|
Sodium Dichromate
Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 Cr2 O7. However, the salt is usually handled as its dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2 H2O. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compounds and materials based on chromium are prepared from this salt.Gerd Anger, Jost Halstenberg, Klaus Hochgeschwender, Christoph Scherhag, Ulrich Korallus, Herbert Knopf, Peter Schmidt, Manfred Ohlinger, "Chromium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. In terms of reactivity and appearance, sodium dichromate and potassium dichromate are very similar. The sodium salt is, however, around twenty times more soluble in water than the potassium salt (49 g/L at 0 °C) and its equivalent weight is also lower, which is often desirable.Freeman, F. "Sodium Dichromate" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. . Preparation Sodium dichromate is g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate (natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily efflorescence, effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate (thermonatrite), Na2CO3·H2O. Also known as crystal carbonate. * anhydrous sodium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorene
Fluorene , or 9''H''-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. It has a violet fluorescence, hence its name. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity Although fluorene is obtained from coal tar, it can also be prepared by dehydrogenation of diphenylmethane. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reduction of fluorenone with zinc or hypophosphorous acid–iodine. The fluorene molecule is nearly planar,D. M. Burns, John Iball (1954), ''Molecular Structure of Fluorene'' Nature volume 173, p. 635. although each of the two benzene rings is coplanar with the central carbon 9. Fluorene can be found after the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menthone
Menthone is a monoterpene with a minty flavor that occurs naturally in a number of essential oils. ''l''-Menthone (or (2''S'',5''R'')-''trans''-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone), shown at right, is the most abundant in nature of the four possible stereoisomers. It is structurally related to menthol, which has a secondary alcohol in place of the carbonyl. Menthone is used in flavoring, perfume and cosmetics for its characteristic aromatic and minty odor. Occurrence Menthone is a constituent of the essential oils of pennyroyal, peppermint, ''Mentha arvensis'', ''Pelargonium'' geraniums, and others. In most essential oils, it is a minor compound; it was first synthesized by oxidation of menthol in 1881 before it was found in essential oils in 1891. Structure and preparation 2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone has two asymmetric carbon centers, meaning that it can have four different stereoisomers: (2''S'',5''S''), (2''R'',5''S''), (2''S'',5''R'') and (2''R'',5''R''). The ''S'','' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menthol
Menthol is an organic compound, more specifically a monoterpenoid, made synthetically or obtained from the oils of corn mint, peppermint, or other mints. It is a waxy, clear or white crystalline substance, which is solid at room temperature and melts slightly above. The main form of menthol occurring in nature is (−)-menthol, which is assigned the (1''R'',2''S'',5''R'') configuration. Menthol has local anesthetic and counterirritant qualities, and it is widely used to relieve minor throat irritation. Menthol also acts as a weak κ-opioid receptor agonist. Structure Natural menthol exists as one pure stereoisomer, nearly always the (1''R'',2''S'',5''R'') form (bottom left corner of the diagram below). The eight possible stereoisomers are: : In the natural compound, the isopropyl group is in the ''trans'' orientation to both the methyl and hydroxyl groups. Thus, it can be drawn in any of the ways shown: : The (+)- and (−)-enantiomers of menthol are the most stable among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,4,6-trinitrotoluene
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts. History TNT was first prepared in 1863 by German chemist Julius Wilbrand and originally used as a yellow dye. Its potential as an explosive was not recognized for three decades, mainly because it was too difficult to detonate because it was less sensitive than alternatives. Its explosive properties were first discovered in 1891 by another German chemist, Carl Häussermann. TNT can be safely poured when liquid into shell cases, and is so insensitive that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
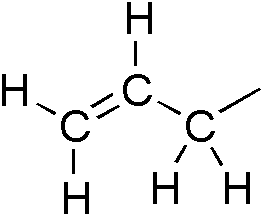
Allylic
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylic
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group. Nomenclature In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substituent, for example benzyl chloride or benzyl benzoate. Benzyl is not to be confused with phenyl with the formula . The term benzylic is used to describe the position of the first carbon bonded to a benzene or other aromatic ring. For example, is referred to as a "benzylic" carbocation. The benzyl free radical has the formula . The benzyl cation or phenylcarbenium ion is the carbocation with formula ; the benzyl anion or phenylmethanide ion is the carbanion with the formula . None of these species can be formed in significant amounts in the solution phase under normal conditions, but they are useful referents for discussion of reaction mechanisms and may exist as reactive intermediates. Abbreviations The abbreviation "Bn" denotes benzyl. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |