|
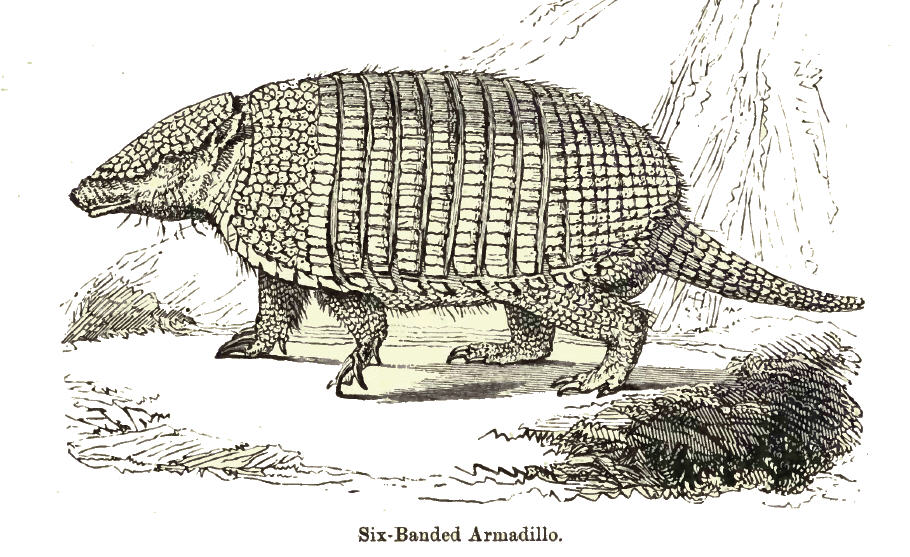
Six-banded Armadillo
The six-banded armadillo (''Euphractus sexcinctus''), also known as the yellow armadillo, is an armadillo found in South America. The sole extant member of its genus, it was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The six-banded armadillo is typically between in head-and-body length, and weighs . The carapace (hard shell on the back) is pale yellow to reddish brown, marked by scales of equal length, and scantily covered by buff to white bristle-like hairs. The forefeet have five distinct toes, each with moderately developed claws. Six-banded armadillos are efficient diggers and form burrows to live in and search for prey. The armadillo is alert and primarily solitary. An omnivore, it feeds on insects, ants, carrion, and plant material. Due to their poor eyesight, armadillos rely on their sense of smell to detect prey and predators. Births take place throughout the year; gestation is 60 to 64 days long, after which a litter of one to three is born. Weaning o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantanal
The Pantanal () is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area, and the world's largest flooded grasslands. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between . Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.Susan Mcgrath, photos by Joel Sartore, ''Brazil's Wild Wet'', National Geographic Magazine, August 2005 Roughly 80% of the Pantanal floodplains are submerged during the rainy seasons, nurturing a biologically diverse collection of aquatic plants and helping to support a dense array of animal species. Etymology The name "Pantanal" comes from the Portuguese word ''pântano'' that means "big wetland", "big bog", "big swamp", "big quagmire" or "big marsh" plus the suffix ''-al'', that means "abundance, agglomeratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Maximilian Of Wied-Neuwied
Prince Alexander Philipp Maximilian zu Wied-Neuwied (23 September 1782 – 3 February 1867) was a German explorer, ethnologist and naturalist. He led a pioneering expedition to southeast Brazil between 1815–1817, from which the album ''Reise nach Brasilien,'' which first revealed to Europe real images of Brazilian Indians, was the ultimate result. It was translated into several languages and recognized as one of the greatest contributions to the knowledge of Brazil at the beginning of the nineteenth century. In 1832 he embarked on another expedition, this time to United States, together with the Swiss painter Karl Bodmer. Prince Maximilian collected many examples of ethnography, and many specimens of flora and fauna of the area, still preserved in museum collections, notably in the Lindenmuseum, Stuttgart. The genus '' Neuwiedia'' Blume (Orchidaceae) was named for him. Also, Prince Maximilian is honored in the scientific names of eight species of reptiles: '' Hydromedusa max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – lit. "Thick Bush") is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP. Neighboring states (from west clockwise) are: Rondônia, Amazonas, Pará, Tocantins, Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul. The state is roughly 82.2% of the size of its southwest neighbor, the nation of Bolivia. A state with a flat landscape that alternates between vast ''chapadas'' and plain areas, Mato Grosso contains three main ecosystems: the Cerrado, the Pantanal and the Amazon rainforest. The Chapada dos Guimarães National Park, with caves, grottoes, tracks, and waterfalls, is one of its tourist attractions. The extreme northwest of the state has a small part of the Amazonian forest. The Xingu Indigenous Park and the Araguaia River are in Mato Grosso. Farther south, the Pantanal, the world's largest wetland, is the habitat for nearly one thousand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest
Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest (6 March 1784 – 4 June 1838) was a French Zoology, zoologist and author. He was the son of Nicolas Desmarest and father of Eugène Anselme Sébastien Léon Desmarest. Desmarest was a disciple of Georges Cuvier and Alexandre Brongniart, and in 1815, he succeeded Pierre André Latreille to the professorship of zoology at the '. