|
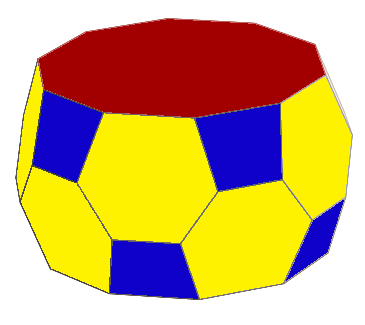
Snub Square Antiprism
In geometry, the snub square antiprism is one of the Johnson solids (). It is one of the elementary Johnson solids that do not arise from "cut and paste" manipulations of the Platonic and Archimedean solids, although it is a relative of the icosahedron that has fourfold symmetry instead of threefold. Construction The ''snub square antiprism'' is constructed as its name suggests, a square antiprism which is snubbed, and represented as ss, with s as a square antiprism. It can be constructed in Conway polyhedron notation as sY4 (''snub square pyramid''). It can also be constructed as a square gyrobianticupolae, connecting two anticupolae with gyrated orientations. Cartesian coordinates Let ''k'' ≈ 0.82354 be the positive root of the cubic polynomial :9x^3+3\sqrt\left(5-\sqrt\right)x^2-3\left(5-2\sqrt\right)x-17\sqrt+7\sqrt. Furthermore, let ''h'' ≈ 1.35374 be defined by :h=\frac. Then, Cartesian coordinates of a snub square antiprism with edge length 2 are given by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that isohedral, each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each Vertex (geometry), vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based Pyramid (geometry), pyramid with equilateral sides (square pyramid, ); it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform polyhedron, uniform (i.e., not Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism (geometry), uniform prism, or uniform antiprism) before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”. As in any strictly convex solid, at least three faces meet at every vertex, and the total of their angles is less than 360 degrees. Since a regular polygon has angles at least 60 degrees, it follows that at most five faces meet at any vertex. The pentagonal pyramid () is an example that has a degree-5 vertex. Although there is no obvious restriction tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line is called a ''coordinate axis'' or just ''axis'' (plural ''axes'') of the system, and the point where they meet is its ''origin'', at ordered pair . The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin. One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, ''n'' Cartesian coordinates (an element of real ''n''-space) specify the point in an ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentagonal Antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for a total of 12 faces. Hence, it is a non-regular dodecahedron. Geometry If the faces of the pentagonal antiprism are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron. It can also be considered as a parabidiminished icosahedron, a shape formed by removing two pentagonal pyramids from a regular icosahedron leaving two nonadjacent pentagonal faces; a related shape, the metabidiminished icosahedron (one of the Johnson solids), is likewise form from the icosahedron by removing two pyramids, but its pentagonal faces are adjacent to each other. The two pentagonal faces of either shape can be augmented with pyramids to form the icosahedron. Relation to polytopes The pentagonal antiprism occurs as a constituent element in some higher-dimensional p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentagonal Antiprism
In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for a total of 12 faces. Hence, it is a non-regular dodecahedron. Geometry If the faces of the pentagonal antiprism are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron. It can also be considered as a parabidiminished icosahedron, a shape formed by removing two pentagonal pyramids from a regular icosahedron leaving two nonadjacent pentagonal faces; a related shape, the metabidiminished icosahedron (one of the Johnson solids), is likewise form from the icosahedron by removing two pyramids, but its pentagonal faces are adjacent to each other. The two pentagonal faces of either shape can be augmented with pyramids to form the icosahedron. Relation to polytopes The pentagonal antiprism occurs as a constituent element in some higher-dimensional p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite family of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It is also known as an ''anticube''. If all its faces are regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron or uniform polyhedron. A nonuniform ''D''4-symmetric variant is the cell of the noble square antiprismatic 72-cell. Points on a sphere When eight points are distributed on the surface of a sphere with the aim of maximising the distance between them in some sense, the resulting shape corresponds to a square antiprism rather than a cube. Specific methods of distributing the points include, for example, the Thomson problem (minimizing the sum of all the reciprocals of distances between points), maximising the distance of each point to the nearest point, or minimising the sum of all reciprocals of squares of distances between points. Molecules with square antiprismatic geometry According to the VSEPR theory of molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonal Antiprism
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
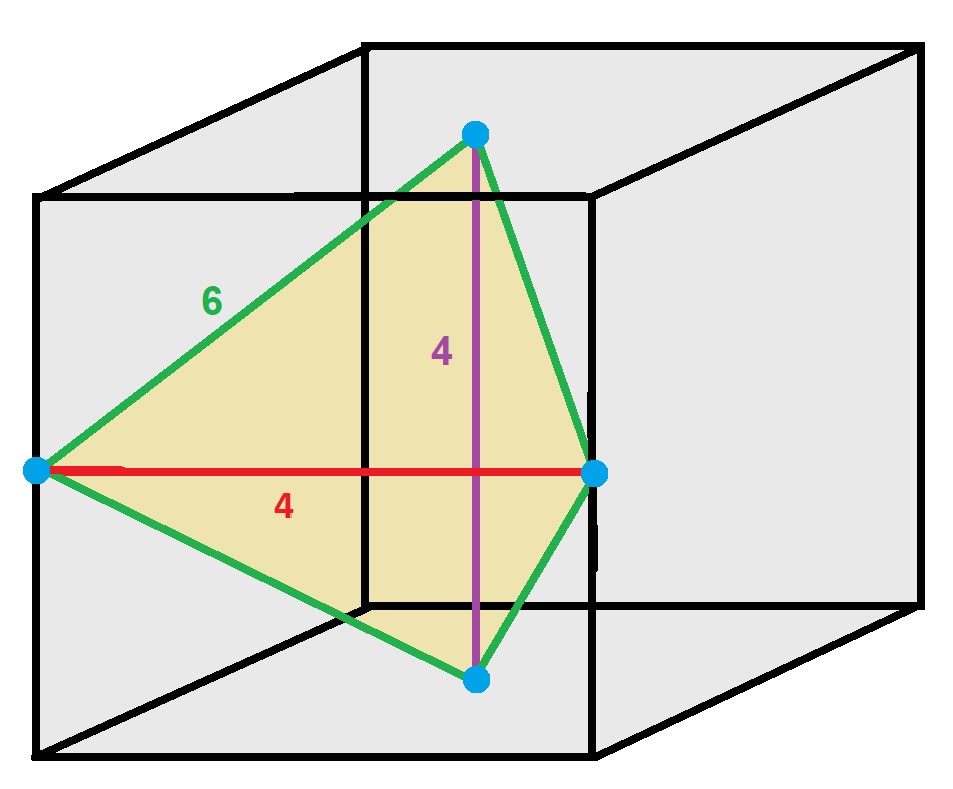
Disphenoid
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four faces are congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same shape are isotetrahedron,. sphenoid,. bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron,. equifacial tetrahedron, almost regular tetrahedron, and tetramonohedron. All the solid angles and vertex figures of a disphenoid are the same, and the sum of the face angles at each vertex is equal to two right angles. However, a disphenoid is not a regular polyhedron, because, in general, its faces are not regular polygons, and its edges have three different lengths. Special cases and generalizations If the faces of a disphenoid are equilateral triangles, it is a regular tetrahedron with Td tetrahedral symmetry, although this is not normally called a disphenoid. When the faces of a disphenoid are isosceles triangles, it is called a tetragonal disphenoid. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digonal Antiprism
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four faces are congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same shape are isotetrahedron,. sphenoid,. bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron,. equifacial tetrahedron, almost regular tetrahedron, and tetramonohedron. All the solid angles and vertex figures of a disphenoid are the same, and the sum of the face angles at each vertex is equal to two right angles. However, a disphenoid is not a regular polyhedron, because, in general, its faces are not regular polygons, and its edges have three different lengths. Special cases and generalizations If the faces of a disphenoid are equilateral triangles, it is a regular tetrahedron with Td tetrahedral symmetry, although this is not normally called a disphenoid. When the faces of a disphenoid are isosceles triangles, it is called a tetragonal disphenoid. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprism
In geometry, an antiprism or is a polyhedron composed of two parallel direct copies (not mirror images) of an polygon, connected by an alternating band of triangles. They are represented by the Conway notation . Antiprisms are a subclass of prismatoids, and are a (degenerate) type of snub polyhedron. Antiprisms are similar to prisms, except that the bases are twisted relatively to each other, and that the side faces (connecting the bases) are triangles, rather than quadrilaterals. The dual polyhedron of an -gonal antiprism is an -gonal trapezohedron. History At the intersection of modern-day graph theory and coding theory, the triangulation of a set of points have interested mathematicians since Isaac Newton, who fruitlessly sought a mathematical proof of the kissing number problem in 1694. The existence of antiprisms was discussed, and their name was coined by Johannes Kepler, though it is possible that they were previously known to Archimedes, as they satisfy the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digonal Antiprism
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four faces are congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same shape are isotetrahedron,. sphenoid,. bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron,. equifacial tetrahedron, almost regular tetrahedron, and tetramonohedron. All the solid angles and vertex figures of a disphenoid are the same, and the sum of the face angles at each vertex is equal to two right angles. However, a disphenoid is not a regular polyhedron, because, in general, its faces are not regular polygons, and its edges have three different lengths. Special cases and generalizations If the faces of a disphenoid are equilateral triangles, it is a regular tetrahedron with Td tetrahedral symmetry, although this is not normally called a disphenoid. When the faces of a disphenoid are isosceles triangles, it is called a tetragonal disphenoid. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digon
In geometry, a digon is a polygon with two sides (edges) and two vertices. Its construction is degenerate in a Euclidean plane because either the two sides would coincide or one or both would have to be curved; however, it can be easily visualised in elliptic space. A regular digon has both angles equal and both sides equal and is represented by Schläfli symbol . It may be constructed on a sphere as a pair of 180 degree arcs connecting antipodal points, when it forms a lune. The digon is the simplest abstract polytope of rank 2. A truncated ''digon'', t is a square, . An alternated digon, h is a monogon, . In Euclidean geometry The digon can have one of two visual representations if placed in Euclidean space. One representation is degenerate, and visually appears as a double-covering of a line segment. Appearing when the minimum distance between the two edges is 0, this form arises in several situations. This double-covering form is sometimes used for defining degener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |