|
Skin Immunity
Skin immunity is a property of skin that allows it to resist infections from pathogens. In addition to providing a passive physical barrier against infection, the skin also contains elements of the innate and adaptive immune systems which allows it to actively fight infections. Hence the skin provides defense in depth against infection. The skin acts as a barrier, a kind of sheath, made of several layers of cells and their related glands. The skin is a dynamic organ that contains different cells which contains elements of the innate and the adaptive immune systems which are activated when the tissue is under attack by invading pathogens. Shortly after infection, the immune adaptive response is induced by dendritic cells ( Langerhans cells) present in the epidermis; they are responsible for the capture, processing, and presentation of antigens to T lymphocytes in local lymphoid organs. As a result, T lymphocytes express the cutaneous lymphocyte antigen (CLA) molecule, a modified f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. In contrast, too much inflammation, in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that causes the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 17
Interleukin 17 family (IL17 family) is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier ''et al.'' who isolated IL17A transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma. The protein encoded by ''IL17A'' is a founding member of IL-17 family (see below). IL17A protein exhibits a high homology with a viral IL-17-like protein () encoded in the genome of T-lymphotropic rhadinovirus ''Herpesvirus saimiri''. In rodents, IL-17A is often referred to as CTLA8. The biologically active IL-17 interacts with type I cell surface receptor IL-17R. In turn, there are at least three variants of IL-17R referred to as IL17RA, IL17RB, and IL17RC. After binding to the receptor, IL-17 activates several signalling cascades that, in turn, lead to the induction of chemokines. Acting as chemoattractants, these chemokines recruit the immun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
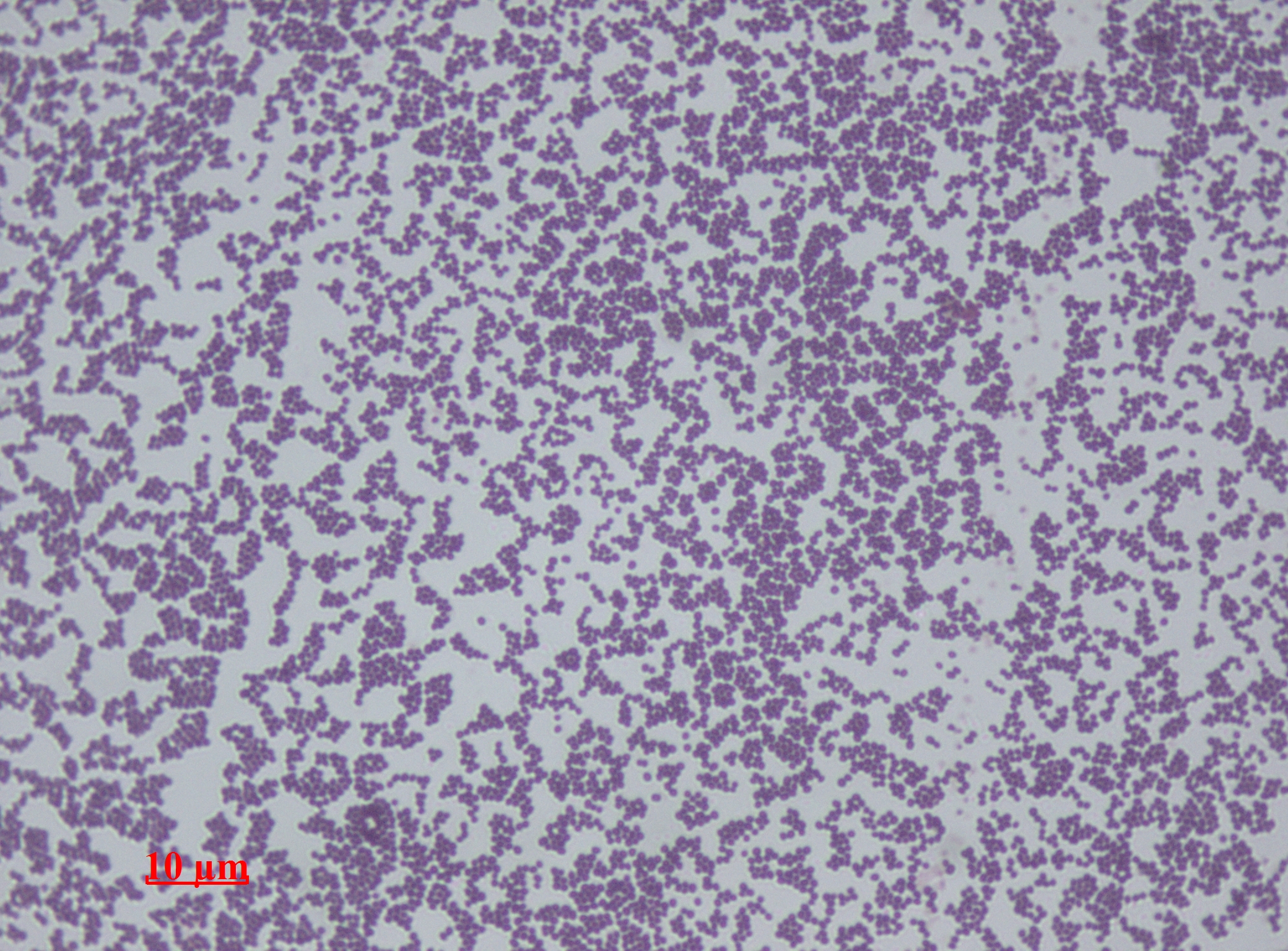
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus '' Staphylococcus''. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified salt tolerant strains of ''S. epiderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Microbiome
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density recorded in any habitat on Earth, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. Up to 60% of the dry mass of feces is bacteria. Over 99% of the bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC-I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from cytosolic proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called ''cytosolic'' or ''endogenous pathway''. In humans, the HLAs corresponding to MHC class I are HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C. Function Class I MHC molecules bind peptides generated mainly from degradation of cytosolic proteins by the proteasome. The MHC I:peptide complex is then inserted via endoplasmic reticulum into the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 1
The Interleukin-1 family (IL-1 family) is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults. Discovery Discovery of these cytokines began with studies on the pathogenesis of fever. The studies were performed by Eli Menkin and Paul Beeson in 1943–1948 on the fever-producing properties of proteins released from rabbit peritoneal exudate cells. These studies were followed by contributions of several investigators, who were primarily interested in the link between fever and infection/inflammation. The basis for the term "interleukin" was to streamline the growing number of biological properties attributed to soluble factors from macrophages and lymphocytes. IL-1 was the name given to the macrophage product, whereas IL-2 was used to define the lymphocyte product. At the time of the assignment of these names, there was no amino acid sequence analysis known and the terms were used to define bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been important for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC-II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on antigen-presenting cell#Types and functions, professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, monocyte, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelium, endothelial cells, thymus, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating Immune response, immune responses. The antigens presented by class II peptides are derived from extracellular proteins (not cytosolic as in MHC class I). Loading of a MHC class II molecule occurs by phagocytosis; extracellular proteins are endocytosis, endocytosed, digested in lysosomes, and the resulting epitope, epitopic peptide fragments are loaded onto MHC class II molecules prior to their migration to the cell surface. In humans, the MHC class II protein complex is encoded by the human leukocyte antigen, human leukocyte antigen gene complex (HLA). HLAs corresponding to MHC class II are HLA-DP, HLA-DM, HLA-D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Response
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. In contrast, too much inflammation, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |