|
Siege Of Tönning
During the Great Northern War, the fortress of Tönning (Tønning) in the territory of Holstein-Gottorp, an ally of the Swedish Empire, was besieged twice. Denmark-Norway was forced to lift the first siege in 1700, but a combined force of the anti-Swedish coalition successfully besieged and took Tönning in 1713–1714. 1700 The first siege was one of the first military actions of the Great Northern War. Denmark-Norway, Saxe- Poland-Lithuania and Russia had agreed on invading the Swedish Empire on three fronts, and accordingly, Danish forces moved into Holstein-Gottorp,Frost (2000), p.228 allied and dynastically tied to Sweden,Frost (2000), p.227 and laid siege to Tönning in March 1700. The siege had to be lifted when Charles XII of Sweden, backed by the Maritime Powers, in a surprise move deployed an army in front of Copenhagen, forcing Frederik IV of Denmark-Norway out of the war by the Peace of Travendal on 18 August 1700.Frost (2000), p.229 Denmark re-entered the war onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tönning
Tönning (German; Low German ''Tünn'', ''Tönn'' or ''Tönnen''; Danish: ''Tønning''; North Frisian: ''Taning'') is a town in the district of Nordfriesland in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. History Tönning was destroyed in the Burchardi flood in 1634. During the Great Northern War, (1700–1721), Tönning was besieged twice. Geography It is located on the northern bank of the Eider river, approximately eight kilometers away from its mouth at the North Sea. Tönning has a population of some 5,000 people. Transport Tönning is connected by a regional train with Sankt Peter-Ording to the West, and Husum to the North-East. Tönning is also served by several bus routes. See also * Eiderstedt peninsula *Eider Barrage Personalities Honorary citizen * Friedrich Wilhelm Selck (1821–1911), councilor of commerce, honorary citizen since 1899 * Friedrich von Esmarch (1823–1908), German physician and the founder of the civilian Samaritan system in Germany, honora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania ruled by a common Monarchy, monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and List of Lithuanian monarchs, Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish language, Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages. The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a ''de facto'' personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1700 In Europe
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Great Northern War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power. Through a number of successful wars, he captured ports at Azov and the Baltic Sea, laying the groundwork for the Imperial Russian Navy, ending uncontested Swedish supremacy in the Baltic and beginning the Tsardom's expansion into a much larger empire that became a major European power. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment. Peter's reforms had a lasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Heinrich Von Görtz
Georg Heinrich von Görtz, Baron of Schlitz (1668 – 19 February 1719), diplomat in Swedish service, was born in Holstein and educated at Jena. Career He entered the Holstein-Gottorp service, and after the death of the duchess Hedwig Sophia, Charles XII of Sweden's sister, became very influential during the minority of her son Duke Charles Frederick. His earlier policy aimed at strengthening Holstein-Gottorp at the expense of Denmark. With this object, during Charles XII's stay at Altranstädt (1706–1707), he tried to divert the king's attention to the Holstein question, and six years later, when the Swedish commander, Magnus Stenbock, crossed the Elbe, Görtz rendered him as much assistance as was compatible with not openly breaking with Denmark, even going so far as to surrender the fortress of Tönning to the Swedes. Görtz next attempted to undermine the grand alliance against Sweden by negotiating with Russia, Prussia and Saxony for the purpose of isolating Denmark, or ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Frederick Of Holstein-Gottorp
Charles Frederick, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp () (30 April 1700 – 18 June 1739) was a Prince of Sweden and Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp and an important member of European royalty. His dynasty, the Dukes of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, were a cadet branch of the ancient House of Oldenburg, which at that time was ruling Denmark-Norway. His mother was a sister of Charles XII of Sweden. Charles Frederick married a daughter of Peter the Great and became the father of the future Peter III of Russia. As such, he is the progenitor of the Russian imperial house of Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov and the patrilineal ancestor of all Russian emperors starting with Peter III, except for Catherine II. Early life Charles Frederick was born in Sweden, the son of Frederick IV of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp and his consort, Hedvig Sophia, daughter of King Charles XI of Sweden. He became reigning duke in infancy, upon his father's death in 1702 at the Battle of Kliszów, co-ruling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gadebusch
The Battle of Gadebusch or Wakenstädt (20 December 1712) was Sweden's final great victory in the Great Northern War. It was fought by the Swedes to prevent the Siege of Stralsund (1711–1715), loss of the city of Stralsund to Denmark, Danish and Saxony, Saxon forces. Prelude During 1712, all of Sweden's Dominions of Sweden, dominions south of the Baltic Sea, apart from forts, had been conquered by the allies Denmark, Saxony, and Russia. In the Baltic the Danish admiral Ulrik Christian Gyldenløve, Gyldenløve patrolled with a squadron to disrupt Swedish supply lines to the Continent. It was vital for Sweden not to lose Stralsund, as it was the gateway to campaigns in Poland. While a Danish army moved in the region of Hamburg, a large Russian-Saxon force stood south of Stralsund. Stenbock could hardly attack this force with a frontal assault, but hoped that by moving west towards Mecklenburg it could be encirclement, encircled or scattered. Such a movement would also prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Stralsund (1711–1715)
The siege of Stralsund was a battle during the Great Northern War. The Swedish Empire defended her Swedish Pomeranian port of Stralsund against a coalition of Denmark-Norway, the Electorate of Saxony and the Tsardom of Russia, which was joined by the Kingdom of Prussia during the siege. A first attempt to take Stralsund was made in 1711, when the allies closed in on the town. Swedish relief forced the coalition to withdraw from the fortifications, whereupon the besieging armies drew a wider ring along the lines of the Recknitz and Peene rivers. Magnus Stenbock's Battle of Gadebusch, victory at Gadebusch for a short time distracted the allies, but after Stenbock's pursuit and subsequent defeat, Prussia as well as Hanover, ruled in personal union with Great Britain, joined the anti-Swedish alliance. The allies agreed that Denmark should cede her claims to Bremen-Verden to Hanover, and in turn Denmark was promised the northern parts of Swedish Pomerania with Stralsund, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salients, Re-entrants And Pockets
A salient, also known as a bulge, is a battlefield feature that projects into enemy territory. The salient is surrounded by the enemy on multiple sides, making the troops occupying the salient vulnerable. The opponent's front line that borders a salient is referred to as a re-entrant – that is, an angle pointing inwards. A deep salient is vulnerable to being "pinched off" through the base, and this will result in a pocket in which the forces in the salient become isolated and without a supply line. On the other hand, a breakout of the forces within the salient through its tip can threaten the rear areas of the opposing forces outside it, leaving them open to an attack from behind. Implementation Salients can be formed in a number of ways. An attacker can produce a salient in the defender's line by either intentionally making a pincer movement around the military flanks of a strongpoint, which becomes the tip of the salient, or by making a broad, frontal attack which is held u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
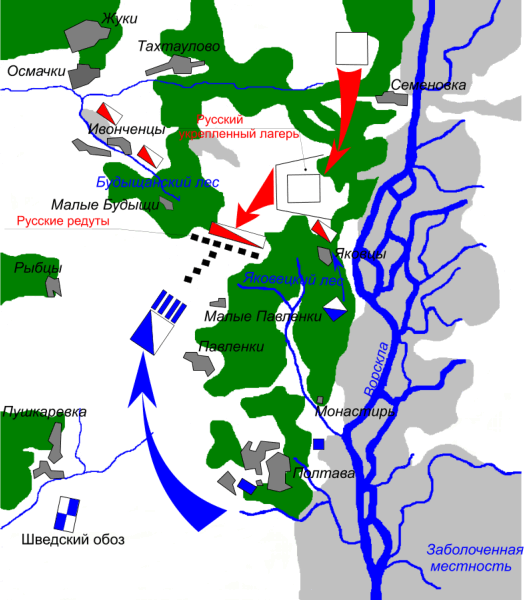
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated a Swedish army, under the command of Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle put an end to the status of the Swedish Empire as a European great power, as well as its eastbound expansion, and marked the beginning of Russian hegemony in Northern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter under Tsar Peter I's rule was the only one still undefeated. Charles XII therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederik IV Of Denmark-Norway
Frederick IV (Danish: ''Frederik''; 11 October 1671 – 12 October 1730) was King of Denmark and Norway from 1699 until his death. Frederick was the son of Christian V of Denmark-Norway and his wife Charlotte Amalie of Hesse-Kassel. Early life Frederick was born on 11 October 1671 at Copenhagen Castle as the eldest son of King Christian V and his spouse Charlotte Amalie of Hesse-Kassel. The newborn prince was baptized the same evening with the name Frederick by the royal confessional Hans Leth. His grandfather King Frederick III had died a year and a half before he was born, and as the eldest son of the ruling king he was thus crown prince from birth. At the age of 18, he was given a seat on the Council of State as the heir apparent to the throne. As crown prince, Frederick broadened his education by travelling in Europe, led by his chamberlain Ditlev Wibe. He was particularly impressed by the architecture in Italy and, on his return to Denmark, asked his father, Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |