thesis concerning the quantum Hall effect. In the same year, she also earned a diploma in music, as a piano player, at the Conservatory of Music Carlo Gesualdo Da Venosa in Potenza. She completed a Ph.D. in physics at Harvard University in 1999, with the dissertation ''Theoretical studies of Gamma-Ray Bursts'' supervised by Avi Loeb. She continued at Harvard as a Harvard Junior Fellow from 1999 to 2003. She did continued postdoctoral research at Princeton University as a Lyman Spitzer Fellow and then, in 2004, became an assistant professor of astrophysics at the University of Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Parameters
Kerr may refer to: People *Kerr (surname) *Kerr (given name) Places ;United States *Kerr Township, Champaign County, Illinois *Kerr, Montana, A US census-designated place *Kerr, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Kerr County, Texas Other uses *KERR, A US radio station *Kerr, a brand of food Mason jars and lids *Clan Kerr Clan Kerr () is a Scottish clan whose origins lie in the Scottish Borders. During the Middle Ages, it was one of the prominent border reiver clans along the present-day Anglo-Scottish border and played an important role in the history of the B ..., a Scottish clan * Kerr's, a Canadian candy company See also * * * Ker (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Angular Momenta
Spin is a conserved quantity carried by elementary particles, and thus by composite particles (hadrons) and atomic nuclei. Spin is one of two types of angular momentum in quantum mechanics, the other being ''orbital angular momentum''. The orbital angular momentum operator is the quantum-mechanical counterpart to the classical angular momentum of orbital revolution and appears when there is periodic structure to its wavefunction as the angle varies. For photons, spin is the quantum-mechanical counterpart of the polarization of light; for electrons, the spin has no classical counterpart. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The existence of the electron spin can also be inferred theoretically from the spin–statistics theorem and from the Pauli exclusion principle—and vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |