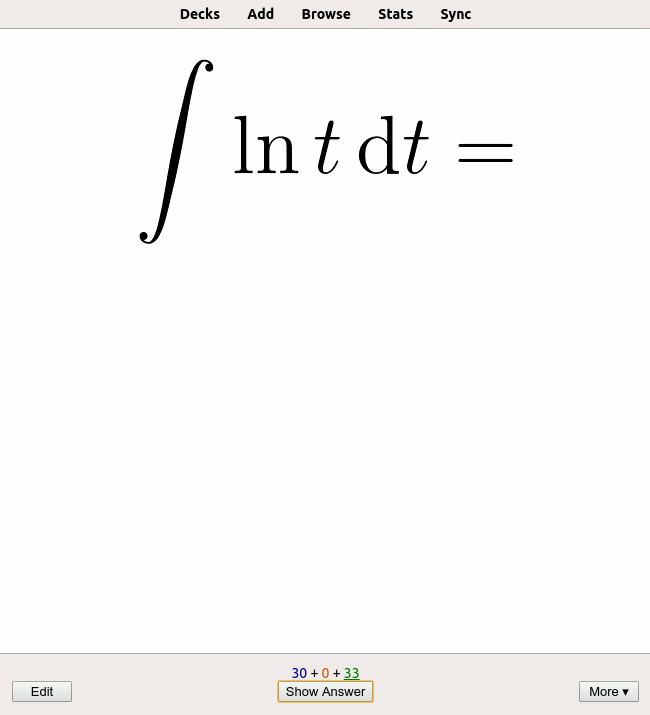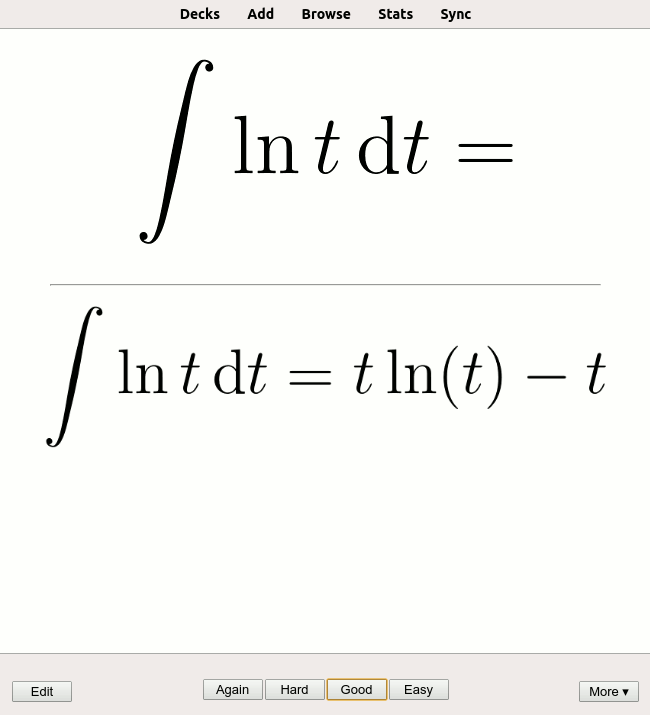|
Spaced Presentation
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that is usually performed with flashcards. Newly introduced and more difficult flashcards are shown more frequently, while older and less difficult flashcards are shown less frequently in order to exploit the psychological spacing effect. The use of spaced repetition has been proven to increase the rate of learning. Although the principle is useful in many contexts, spaced repetition is commonly applied in contexts in which a learner must acquire many items and retain them indefinitely in memory. It is, therefore, well suited for the problem of vocabulary acquisition in the course of second-language learning. A number of spaced repetition software programs have been developed to aid the learning process. It is also possible to perform spaced repetition with flashcards using the Leitner system. Alternative names for spaced repetition include spaced rehearsal, expanding rehearsal, graduated intervals, repetition spacin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leitner System Alternative
Leitner is an Austrian-German surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Alan Leitner (born 1947), American artist *Aloysius Leitner, United States Marine Corps *Anton G. Leitner (born 1961), German writer and publisher *Dummy Leitner (1872–1960), American baseball player *Edward Frederick Leitner (1812–1838), German physician and botanist *Erika Leitner, Italian luger *Ferdinand Leitner (1912–1996), German conductor *Franz Leitner (motorcyclist) (born 1968), Austrian motorcycle speedway rider * Franz Leitner (politician) (1918–2005), Austrian politician * Friedrich Leitner (1874–1945), German economist *Gottlieb Wilhelm Leitner (1840–1899), Anglo-Hungarian orientalist *Hias Leitner (born 1935), Austrian alpine skier *Jan Leitner (born 1953), Czech athlete * Karl Leitner (born 1937), Austrian sprint canoer *Karl Gottfried von Leitner (1800–1890), Austrian writer *Ludwig Leitner (1940–2013), West German alpine skier *Miroslav Leitner (born 1966), Slovak ski mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Melton
Arthur Weever Melton (August 13, 1906 – November 5, 1978) was an American experimental psychologist, researcher, and professor.Pachella, R. G. (2014). Creating the Modern Michigan Psychology Department: The Chairmanship of Donald Marquis, 1945-1957. He served as the editor of the ''Journal of Experimental Psychology'' for twelve years. Background Arthur "Art" Weever Melton was born in Fayetteville, Arkansas on August 13, 1906. At 18 years old, he began undergraduate studies in Psychology at Washington University in St. Louis where he worked with John A. McGeoch, a functionalist, who performed studies exploring how the distribution of practice, rest, and interpolated learning affects the formation and loss of association. Melton received a BA in psychology in 1928. He went on to graduate school at Yale University under the mentorship of Edward S. Robinson, another functionalist, whose research focused on verbal learning. Melton obtained his PhD in experimental psychology.in 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology Of Learning
The psychology of learning is a theoretical science that covers the various psychological theories that relate with learning. Throughout history, there has been many various psychological learning theories. Some take on a more behaviorist approach which focuses on inputs and reinforcements. Other approaches, such as theories related to neuroscience and social cognition, focus more on the brain's organization and structure to define learning. Some psychological approaches, such as social constructivism, focus more on one's interaction with the environment and with others. Other theories, such as those related to motivation, like the growth mindset, focus more on the individual. Psychology of learning is also very applicable today. There has been extensive research in recent years that looks closely at how students are learning both inside and outside the classroom. This information is then used to present new and more cooperative approaches to homework, tests and the student's abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning Methods
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before in terms of an embryo's need for both interaction with, and freedom within its environment within the womb.) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fields (including educational psychology, neuropsychology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorization
Memorization is the process of committing something to memory. It is a mental process undertaken in order to store in memory for later recall visual, auditory, or tactical information. The scientific study of memory is part of cognitive neuroscience, an interdisciplinary link between cognitive psychology and neuroscience. Development of memorization Within the first three years of a child's life, they begin to show signs of memory that is later improved into their adolescent years. This includes short-term memory, long-term memory, working memory, and autobiographical memory. Memory is a fundamental capacity that plays a special role in social, emotional, and cognitive functioning. Problems with studying the development of memorization include having to use verbal response and confirmation. Techniques Some principles and techniques that have been used to assist in memorization include: *Rote learning, a learning technique which focuses not on understanding but on memorization b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Pimsleur
Paul Pimsleur (October 17, 1927 – June 22, 1976) was a French-American linguist and scholar in the field of applied linguistics. He developed the Pimsleur language learning system, which, along with his many publications, had a significant effect upon theories of language learning and teaching. Pimsleur Language Programs is an American language learning company that develops and publishes courses based on the Pimsleur Method. Early life and education Paul M. Pimsleur was born in New York City and grew up in The Bronx. His father, Solomon Pimsleur, was a Jewish immigrant from France and a composer of music; his American-born mother, Miera, was a librarian at Columbia University. Pimsleur earned a bachelor's degree at the City College of New York, and from Columbia University he earned a master's degree in psychological statistics and a PhD in French. Career His first position involved teaching French phonetics and phonemics at the University of California, Los Angeles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leitner System Animation
Leitner is an Austrian-German surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Alan Leitner (born 1947), American artist *Aloysius Leitner, United States Marine Corps *Anton G. Leitner (born 1961), German writer and publisher *Dummy Leitner (1872–1960), American baseball player *Edward Frederick Leitner (1812–1838), German physician and botanist *Erika Leitner, Italian luger *Ferdinand Leitner (1912–1996), German conductor *Franz Leitner (motorcyclist) (born 1968), Austrian motorcycle speedway rider * Franz Leitner (politician) (1918–2005), Austrian politician * Friedrich Leitner (1874–1945), German economist *Gottlieb Wilhelm Leitner (1840–1899), Anglo-Hungarian orientalist *Hias Leitner (born 1935), Austrian alpine skier *Jan Leitner (born 1953), Czech athlete * Karl Leitner (born 1937), Austrian sprint canoer *Karl Gottfried von Leitner (1800–1890), Austrian writer *Ludwig Leitner (1940–2013), West German alpine skier *Miroslav Leitner (born 1966), Slovak ski mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anki 2 () (Anki), Quanzhou, Fujian, People's Republic of China
{{disambig ...
Anki may refer to: * Anki (software), spaced repetition software * Anki (company), a now-defunct American robotics and artificial intelligence startup * Anki (Finnish company), a manufacturer of rugs * Anxi County () is a County (People's Republic of China), county of the prefecture-level city of Quanzhou, in southern Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It lies adjacent to and directly north of Xiamen. Anxi is well known for a number of varietie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SuperMemo
SuperMemo (from "Super Memory") is a learning method and software package developed by SuperMemo World and SuperMemo R&D with Piotr Woźniak (researcher), Piotr Woźniak in Poland from 1985 to the present. It is based on research into long-term memory, and is a practical application of the spaced repetition learning method that has been proposed for efficient instruction by a number of psychologists as early as in the 1930s. The method is available as a computer program for Microsoft Windows, Windows, Windows CE, Windows Mobile, (Pocket PC), Palm OS (PalmPilot), etc. Course software by the same company (''SuperMemo World'') can also be used in a web browser or even without a computer. The desktop version of SuperMemo (since v. 2002) supports incremental reading, as well as traditional creation of question and answer flashcards. Software implementation The SuperMemo program stores a database of questions and answers constructed by the user. When reviewing information saved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network
A neural network is a network or circuit of biological neurons, or, in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus, a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of biological neurons, or an artificial neural network, used for solving artificial intelligence (AI) problems. The connections of the biological neuron are modeled in artificial neural networks as weights between nodes. A positive weight reflects an excitatory connection, while negative values mean inhibitory connections. All inputs are modified by a weight and summed. This activity is referred to as a linear combination. Finally, an activation function controls the amplitude of the output. For example, an acceptable range of output is usually between 0 and 1, or it could be −1 and 1. These artificial networks may be used for predictive modeling, adaptive control and applications where they can be trained via a dataset. Self-learning resulting from e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Method Of Memorization
Pythagorean, meaning of or pertaining to the ancient Ionian mathematician, philosopher, and music theorist Pythagoras, may refer to: Philosophy * Pythagoreanism, the esoteric and metaphysical beliefs purported to have been held by Pythagoras * Neo-Pythagoreanism, a school of philosophy reviving Pythagorean doctrines that became prominent in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD * Pythagorean diet, the name for vegetarianism before the nineteenth century Mathematics * Pythagorean theorem * Pythagorean triple * Pythagorean prime * Pythagorean trigonometric identity * Table of Pythagoras, another name for the multiplication table Music * Pythagorean comma * Pythagorean hammers * Pythagorean tuning Other uses * Pythagorean cup * Pythagorean expectation, a baseball statistical term * Pythagorean letter Upsilon (, ; uppercase Υ, lowercase υ; el, ''ýpsilon'' ) or ypsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, grc, Υʹ, label=none has a value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ..., linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's ''An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |