|
Socioeconomic Status And Mental Health
Numerous studies around the world have found a relationship between socioeconomic status and mental health. There are higher rates of mental illness in groups with lower socioeconomic status (SES), but there is no clear consensus on the exact causative factors. The two principal models that attempt to explain this relationship are the social causation theory, which posits that socioeconomic inequality causes stress that gives rise to mental illness, and the downward drift approach, which assumes that people predisposed to mental illness are reduced in socioeconomic status as a result of the illness. Most literature on these concepts dates back to the mid-1990s and leans heavily towards the social causation model. Social causation The social causation theory is an older theory with more evidence and research behind it. This hypothesis states that one's socioeconomic status (SES) is the cause of weakening mental functions. As Perry writes in ''The Journal of Primary Prevention'', " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
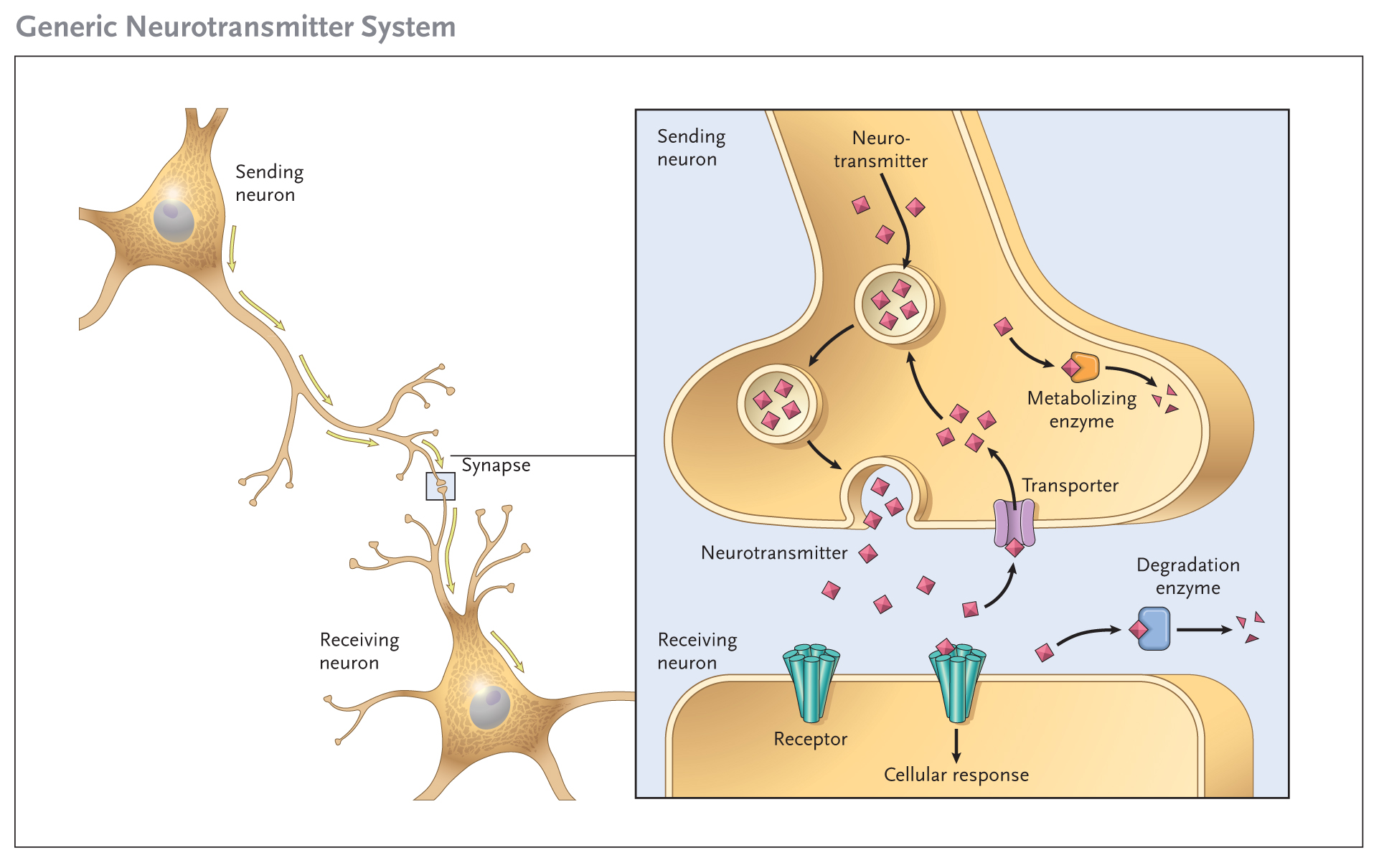
Mental Illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitting, or occur as single episodes. Many disorders have been described, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. Such disorders may be diagnosed by a mental health professional, usually a clinical psychologist or psychiatrist. The causes of mental disorders are often unclear. Theories may incorporate findings from a range of fields. Mental disorders are usually defined by a combination of how a person behaves, feels, perceives, or thinks. This may be associated with particular regions or functions of the brain, often in a social context. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health. Cultural and religious beliefs, as well as social norms, should be taken into account when making a diagnosis. Services are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's SES, the household income, earners' education, and occupation are examined, as well as combined income, whereas for an individual's SES only their own attributes are assessed. Recently, research has revealed a lesser recognized attribute of SES as perceived financial stress, as it defines the "balance between income and necessary expenses". Perceived financial stress can be tested by deciphering whether a person at the end of each month has more than enough, just enough, or not enough money or resources. However, SES is more commonly used to depict an economic difference in society as a whole. Socioeconomic status is typically broken into three levels (high, middle, and low) to describe the three places a family or an individual may fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Model
A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people knowledge, know, understanding, understand, or simulation, simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, physical models are physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents. The term may refer to models that are formed after a wikt:concept#Noun, conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantics, Semantic studies are relevant to various stages of process of concept formation, concept formation. Semantics is basically about concepts, the meaning that thinking beings give to various elements of their experience. Overview Models of concepts and models that are conceptual The term ''conceptual model'' is normal. It could mean "a model of concept" or it could mean "a model that is conceptual." A distinction can be made bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final phase of basic education, and level 3 (upper) secondary education or senior secondary education is the stage before tertiary education. Every country aims to provide basic education, but the systems and terminology remain unique to them. Secondary education typically takes place after six years of primary education and is followed by higher education, vocational education or employment. In most countries secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, at least until the age of 16. Children typically enter the lower secondary phase around age 12. Compulsory education sometimes extends to age 19. Since 1989, education has been seen as a basic human right for a child; Article 28, of the Convention on the Rights of the Child states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including university, universities as well as trade schools and colleges. Higher education is taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, while vocational education beyond secondary education is known as ''further education'' in the United Kingdom, or included under the category of ''continuing education'' in the United States. Tertiary education generally culminates in the receipt of Academic certificate, certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees. UNESCO stated that tertiary education focuses on learning endeavors in specialized fields. It includes academic and higher vocational education. The World Bank's 2019 World Development Report on the future of work argues that given the future of work and the increasing role of technology in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodromal Symptoms
In medicine, a prodrome is an early Medical sign, sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. It is derived from the Greek word ''prodromos'', meaning "running before". Prodromes may be non-specific symptoms or, in a few instances, may clearly indicate a particular disease, such as the prodromal migraine aura. For example, fever, malaise, headache and lack of appetite frequently occur in the prodrome of many Infection, infective disorders. A prodrome can be the early precursor to an episode of a chronic neurological disorder such as a migraine headache or an epileptic seizure, where prodrome symptoms may include euphoria or other changes in mood (psychology), mood, insomnia, abdominal aura, abdominal sensations, disorientation, aphasia, or photophobia, photosensitivity. Such a prodrome occurs on a scale of days to an hour before the episode, where an aura (symptom), aura oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causes Of Mental Disorders
A mental disorder is an impairment of the mind disrupting normal thinking, feeling, mood, behavior, or social interactions, and accompanied by significant distress or dysfunction. The causes of mental disorders are very complex and vary depending on the particular disorder and the individual. Although the causes of most mental disorders are not fully understood, researchers have identified a variety of biological, psychological, and environmental factors that can contribute to the development or progression of mental disorders. Most mental disorders result in a combination of several different factors rather than just a single factor. Research results Risk factors for mental illness include psychological trauma, adverse childhood experiences, genetic predisposition, and personality traits. Correlations of mental disorders with drug use include almost all psychoactive substances, e.g., cannabis, alcohol, and caffeine. Mental illnesses have risk factors, for instance including une ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homelessness And Mental Health
In a study in Western societies, homeless people have a higher prevalence of mental illness when compared to the general population. They also are more likely to suffer from alcoholism and drug dependency. It is estimated that 20–25% of homeless people, compared with 6% of the non-homeless, have severe mental illness. Others estimate that up to one-third of the homeless have a mental illness. In January 2015, the most extensive survey ever undertaken found 564,708 people were homeless on a given night in the United States. Depending on the age group in question and how homelessness is defined, the consensus estimate as of 2014 was that, at minimum, 25% of the American homeless—140,000 individuals—were seriously mentally ill at any given point in time. 45% percent of the homeless—250,000 individuals—had any mental illness. More would be labeled homeless if these were annual counts rather than point-in-time counts. Being chronically homeless also means that people with mental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Health Inequality
Mental health inequality refers to the differences in the quality, access, and health care different communities and populations receive for mental health services. Globally, the World Health Organization estimates that 350 million people are affected with depressive disorders. Mental health can be defined as an individual's well-being and/or the absence of clinically defined mental illness. Inequalities that can occur in mental healthcare may include mental health status, access to and quality of care, and mental health outcomes, which may differ across populations of different race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, sex, gender, socioeconomic statuses, education level, and geographic location. Social determinants of health, more specifically the social determinants of mental health, that can influence an individual's susceptibility to developing mental disorders and illnesses include, but are not limited to, economic status, education level, demographics, geographic location and gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
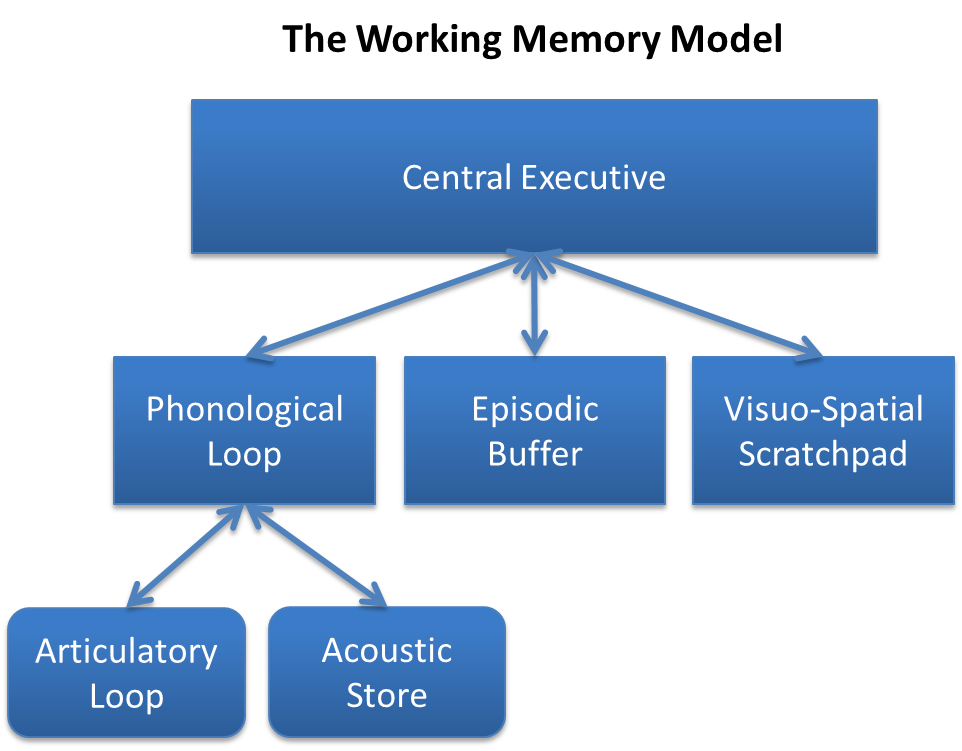
Socioeconomic Status And Memory
Memory is one of the brain's most critical functions. It has the infinite ability to store information about events and experiences that occur constantly.Pinel, J.P.J., & Edwards, M. (2008). A colorful introduction to the anatomy of the human brain: A brain and psychology coloring book (2nd ed.). USA: Pearson.2 Experiences shape the way memories form, so major stressors on socioeconomic status can impact memory development. Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement of social standing based on income, education, and other factors.Siegler, R., Eisenberg, N., DeLoache, J., Saffran, J., & Graham, S. (2014). How Children Develop (4th ed. New York: Worth. Socioeconomic status can differ cross-culturally, but is also commonly seen within cultures themselves. It influences all spectrums of a child's life, including cognitive development, which is in a crucial and malleable state during early stages of childhood. In Canada, most children grow up in agreeable circumstances, however an u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |