|
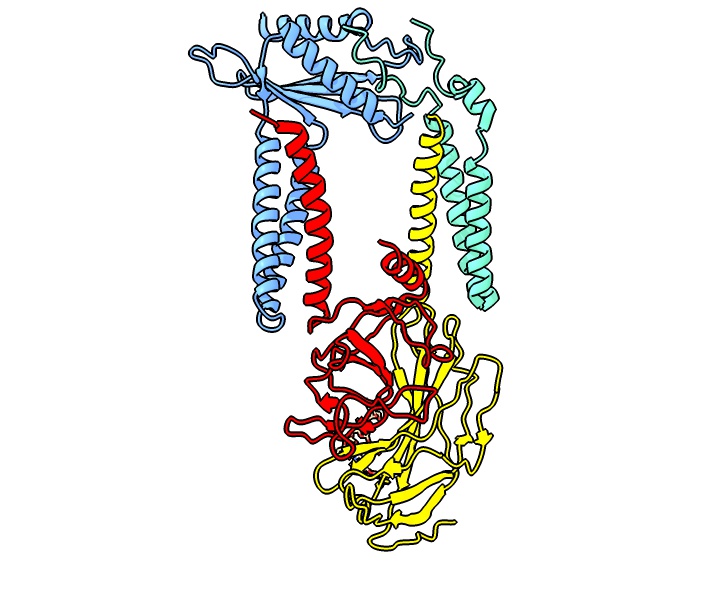
Signal Recognition Particle
The signal recognition particle (SRP) is an abundant, cytosolic, universally conserved ribonucleoprotein (protein-RNA complex) that recognizes and targets specific proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes and the plasma membrane in prokaryotes. History The function of SRP was discovered by the study of processed and unprocessed secretory proteins, particularly immunoglobulin light chains; and bovine preprolactin. Newly synthesized proteins in eukaryotes carry N-terminal hydrophobic Signal peptide, signal sequences, which are bound by SRP when they emerge from the ribosome. Mechanism In eukaryotes, SRP binds to the signal sequence of a newly synthesized peptide as it emerges from the ribosome. This binding leads to the slowing of protein synthesis known as "elongation arrest", a conserved function of SRP that facilitates the coupling of the protein translation and the protein translocation processes. SRP then targets this entire complex (the ribosome-nascent cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
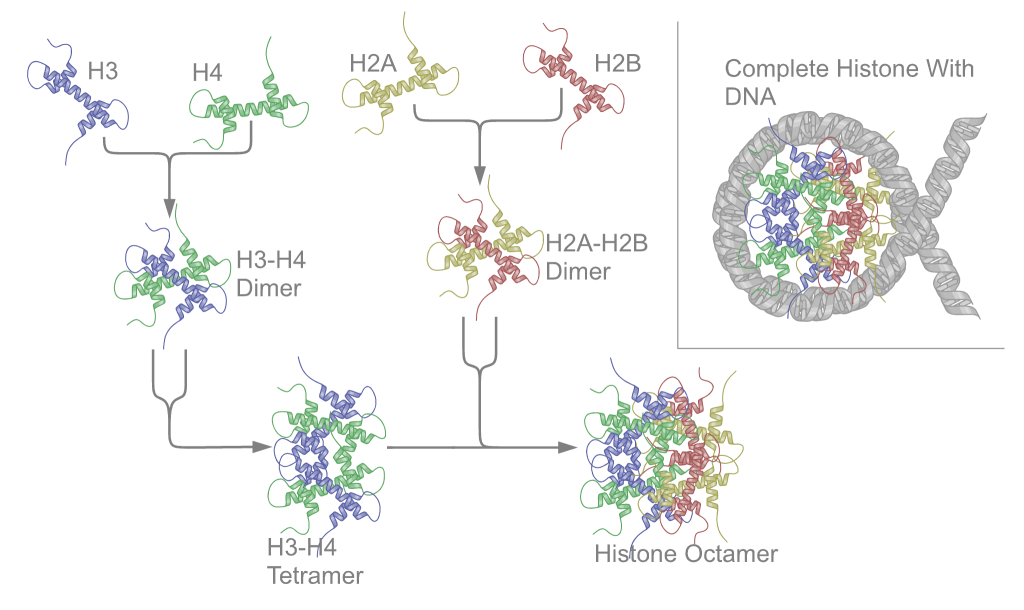
Ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins. Structures Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The tertiary structures and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy. Viruses Virus genomes (either DNA or RNA) are extremely tightly packed into the viral capsid. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins include influenza, rabies, Ebola, Bunyamwera, Schma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptidase
Signal peptidases are enzymes that convert secretory and some membrane proteins to their mature or pro forms by cleaving their signal peptides from their N-termini. Signal peptidases were initially observed in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived membrane fractions isolated from mouse myeloma cells. The key observation by César Milstein and colleagues was that immunoglobulin light chains were produced in a higher molecular weight form, which became processed by the ER membrane fraction. This finding was directly followed by the discovery of the translocation machinery. Signal peptidases are also found in prokaryotes as well as the protein import machinery of mitochondria and chloroplasts. All signal peptidases described so far are serine proteases. The active site that endoproteolytically cleaves signal peptides from translocated precursor proteins is located at the extracytoplasmic site of the membrane. The eukaryotic signal peptidase is an integral membrane protein Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-signal Recognition Particle Antibodies
Inflammatory myopathy is disease featuring weakness and inflammation of muscles and (in some types) muscle pain. The cause of much inflammatory myopathy is unknown (idiopathic), and such cases are classified according to their symptoms and signs and electromyography, MRI and laboratory findings. It can also be associated with underlying cancer. The main classes of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy are polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and inclusion-body myositis (IBM). Diagnosis There are a number of known causes of myopathy, and it is only once these have been ruled out that a clinician will assign an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) syndrome to a case. The usual criteria for a diagnosis of PM are weakness in muscles of the head, neck, trunk, upper arms or upper legs; raised blood serum concentrations of some muscle enzymes such as creatine kinase; unhealthy muscle changes on electromyography; and biopsy findings of (i) muscle cell degeneration and regeneration an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanocaldococcus
''Methanocaldococcus'' formerly known as ''Methanococcus'' is a genus of coccoid methanogen archaea. They are all mesophiles, except the thermophilic ''M. thermolithotrophicus'' and the hyperthermophilic ''M. jannaschii''. The latter was discovered at the base of a “white smoker” chimney at 21° N on the East Pacific Rise and it was the first archaean genome to be completely sequenced, revealing many novel and eukaryote-like elements. Nomenclature The name ''Methanocaldococcus'' has Latin and Greek roots, ''methano'' for methane, ''caldo'' for hot, and the Greek ''kokkos'' for the spherical shape of the cells. Overall, the name means ''spherical cell that produces methane at hot temperatures''. Metabolism All species in ''Methanocaldococcus'' are obligate methanogens. They use hydrogen to reduce carbon dioxide. Unlike many other species within Euryarchaeota, they cannot use formate, acetate, methanol or methylamines as substrates. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7SL RNA
The signal recognition particle RNA, (also known as 7SL, 6S or 4.5S RNA) is part of the signal recognition particle (SRP) ribonucleoprotein complex. SRP recognizes the signal peptide and binds to the ribosome, halting protein synthesis. Signal recognition particle receptor, is a protein that is embedded in a membrane, and which contains a Transmembrane channels, transmembrane pore. When the complex binds to , SRP releases the ribosome and drifts away. The ribosome resumes protein synthesis, but now the protein is moving through the transmembrane pore. In this way SRP directs the movement of proteins within the Cell (biology), cell to bind with a transmembrane pore which allows the protein to cross the membrane to where it is needed. The RNA and protein components of this complex are highly Conserved sequence, conserved but do vary between the different Kingdom (biology), kingdoms of life. The common Short interspersed nuclear element, SINE family Alu sequence, Alu probably or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRP9
Signal recognition particle 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRP9 gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * External links PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Signal recognition particle 9 kDa protein {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |