|
Spatial Epidemiology
Spatial epidemiology is a subfield of epidemiology focused on the study of the spatial distribution of health outcomes; it is closely related to health geography. Specifically, spatial epidemiology is concerned with the description and examination of disease and its geographic variations. This is done in consideration of “demographic, environmental, behavioral, socioeconomic, genetic, and infections risk factors." Types of studies ;Disease Mapping: * Disease maps are visual representations of intricate geographic data that provide a quick overview of said information. Mainly used for explanatory purposes, disease maps can be presented to survey high-risk areas and to help policy and resource allocation in said areas. ;Geographic correlation studies * Geographic correlation studies attempt to study the geographical factors and their effects on geographically differentiated health outcomes. Measured on an ecologic scale, these factors include environmental variables (quality of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discipline (academia)
An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined (in part) and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, and the learned societies and academic departments or faculties within colleges and universities to which their practitioners belong. Academic disciplines are conventionally divided into the humanities (including philosophy, language, art and cultural studies), the scientific disciplines (such as physics, chemistry, and biology); and the formal sciences like mathematics and computer science. The social sciences are sometimes considered a fourth category. It is also known as a ''field of study'', ''field of inquiry'', ''research field'' and ''branch of knowledge''. The different terms are used in different countries and fields. Individuals associated with academic disciplines are commonly referred to as ''experts'' or ''specialists''. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
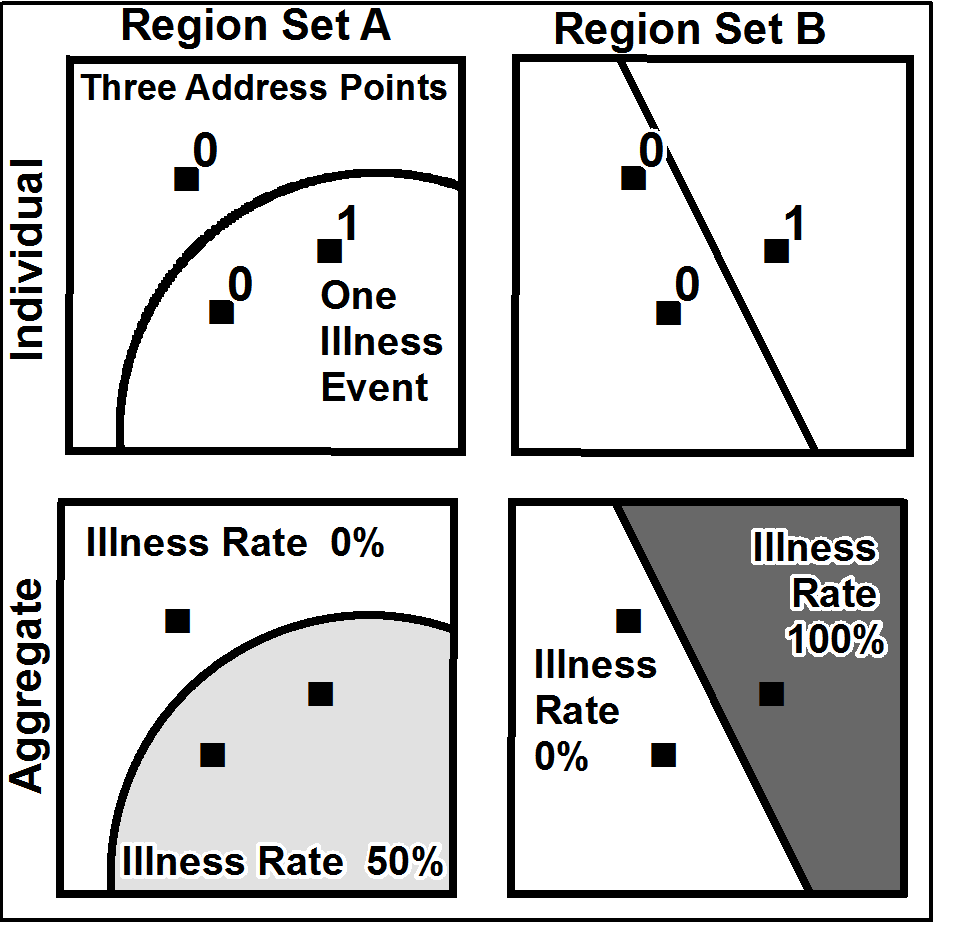
Modifiable Areal Unit Problem
__NOTOC__ The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) is a source of statistical bias that can significantly impact the results of statistical hypothesis tests. MAUP affects results when point-based measures of spatial phenomena are Aggregate data, aggregated into spatial partitions or ''areal units'' (such as regions or districts) as in, for example, population density or illness rates. The resulting summary values (e.g., totals, rates, proportions, densities) are influenced by both the shape and Scale (geography), scale of the aggregation unit. For example, census data may be aggregated into county districts, census tracts, postcode areas, police precincts, or any other arbitrary spatial partition. Thus the results of data aggregation are dependent on the mapmaker's choice of which "modifiable areal unit" to use in their analysis. A census choropleth map calculating population density using state boundaries will yield radically different results from a map that calculates density ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Time Geography
Time geography or time-space geography is an evolving transdisciplinary perspective on spatial and temporal processes and events such as social interaction, ecological interaction, social and environmental change, and biographies of individuals. Time geography "is not a subject area per se", but rather an integrative ontological framework and visual language in which space and time are basic dimensions of analysis of dynamic processes. Time geography was originally developed by human geographers, but today it is applied in multiple fields related to transportation, regional planning, geography, anthropology, time-use research, ecology, environmental science, and public health. According to Swedish geographer Bo Lenntorp: "It is a basic approach, and every researcher can connect it to theoretical considerations in her or his own way." Origins The Swedish geographer Torsten Hägerstrand created time geography in the mid-1960s based on ideas he had developed during his earlie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial analysis is any of the formal techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties, primarily used in Urban Design. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques using different analytic approaches, especially ''spatial statistics''. It may be applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, or to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is geospatial analysis, the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data. It may also applied to genomics, as in transcriptomics data, but is primarily for spatial data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current research. The most fundamental of these is the problem of defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis is any of the formal Scientific technique, techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties, primarily used in Urban design, Urban Design. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques using different analytic approaches, especially ''spatial statistics''. It may be applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, or to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is geospatial analysis, the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data. It may also applied to genomics, as in Spatial transcriptomics, transcriptomics data, but is primarily for spatial data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mutual Standardisation
{{One source, date=February 2022 Mutual Standardisation is a term used within spatial epidemiology to refer to when ecological bias results as a consequence of adjusting disease rates for confounding In causal inference, a confounder is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Confounding is a causal concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlatio ... at the area level but leaving the exposure unadjusted and vice versa. This bias is prevented by adjusting in the same way both the exposure and disease rates. This adjustment is rarely possible as it requires data on within-area distribution of the exposure and confounder variables. (Elliot, 2001) See also * Outline of public health References *Elliott, P., J. C. Wakefield, N. G. Best and D. J. Briggs (eds.) 2001. Spatial Epidemiology: Methods and Applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Epidemiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GIS And Public Health
Geographic information systems (GISs) and geographic information science (GIScience) combine computer-mapping capabilities with additional database management and data analysis tools. Commercial GIS systems are very powerful and have touched many applications and industries, including environmental science, urban planning, agricultural applications, and others. Public health is another focus area that has made increasing use of GIS techniques. A strict definition of public health is difficult to pin down, as it is used in different ways by different groups. In general, public health differs from personal health in that it is (1) focused on the health of populations rather than of individuals, (2) focused more on prevention than on treatment, and (3) operates in a mainly governmental (rather than private) context. These efforts fall naturally within the domain of problems requiring use of spatial analysis as part of the solution, and GIS and other spatial analysis tools are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geographic Information Science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans understand the world, and how it can be captured, organized, and analyzed. It is a sub-field of geography, specifically part of technical geography. It has applications to both physical geography and human geography, although its techniques can be applied to many other fields of study as well as many different industries. As a field of study or profession, it can be contrasted with geographic information systems (GIS), which are the actual repositories of geospatial data, the software tools for carrying out relevant tasks, and the profession of GIS users. That said, one of the major goals of GIScience is to find practical ways to improve GIS data, software, and profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data and information, geographic data. Much of this often happens within a spatial database; however, this is not essential to meet the definition of a GIS. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system also to include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, the Geographic Information Science and Technology Body of Knowledge, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. The academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |