|
Spectral Rendering
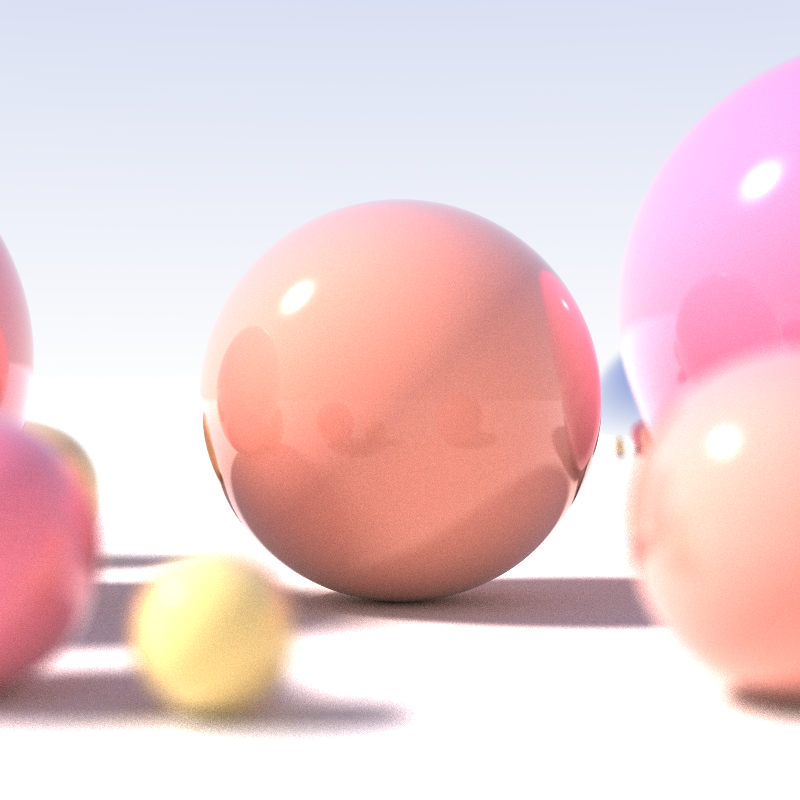
In computer graphics, spectral rendering is a technique in which a scene's light transport is modeled with real wavelengths. This process is typically slower than traditional rendering (computer graphics), rendering, which renders the scene in its red, green, and blue components and then overlays the images. Spectral rendering is often used in Ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing or photon mapping to more accurately simulate the scene, often for comparison with an actual photograph to test the rendering algorithm (as in a Cornell Box) or to simulate different portions of the electromagnetic spectrum for the purpose of scientific work. The images simulated are not necessarily more realistic ''appearing,'' but when compared to a real image pixel for pixel the result is often much closer. Spectral rendering can also simulate light sources and objects more effectively, as the light's emission spectrum can be used to release photons at a particular wavelength in proportion to the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering is the process of generating a physically-based rendering, photorealistic or Non-photorealistic rendering, non-photorealistic image from input data such as 3D models. The word "rendering" (in one of its senses) originally meant the task performed by an artist when depicting a real or imaginary thing (the finished artwork is also called a "architectural rendering, rendering"). Today, to "render" commonly means to generate an image or video from a precise description (often created by an artist) using a computer program. A application software, software application or component-based software engineering, component that performs rendering is called a rendering software engine, engine, render engine, : Rendering systems, rendering system, graphics engine, or simply a renderer. A distinction is made between Real-time computer graphics, real-time rendering, in which images are generated and displayed immediately (ideally fast enough to give the impression of motion or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ray Tracing (graphics)
In 3D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling Light transport theory, light transport for use in a wide variety of Rendering (computer graphics), rendering algorithms for generating digital image, digital images. On a spectrum of Computation time, computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as ray casting, #Recursive ray tracing algorithm, recursive ray tracing, Distributed ray tracing, distribution ray tracing, photon mapping and path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as still computer-generated imagery, CGI images, and film and television visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to real-time computer graphics, real-time applications such as video games, where Frame rate, speed is critical in rendering each Film frame, frame. Since 2018, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photon Mapping
In computer graphics, photon mapping is a two-pass global illumination rendering algorithm developed by Henrik Wann Jensen between 1995 and 2001Jensen, H. (1996). ''Global Illumination using Photon Maps''. nlineAvailable at: http://graphics.stanford.edu/~henrik/papers/ewr7/egwr96.pdf that approximately solves the rendering equation for integrating light radiance at a given point in space. Rays from the light source (like photons) and rays from the camera are traced independently until some termination criterion is met, then they are connected in a second step to produce a radiance value. The algorithm is used to realistically simulate the interaction of light with different types of objects (similar to other photorealistic rendering techniques). Specifically, it is capable of simulating the refraction of light through a transparent substance such as glass or water (including caustics), diffuse interreflection between illuminated objects, the subsurface scattering of light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cornell Box
The Cornell box is a test scene designed to evaluate the accuracy of rendering (computer graphics), rendering software by comparing a 3D rendering, rendered image with a photograph of a real-world model under the same lighting conditions. It has become a List of common 3D test models, commonly used 3D test model in computer graphics research. The box was created by Cindy M. Goral, Kenneth E. Torrance, Donald P. Greenberg, and Bennett Battaile at the ''Cornell University Program of Computer Graphics'' as part of their research on radiosity (computer graphics), radiosity and Diffuse reflection#Interreflection, diffuse interreflection. Their findings were published in the paper ''Modeling the Interaction of Light Between Diffuse Surfaces'', presented at SIGGRAPH '84.Cindy M. Goral, Kenneth E. Torrance, Donald P. Greenberg, and Bennett Battaile. Modeling the Interaction of Light Between Diffuse Surfaces''. SIGGRAPH 1984. Reference Model A physical model of the Cornell box is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be emitted and received by antenna (radio), antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most building materials. Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon energies and the shortest wavelengths—much smaller than an atomic nucleus. Gamma rays, X-rays, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Emission Spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the Spectrum (physical sciences), spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to electrons making a atomic electron transition, transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photons is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Emission In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spectral Reflectance Curve
''Spectral'' is a 2016 Hungarian-American military science fiction action film co-written and directed by Nic Mathieu. Written with Ian Fried & George Nolfi, the film stars James Badge Dale as DARPA research scientist Mark Clyne, with Max Martini, Emily Mortimer, Clayne Crawford, and Bruce Greenwood in supporting roles. The film is set in a civil war-ridden Moldova as invisible entities slaughter any living being caught in their path. The film was released worldwide on December 9, 2016 on Netflix. On February 1, 2017, Netflix released a prequel graphic novel of the film called ''Spectral: Ghosts of War'' which was made available digitally through the website ComiXology. Plot DARPA researcher Mark Clyne is sent to a US military airbase on the outskirts of Chișinău, to consult his created line of hyperspectral imaging goggles issued to US Army Special Forces led by Army General James Orland, who is covertly supporting the Moldovan government in an ongoing civil war agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blackbody Radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific continuous spectrum that depends only on the body's temperature., Chapter 13. A perfectly-insulated enclosure which is in thermal equilibrium internally contains blackbody radiation and will emit it through a hole made in its wall, provided the hole is small enough to have a negligible effect upon the equilibrium. The thermal radiation spontaneously emitted by many ordinary objects can be approximated as blackbody radiation. Of particular importance, although planets and stars (including the Earth and Sun) are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, blackbody radiation is still a good first approximation for the energy they emit. The term ''black body'' was introduced by Gustav Kirchhoff in 1860. Blackbody radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autodesk Vred (software)
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has offices worldwide. Its U.S. offices are located in the states of California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canadian offices are located in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta. The company was founded in 1982 by John Walker, who was a co-author of the first versions of AutoCAD. AutoCAD is the company's flagship computer-aided design (CAD) software and, along with its 3D design software Revit, is primarily used by architects, engineers, and structural designers to design, draft, and model buildings and other structures. Autodesk software has been used in many fields, and on projects from the One World Trade Center to Tesla electric cars. Autodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arion (software)
Arion is a physically based, unbiased render engine developed by RandomControl. Versions Arion standalone is a general purpose rendering tool with a visual UI. There are also versions that integrate into 3ds Max and Rhinoceros. See also * POV-Ray - A historical raytracer. * Octane Render - A commercial unbiased GPU-accelerated renderer. * Sunflow Sunflow is an open-source global illumination rendering system written in Java Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. Wi ... - An open source unbiased renderer. References External links * {{Official website, http://www.randomcontrol.com/arion Rendering systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LuxCoreRender
LuxCoreRender is a free and open-source physically based rendering software. It began as ''LuxRender'' in 2008 before changing its name to LuxCoreRender in 2017 as part of a project reboot. The LuxCoreRender software runs on Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows. Overview LuxCoreRender features a 3D renderer; it relies on other programs ( 3D modeling programs) to create the scenes to render, including the models, materials, lights and cameras. This content can then be exported from the application for rendering. For Luxrender, fully functional exporters are available for Blender, Daz Studio; partially functional ones are available for Cinema 4D, Maya, SketchUp and XSI. Luxrender is also fully supported as a production renderer in 3DS Max. For LuxCoreRender, Blender is supported through the BlendLuxCore plugin. After opening the exported file, LuxCoreRender renders the scene. Various tweaks to post processing settings can be set via graphical user interface and the scene control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mental Ray
Mental Ray (stylized as mental ray) is a production-quality Ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing application for 3D rendering. Its Berlin-based developer Mental Images (firm), Mental Images was acquired by Nvidia in 2007 and Mental Ray was discontinued in 2017. Mental Ray has been used in many feature films, including ''Hulk (film), Hulk'', ''The Matrix Reloaded & The Matrix Revolutions, Revolutions'', ''Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones'', ''The Day After Tomorrow'' and ''Poseidon (film), Poseidon''. In November 2017 Nvidia announced that it would no longer offer new Mental Ray subscriptions, although maintenance releases with bug fixes were published throughout 2018 for existing plugin customers. Features The primary feature of Mental Ray is the achievement of high performance through parallelism on both multiprocessor machines and across render farms. The software uses acceleration techniques such as Scanline rendering, scanline for primary visible surface det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |