|
Snake Bites
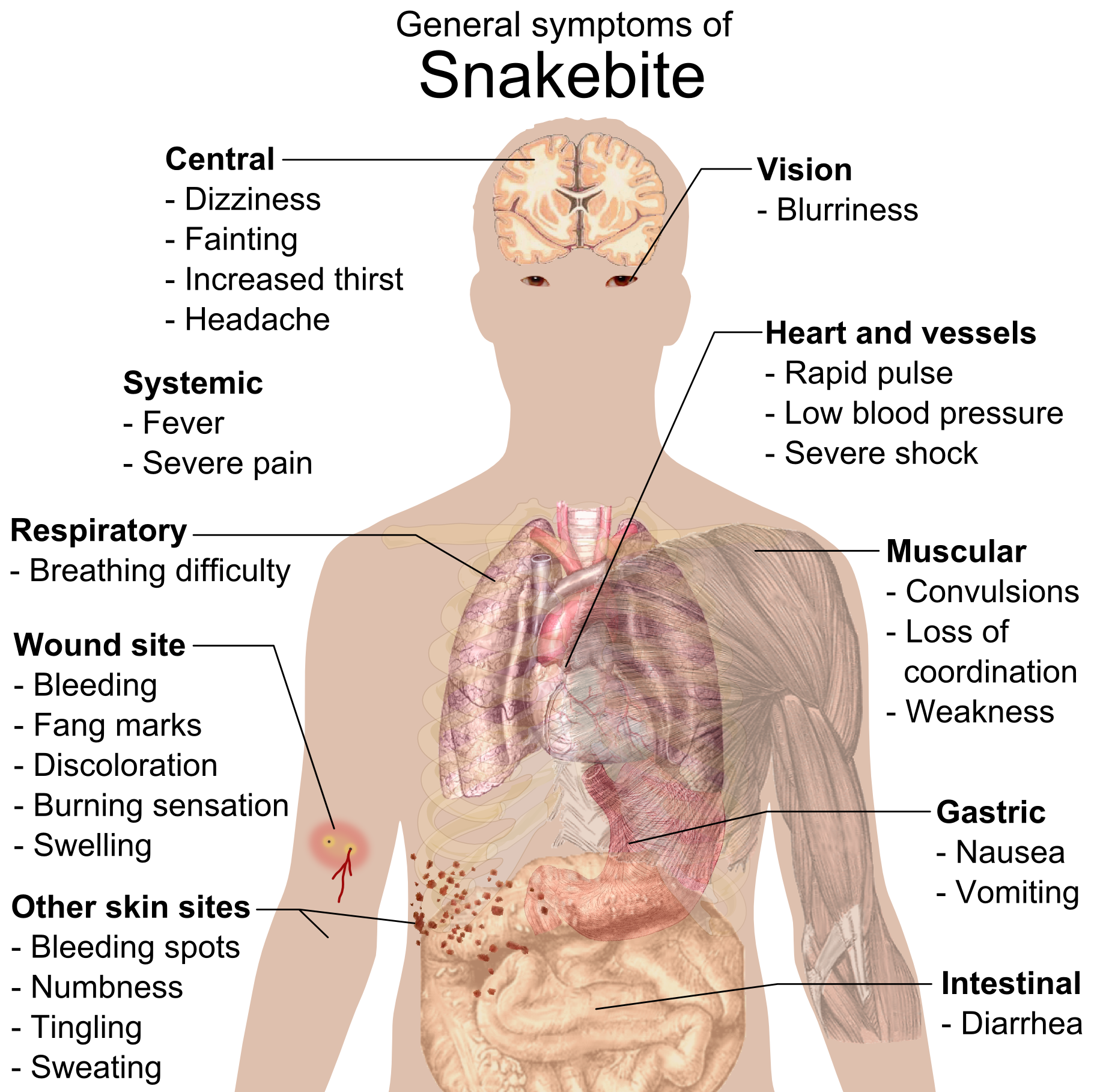
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor in a time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small animals such as birds and rodents. Rattlesnakes receive their name from the rattle located at the end of their tails, which makes a loud rattling noise when vibrated that deters predators or serves as a warning to passers-by. Rattlesnakes are the leading contributor to snakebite injuries in North America, but rarely bite unless provoked or threatened; if treated promptly, the bites are seldom fatal. The 36 known species of rattlesnakes have between 65 and 70 subspecies, all native to the Americas, ranging from British Columbia through Ontario in southern Canada, to central Argentina. The largest rattlesnake, the eastern diamondback, can measure up to in length. Rattlesnakes are preyed upon by hawks, weasels, king snakes, and a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivenom
Antivenom, also known as antivenin, venom antiserum, and antivenom immunoglobulin, is a specific treatment for envenomation. It is composed of antibodies and used to treat certain venomous bites and stings. Antivenoms are recommended only if there is significant toxicity or a high risk of toxicity. The specific antivenom needed depends on the species involved. It is given by injection. Side effects may be severe. They include serum sickness, shortness of breath, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Antivenom is traditionally made by collecting venom from the relevant animal and injecting small amounts of it into a domestic animal. The antibodies that form are then collected from the domestic animal's blood and purified. Versions are available for spider bites, snake bites, fish stings, and scorpion stings. Due to the high cost of producing antibody-based antivenoms and their short shelf lives when not refrigerated, alternative methods of production of antivenoms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krait
''Bungarus'' is a genus of venomous elapid snakes, the kraits ("krait" is pronounced , rhyming with "kite"), found in South and Southeast Asia. The genus ''Bungarus'' has 16 species. Distribution Kraits are found in tropical Asia, from near Iran, through the Indian subcontinent (including Sri Lanka and Bangladesh) and on to Southeast Asia (including Indonesia and Borneo). Description Kraits usually range between in total length (including tail), although specimens as large as have been observed. The banded krait (''B. fasciatus'') may grow as large as . Smith, Malcolm A. (1943). ''The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma, Including the Whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-region. Reptilia and Amphibia. Vol. III.—Serpentes''. London: Secretary of State for India. (Taylor and Francis, printers). xii + 583 pp. (''Bungarus'', genus and species, pp. 407-418). Most species of kraits are covered in smooth, glossy scales arranged in bold, striped patterns of alternating black and lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elapid
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydocephalus. Many members of this family exhibit a threat display of rearing upwards while spreading out a neck flap. Elapids are endemic to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, with terrestrial forms in Asia, Australia, Africa, and the Americas and marine forms in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Members of the family have a wide range of sizes, from the white-lipped snake to the king cobra. Most species have neurotoxic venom which is channeled by their hollow fangs, and some may contain other toxic components in various proportions. The family includes 55 genera with some 360 species and over 170 subspecies. Description Terrestrial elapids look similar to the Colubridae; almost all have long, slender bodies with smooth scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection. Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often used as a synonym. The main difference lies in the realm of practice: medicine (clinical practice) versus public health. As an example from clinical practice, low ingestion of dietary sources of vitamin C is a known risk factor for developing scurvy. Specific to public health policy, a determinant is a health risk that is general, abstract, related to inequalities, and difficult for an individual to control. For example, poverty is known to be a determinant of an individual's standard of health. Correlation vs causation Risk factors or determinants are correlational and not necessarily causal, because correlation does not prove causation. For example, being young cannot be said to cause measles, but young people have a higher rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Venom
Snake venom is a highly toxic saliva containing zootoxins that facilitates in the immobilization and digestion of prey. This also provides defense against threats. Snake venom is injected by unique fangs during a bite, whereas some species are also able to spit venom. The glands that secrete zootoxins are a modification of the parotid salivary glands found in other vertebrates and are usually located on each side of the head, below and behind the eye, and enclosed in a muscular sheath. The venom is stored in large glands called alveoli in which it's stored before being conveyed by a duct to the base of channeled or tubular fangs through which it's ejected. Venom contains more than 20 different compounds, which are mostly proteins and polypeptides. The complex mixture of proteins, enzymes, and various other substances has toxic and lethal properties. Venom serves to immobilize prey. Enzymes in venom play an important role in the digestion of prey, and various other substances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Condition
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Lyme disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV which allow these individuals to live while managing symptoms. In medicine, ''chronic'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals cause tens of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness. Dizziness is a common medical complaint, affecting 20-30% of persons. Dizziness is broken down into 4 main subtypes: vertigo (~25-50%), disequilibrium (less than ~15%), presyncope (less than ~15%), and nonspecific dizziness (~10%). * Vertigo is the sensation of spinning or having one's surroundings spin about them. Many people find vertigo very disturbing and often report associated nausea and vomiting. * Presyncope describes lightheadedness or feeling faint; the name relates to syncope, which is actually fainting. * Disequilibrium is the sensation of being off balance and is most often characterized by frequent falls in a specific direction. This condition is not often associated with nausea or vomiting. * Non-specific dizziness may be psychiatric in origin. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (such as with exercise) or abnormal (such as with electrical problems within the heart). Complications Tachycardia can lead to fainting. When the rate of blood flow becomes too rapid, or fast blood flow passes on damaged endothelium, it increases the friction within vessels resulting in turbulence and other disturbances. According to the Virchow's triad, this is one of the three conditions that can lead to thrombosis (i.e., blood clots within vessels). Causes Some causes of tachycardia include: * Adrenergic storm * Anaemia * Anxiety * Atrial fibrillation * Atrial flutter * Atrial tachycardia * Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia * AV nodal reentrant tachycardia * Brugada syndrome * Circulatory shock and its various causes ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fear
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear in human beings may occur in response to a certain stimulus occurring in the present, or in anticipation or expectation of a future threat perceived as a risk to oneself. The fear response arises from the perception of danger leading to confrontation with or escape from/avoiding the threat (also known as the fight-or-flight response), which in extreme cases of fear ( horror and terror) can be a freeze response or paralysis. In humans and other animals, fear is modulated by the process of cognition and learning. Thus, fear is judged as rational or appropriate and irrational or inappropriate. An irrational fear is called a phobia. Fear is closely related to the emotion anxiety, which occurs as the result of threats that are perceive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging disorder. Complications Aspiration Vomiting is dangerou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