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 1819 and to the Académie Nationale de Médecine in 1820. Desmarest published ' (1805), ' (1825), ' (1820) and ' (1816–30, with André Marie Constant Duméril). The brown algae ''Desmarestia'' is named in honour of Desmarest, as well as the family (Desmarestiaceae) — and in turn, the order (Desmarestiales) — of which the genus is the type species#In botany, type species. References French zoologists French taxonomists 1784 births 1838 deaths French carcinologists French mammalogists French ornithologists 18th-century French zoologists 19th-century French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain. Toponymy The name Chaco comes from a word in Quechua, an indigenous language from the Andes and highlands of South America. The Quechua word ''chaqu'' meaning "hunting land" comes probably from the rich variety of animal life present throughout the entire region. Geography The Gran Chaco is about 647,500 km² (250,000 sq mi) in size, though estimates differ. It is located west of the Paraguay River and east of the Andes, and is mostly an alluvial sedimentary plain shared among Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. It stretches from about 17 to 33°S latitude and between 65 and 60°W longitude, though estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldfield Thomas
Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas (21 February 1858 – 16 June 1929) was a British zoologist. Career Thomas worked at the Natural History Museum on mammals, describing about 2,000 new species and subspecies for the first time. He was appointed to the museum secretary's office in 1876, transferring to the zoological department in 1878. In 1891, Thomas married Mary Kane, daughter of Sir Andrew Clark, heiress to a small fortune, which gave him the finances to hire mammal collectors and present their specimens to the museum. He also did field work himself in Western Europe and South America. His wife shared his interest in natural history, and accompanied him on collecting trips. In 1896, when William Henry Flower took control of the department, he hired Richard Lydekker Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 – 16 April 1915) was an English naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history. Biography Richard Lydekker was born at Tavistock Square in London. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarija
Tarija or San Bernardo de la Frontera de Tarixa is a city in southern Bolivia. Founded in 1574, Tarija is the largest city and capital and municipality within the Tarija Department, with an airport (Capitán Oriel Lea Plaza Airport, (TJA)) offering regular service to primary Bolivian cities, as well as a regional bus terminal with domestic and international connections. Its climate is semi-arid (BSh) with generally mild temperatures in contrast to the harsh cold of the Altiplano (e.g., La Paz) and the year-round humid heat of the Amazon Basin (e.g., Santa Cruz de la Sierra). Tarija has a population of 234,442. History The name of ''Tarija'' is said to come from Francisco de Tarija or Tarifa. However, researched information disproves that probability. Members of the first group of Spaniards to enter the valley where present-day Tarija is situated, stated that the name of Tarija was already in use. This group did not include anyone by the name of Francisco de Tarija. Similar-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South America's southeastern coast. "Buenos Aires" can be translated as "fair winds" or "good airs", but the former was the meaning intended by the founders in the 16th century, by the use of the original name "Real de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre", named after the Madonna of Bonaria in Sardinia, Italy. Buenos Aires is classified as an alpha global city, according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2020 ranking. The city of Buenos Aires is neither part of Buenos Aires Province nor the Province's capital; rather, it is an autonomous district. In 1880, after decades of political infighting, Buenos Aires was federalized and removed from Buenos Aires Province. The city limits were enlarged to include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoa Santa, Minas Gerais
Lagoa Santa (''Holy Lagoon'') is a municipality and region in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. It is located 37 km north-northeast from Belo Horizonte and belongs to the mesoregion Metropolitana de Belo Horizonte and to the microregion of Belo Horizonte. In 2020 the estimated population was 65,657. Cradle of Brazilian paleontology The Danish palaeontologist Peter Wilhelm Lund, known as the father of Brazilian paleontology, discovered a cave filled with human bones (15 skeletons) and megafauna (very large mammals) dating to the Pleistocene era. Eugen Warming assisted Lund 1863–1866, and described the flora of the area and the adaptations of the plants to the hazards of cerrado – drought and fire – in a work that still stands as a paradigm of ecological study ( 'Lagoa Santa'). The tomb of illustrator Peter Andreas Brandt, also an assistant of Lund, is located in the town. The municipality contains 56% of the Sumidouro State Park, created in 1980, which protects t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |