|
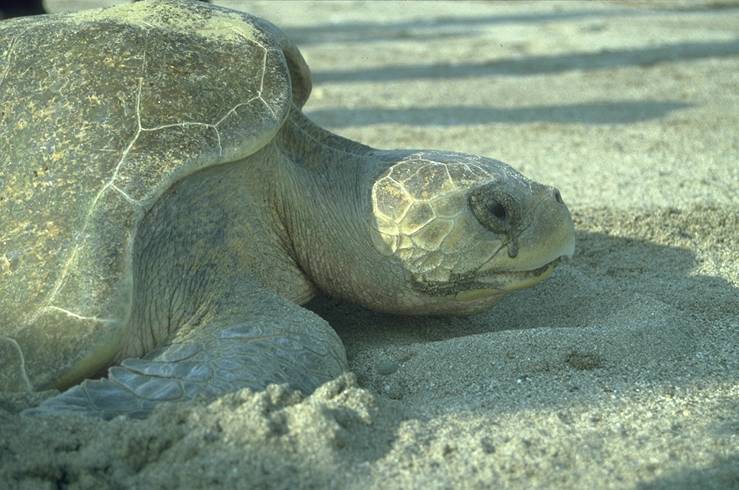
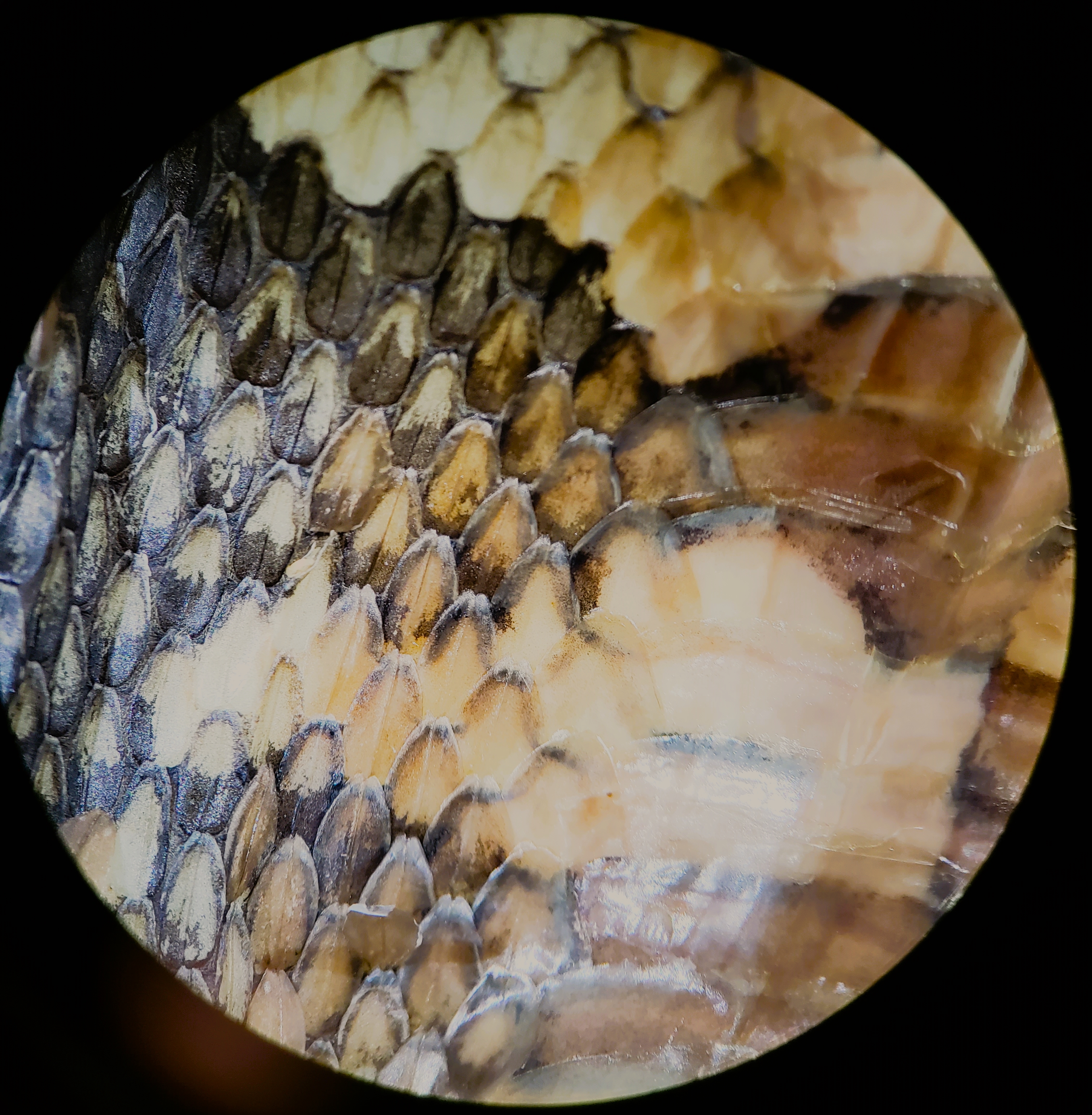
Snake Skin
Snakeskin may either refer to the skin of a live snake, the shed skin of a snake after molting, or to a type of leather that is made from the hide of a dead snake. Snakeskin and scales can have varying patterns and color formations, providing protection via camouflage from predators. The colors and iridescence in these scales are largely determined by the types and amount of chromatophores located in the dermis of the snake skin. The snake's skin and scales are also an important feature to their locomotion, providing protection and minimizing friction when gliding over surfaces. Skin of a living snake In a living snake, its skin often deals with various forms of abrasion. To combat rough substrates, snakes have formed specialized and multilayered organizational epidermal structures to provide a safe and efficient sliding locomotion when maneuvering over rough surfaces. Display Pattern formation Snakes can be ornately patterned. They can be striped, banded, solid, green, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer layer or covering), either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle. In medieval times it was also known as "mewing" (from the French verb "muer", to moult), a term that lives on in the name of Britain's Royal Mews where the King's hawks used to be kept during moulting time before becoming horse stables after Tudor times. Moulting can involve shedding the Epidermis (skin), epidermis (skin), pelage (hair, feathers, fur, wool), or other external layer. In some groups, other body parts may be shed, for example, the entire exoskeleton in arthropods, including the wings in some insects. Examples In birds In birds, moulting is the periodic replacement of feathers by shedding old feathers while producing new o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile Scale
Reptile skin is covered with scutes or scales which, along with many other characteristics, distinguish reptiles from animals of other classes. They are made of alpha and beta-keratin and are formed from the epidermis (contrary to fish, in which the scales are formed from the dermis). The scales may be ossified or tubercular, as in the case of lizards, or modified elaborately, as in the case of snakes. Smith, Malcolm A. (1931). ''The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma. Vol. I.—Loricata, Testudines.'' London: Secretary of State for India in Council. (Taylor and Francis, printers). xxviii + 185 pp. + Plates I-II. ("Skin", p. 30). The scales on the top of lizard and snake heads has also been called ''pileus'', after the Latin word for cap, referring to the fact that these scales sit on the skull like a cap. Lizard scales Lizard scales vary in form from tubercular to platelike, or imbricate (overlapping). These scales, which on the surface are composed of horny (keratinized) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axis, anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribology
Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative Motion (physics), motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear. Tribology is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. People who work in the field of tribology are referred to as ''tribologists''. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. In lubricated tribosystems, contact stress can create tribofilms. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology, space tribology and tribotronics. Etymology The word ''tribology'' derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek root τριβ- of the verb , ''wiktionary:tribo-, tribo'', "I rub" in classic Greek, and the suffix ''-logy'' from , ''wiktionary:-logia, -logia'' "study of", "knowledge of". Peter Jost coined the word in 1966, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Gland
The salt gland is an organ for excreting excess salts. It is found in the cartilaginous fishes subclass elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, and skates), seabirds, and some reptiles. Salt glands can be found in the rectum of sharks. Birds and reptiles have salt glands located in or on the skull, usually in the eyes, nose, or mouth. These glands are lobed containing many secretory tubules which radiate outward from the excretory canal at the center. Secretory tubules are lined with a single layer of epithelial cells. The diameter and length of these glands vary depending on the salt uptake of the species. Salt glands maintain salt balance and allow marine vertebrates to drink seawater. Active transport via sodium–potassium pump, found on the basolateral membrane, moves salt from the blood into the gland, where it is excreted as a concentrated solution. In birds The avian salt gland has two main ducts which are a medial and a lateral. Salt gland activations occurs from increased o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocrine
Holocrine (from Ancient Greek ὅλος; ''hólos'', “whole, entire” + κρῑ́νω; ''krī́nō'', “to separate”) is a term used to classify the mode of secretion in exocrine glands in the study of histology. Holocrine secretions are produced in the cytoplasm of the cell and released by the rupture of the plasma membrane, which destroys the cell and results in the secretion of the product into the lumen. Holocrine gland secretion is the most damaging (to the cell itself and not to the host which begot the cell) type of secretion, with merocrine secretion being the least damaging and apocrine secretion falling in between. Examples of holocrine glands include the sebaceous glands of the skin and the meibomian glands of the eyelid. The sebaceous gland is an example of a holocrine gland because its product of secretion (sebum A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permeation
In physics and engineering, permeation (also called imbuing) is the penetration of a permeate (a fluid such as a liquid, gas, or vapor) through a solid. It is directly related to the concentration gradient of the permeate, a material's intrinsic permeability, and the materials' mass diffusivity. Permeation is modeled by equations such as Fick's laws of diffusion, and can be measured using tools such as a minipermeameter. Description The process of permeation involves the diffusion of molecules, called the permeant, through a membrane or interface. Permeation works through diffusion; the permeant will move from high concentration to low concentration across the interface. A material can be semipermeable, with the presence of a semipermeable membrane. Only molecules or ions with certain properties will be able to diffuse across such a membrane. This is a very important mechanism in biology where fluids inside a blood vessel need to be regulated and controlled. Permeation can occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposed Integument Under A Garter Snake Scute
Expose, exposé, or exposed may refer to: News sources * Exposé (journalism), a form of investigative journalism * '' The Exposé'', a British conspiracist website Film and TV Film * ''Exposé'' (film), a 1976 thriller film * ''Exposed'' (1932 film), a 1932 film starring Barbara Kent * ''Exposed'' (1938 film), a 1938 film starring Glenda Farrell * ''Exposed'' (1947 film), a 1947 film starring Adele Mara * ''Exposed'' (1983 film), a 1983 film starring Nastassja Kinski * ''Exposed'' (2003 film), a 2003 American independent comedy film * ''Exposed'' (2011 film), a 2011 film starring Jodi Lyn O'Keefe * ''Exposed'' (2016 film), a 2016 film starring Keanu Reeves Television * "Exposé" (''Lost''), a 2007 episode of ''Lost'' * '' Exposé: America's Investigative Reports'', a PBS news/documentary series * ''eXposed'', the pilot of the American television show ''The Gifted'' * ''Exposed'' (U.S. game show), a 2007 American dating game show that aired on MTV * ''Exposed'' (Canadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneous
Corneous is a biological and medical term meaning horny, in other words made out of a substance similar to that of horns and hooves in some mammals. The word is generally used to describe natural or pathological anatomical structures made out of a hard layer of protein. In mammals this protein would usually be keratin. The word corneous is also often used to describe the operculum of a snail, a gastropod mollusc. Not all gastropods have opercula, but in the great majority of those that do have one, the operculum is corneous. (However in several genera within a few families including the marine Naticidae and the terrestrial Pomatiidae, the operculum is primarily calcareous, in other words mostly made of calcium carbonate.) Corneous opercula are made out of the protein conchiolin. References Corneousat dictionary.com Dictionary.com is an online dictionary whose domain was first registered on May 14, 1995. The primary content on Dictionary.com is a proprietary dictionary bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-keratin
Alpha-keratin, or α-keratin, is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. This protein is the primary component in hairs, horns, mammalian claws, nails and the epidermis layer of the skin. α-keratin is a fibrous structural protein, meaning it is made up of amino acids that form a repeating secondary structure. The secondary structure of α-keratin is very similar to that of a traditional protein α-helix and forms a coiled coil. Due to its tightly wound structure, it can function as one of the strongest biological materials and has various functions in mammals, from predatory claws to hair for warmth. α-keratin is synthesized through protein biosynthesis, utilizing transcription and translation, but as the cell matures and is full of α-keratin, it dies, creating a strong non-vascular unit of keratinized tissue. Structure α-keratin is a polypeptide chain, typically high in alanine, leucine, arginine, and cysteine, that forms a right-handed α-helix. Two of these polypeptide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue, and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |