|
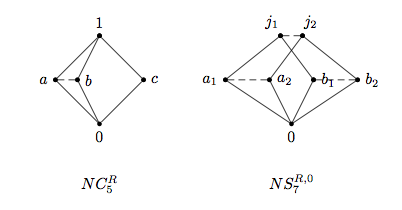
Skew Lattice
In abstract algebra, a skew lattice is an algebraic structure that is a non-commutative generalization of a lattice. While the term ''skew lattice'' can be used to refer to any non-commutative generalization of a lattice, since 1989 it has been used primarily as follows. Definition A skew lattice is a set ''S'' equipped with two associative, idempotent binary operations \wedge and \vee, called ''meet'' and ''join'', that validate the following dual pair of absorption laws x\wedge (x\vee y) = x = (y\vee x)\wedge x , x\vee (x\wedge y) = x = (y\wedge x)\vee x . Given that \vee and \wedge are associative and idempotent, these identities are equivalent to validating the following dual pair of statements: x\vee y= x if x\wedge y=y, x\wedge y=x if x\vee y=y.Leech, J, Skew lattices in rings, Algebra Universalis, 26(1989), 48-72. Historical background For over 60 years, noncommutative variations of lattices have been studied with differing motivations. For some the motivation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Algebra
In mathematics, more specifically algebra, abstract algebra or modern algebra is the study of algebraic structures. Algebraic structures include groups, rings, fields, modules, vector spaces, lattices, and algebras over a field. The term ''abstract algebra'' was coined in the early 20th century to distinguish this area of study from older parts of algebra, and more specifically from elementary algebra, the use of variables to represent numbers in computation and reasoning. Algebraic structures, with their associated homomorphisms, form mathematical categories. Category theory is a formalism that allows a unified way for expressing properties and constructions that are similar for various structures. Universal algebra is a related subject that studies types of algebraic structures as single objects. For example, the structure of groups is a single object in universal algebra, which is called the ''variety of groups''. History Before the nineteenth century, algebra meant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Identities
In algebra, the absorption law or absorption identity is an identity linking a pair of binary operations. Two binary operations, ¤ and ⁂, are said to be connected by the absorption law if: :''a'' ¤ (''a'' ⁂ ''b'') = ''a'' ⁂ (''a'' ¤ ''b'') = ''a''. A set equipped with two commutative and associative binary operations \scriptstyle \lor ("join") and \scriptstyle \land ("meet") that are connected by the absorption law is called a lattice; in this case, both operations are necessarily idempotent. Examples of lattices include Heyting algebras and Boolean algebras,See Boolean algebra (structure)#Axiomatics for a proof of the absorption laws from the distributivity, identity, and boundary laws. in particular sets of sets with ''union'' and ''intersection'' operators, and ordered sets with ''min'' and ''max'' operations. In classical logic, and in particular Boolean algebra, the operations OR and AND, which are also denoted by \scriptstyle \lor and \scriptstyle \land, sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skew Pullback
Skew may refer to: In mathematics * Skew lines, neither parallel nor intersecting. * Skew normal distribution, a probability distribution * Skew field or division ring * Skew-Hermitian matrix * Skew lattice * Skew polygon, whose vertices do not lie on a plane * Infinite skew polyhedron * Skew-symmetric graph * Skew-symmetric matrix * Skew tableau, a generalization of Young tableau * Skewness, a measure of the asymmetry of a probability distribution * Shear mapping In science and technology *Skew, also synclinal or gauche in alkane stereochemistry *Skew ray (optics), an optical path not in a plane of symmetry * Skew arch, not at a right angle In computing * Clock skew * Transitive data skew, an issue of data synchronization In telecommunications * Skew (fax), unstraightness * Skew (antenna) a method to improve the horizontal radiation pattern Other uses * Volatility skew, in finance, a downward-sloping volatility smile * Skew flip turnover Skew may refer to: In mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred H
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *''Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album ''Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England *Alfred Music, an American music publisher *Alfred University, New York, U.S. *The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario * Alfred Island, Nunavut * Mount Alfred, British Columbia United States * Alfred, Maine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quotient (universal Algebra)
In mathematics, a quotient algebra is the result of partitioning the elements of an algebraic structure using a congruence relation. Quotient algebras are also called factor algebras. Here, the congruence relation must be an equivalence relation that is additionally ''compatible'' with all the operations of the algebra, in the formal sense described below. Its equivalence classes partition the elements of the given algebraic structure. The quotient algebra has these classes as its elements, and the compatibility conditions are used to give the classes an algebraic structure. The idea of the quotient algebra abstracts into one common notion the quotient structure of quotient rings of ring theory, quotient groups of group theory, the quotient spaces of linear algebra and the quotient modules of representation theory into a common framework. Compatible relation Let ''A'' be the set of the elements of an algebra \mathcal, and let ''E'' be an equivalence relation on the set ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congruence Relation
In abstract algebra, a congruence relation (or simply congruence) is an equivalence relation on an algebraic structure (such as a group, ring, or vector space) that is compatible with the structure in the sense that algebraic operations done with equivalent elements will yield equivalent elements. Every congruence relation has a corresponding quotient structure, whose elements are the equivalence classes (or congruence classes) for the relation. Basic example The prototypical example of a congruence relation is congruence modulo n on the set of integers. For a given positive integer n, two integers a and b are called congruent modulo n, written : a \equiv b \pmod if a - b is divisible by n (or equivalently if a and b have the same remainder when divided by n). For example, 37 and 57 are congruent modulo 10, : 37 \equiv 57 \pmod since 37 - 57 = -20 is a multiple of 10, or equivalently since both 37 and 57 have a remainder of 7 when divided by 10. Congruence modulo n (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skew Diag
Skew may refer to: In mathematics * Skew lines, neither parallel nor intersecting. * Skew normal distribution, a probability distribution * Skew field or division ring * Skew-Hermitian matrix * Skew lattice * Skew polygon, whose vertices do not lie on a plane * Infinite skew polyhedron * Skew-symmetric graph * Skew-symmetric matrix * Skew tableau, a generalization of Young tableau * Skewness, a measure of the asymmetry of a probability distribution * Shear mapping In science and technology *Skew, also synclinal or gauche in alkane stereochemistry *Skew ray (optics), an optical path not in a plane of symmetry * Skew arch, not at a right angle In computing * Clock skew * Transitive data skew, an issue of data synchronization In telecommunications * Skew (fax), unstraightness * Skew (antenna) a method to improve the horizontal radiation pattern Other uses * Volatility skew, in finance, a downward-sloping volatility smile * Skew flip turnover, an aircraft maneuver * SKEW, the ticke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasse Diagram
In order theory, a Hasse diagram (; ) is a type of mathematical diagram used to represent a finite partially ordered set, in the form of a drawing of its transitive reduction. Concretely, for a partially ordered set ''(S, ≤)'' one represents each element of ''S'' as a vertex in the plane and draws a line segment or curve that goes ''upward'' from ''x'' to ''y'' whenever ''y'' ≠ ''x'' and ''y'' covers ''x'' (that is, whenever ''x'' ≤ ''y'' and there is no ''z'' such that ''x'' ≤ ''z'' ≤ ''y''). These curves may cross each other but must not touch any vertices other than their endpoints. Such a diagram, with labeled vertices, uniquely determines its partial order. The diagrams are named after Helmut Hasse (1898–1979); according to , they are so called because of the effective use Hasse made of them. However, Hasse was not the first to use these diagrams. One example that predates Hasse can be found in . Although Hasse diagrams were originally devised as a technique for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalence Relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a binary relation that is reflexive, symmetric and transitive. The equipollence relation between line segments in geometry is a common example of an equivalence relation. Each equivalence relation provides a partition of the underlying set into disjoint equivalence classes. Two elements of the given set are equivalent to each other if and only if they belong to the same equivalence class. Notation Various notations are used in the literature to denote that two elements a and b of a set are equivalent with respect to an equivalence relation R; the most common are "a \sim b" and "", which are used when R is implicit, and variations of "a \sim_R b", "", or "" to specify R explicitly. Non-equivalence may be written "" or "a \not\equiv b". Definition A binary relation \,\sim\, on a set X is said to be an equivalence relation, if and only if it is reflexive, symmetric and transitive. That is, for all a, b, and c in X: * a \sim a ( ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preorder
In mathematics, especially in order theory, a preorder or quasiorder is a binary relation that is reflexive and transitive. Preorders are more general than equivalence relations and (non-strict) partial orders, both of which are special cases of a preorder: an antisymmetric (or skeletal) preorder is a partial order, and a symmetric preorder is an equivalence relation. The name comes from the idea that preorders (that are not partial orders) are 'almost' (partial) orders, but not quite; they are neither necessarily antisymmetric nor asymmetric. Because a preorder is a binary relation, the symbol \,\leq\, can be used as the notational device for the relation. However, because they are not necessarily antisymmetric, some of the ordinary intuition associated to the symbol \,\leq\, may not apply. On the other hand, a preorder can be used, in a straightforward fashion, to define a partial order and an equivalence relation. Doing so, however, is not always useful or worth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Order
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partially ordered set (also poset) formalizes and generalizes the intuitive concept of an ordering, sequencing, or arrangement of the elements of a set. A poset consists of a set together with a binary relation indicating that, for certain pairs of elements in the set, one of the elements precedes the other in the ordering. The relation itself is called a "partial order." The word ''partial'' in the names "partial order" and "partially ordered set" is used as an indication that not every pair of elements needs to be comparable. That is, there may be pairs of elements for which neither element precedes the other in the poset. Partial orders thus generalize total orders, in which every pair is comparable. Informal definition A partial order defines a notion of comparison. Two elements ''x'' and ''y'' may stand in any of four mutually exclusive relationships to each other: either ''x'' ''y'', or ''x'' and ''y'' are ''incompar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band (mathematics)
In mathematics, a band (also called idempotent semigroup) is a semigroup in which every element is idempotent (in other words equal to its own square). Bands were first studied and named by ; the lattice of varieties of bands was described independently in the early 1970s by Biryukov, Fennemore and Gerhard. Semilattices, left-zero bands, right-zero bands, rectangular bands, normal bands, left-regular bands, right-regular bands and regular bands, specific subclasses of bands that lie near the bottom of this lattice, are of particular interest and are briefly described below. Varieties of bands A class of bands forms a variety if it is closed under formation of subsemigroups, homomorphic images and direct product. Each variety of bands can be defined by a single defining identity. Semilattices Semilattices are exactly commutative bands; that is, they are the bands satisfying the equation * for all and . Bands induce a preorder that may be defined as x \leq y if and only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |