|
Siege Of Danzig (1813)
The siege of Danzig (16 January 1813 – 2 January 1814) was a siege of the city of Danzig during the War of the Sixth Coalition by Russian and Prussian forces against Jean Rapp's permanent French garrison, which had been augmented by soldiers from the Grande Armée retreating from its Russian campaign. The garrison included two crack divisions under Étienne Heudelet de Bierre and Charles Louis Dieudonné Grandjean plus whole units and stragglers that had lost contact with their units, all with their health and morale both weakened and most of their equipment lost and carrying their wounded. The siege was begun by cossacks under hetman Matvei Platov, then was continued mainly by infantry, mainly militiamen and irregulars. It lasted ended in a French surrender to Coalition forces. Background The Treaty of Tilsit of 1807 had made the city a Free City nominally under Prussian control. It was sited at the mouth of the River Vistula and along the coast of the Baltic Sea and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Campaign Of 1813
The German campaign (german: Befreiungskriege , lit=Wars of Liberation ) was fought in 1813. Members of the Sixth Coalition, including the German states of Austria and Prussia, plus Russia and Sweden, fought a series of battles in Germany against the French Emperor Napoleon, his marshals, and the armies of the Confederation of the Rhine - an alliance of most of the other German states - which ended the domination of the First French Empire. After the devastating defeat of Napoleon's '' Grande Armée'' in the Russian campaign of 1812, Johann Yorck – the general in command of the ''Grande Armée'''s German auxiliaries (') – declared a ceasefire with the Russians on 30 December 1812 via the Convention of Tauroggen. This was the decisive factor in the outbreak of the German campaign the following year. The spring campaign between France and the Sixth Coalition ended inconclusively with a summer truce (Truce of Pläswitz). Via the Trachenberg Plan, developed during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
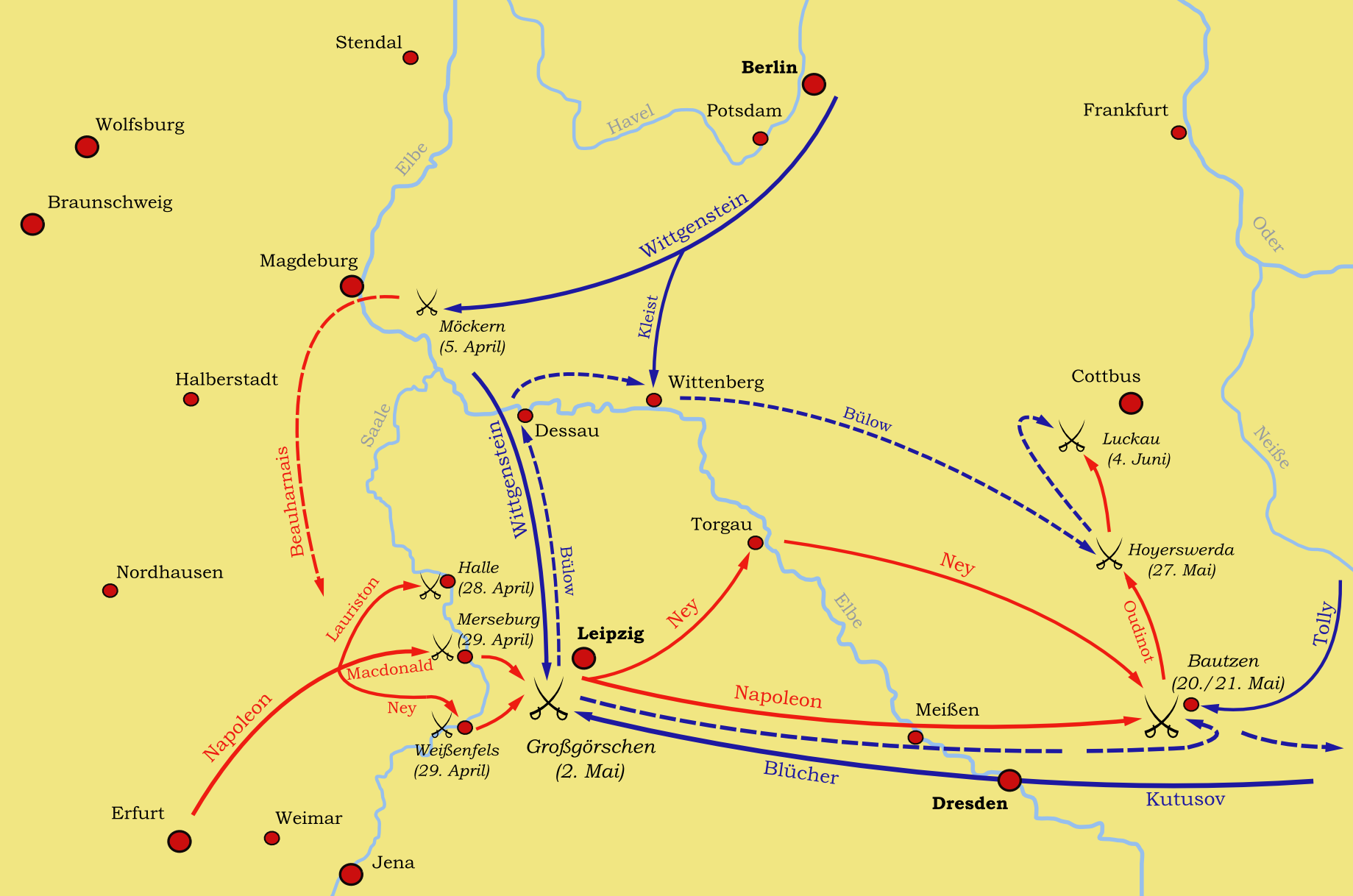
Battle Of Lützen (1813)
In the Battle of Lützen (German: ''Schlacht von Großgörschen'', 2 May 1813), Napoleon I of France defeated an allied army of the Sixth Coalition. The Russian commander, Prince Peter Wittgenstein, attempting to forestall Napoleon's capture of Leipzig, attacked the French right wing near Lützen, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, surprising Napoleon. Quickly recovering, he ordered a double envelopment of the allies. After a day of heavy fighting, the imminent encirclement of his army prompted Wittgenstein to retreat. Due to a shortage of cavalry, the French did not pursue. The next battle would be fought at Bautzen three weeks later. Prelude Following the disaster of French invasion of Russia in 1812, a new Coalition consisting of Britain, Sweden, Prussia and Russia formed against France. In response to this, Napoleon hastily assembled an army of just over 200,000 which included inexperienced recruits, troops from Spain and garrison battalions but was severely short of horses (a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva narodov), was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I and Karl von Schwarzenberg, decisively defeated the '' Grande Armée'' of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleon's army also contained Polish and Italian troops, as well as Germans from the Confederation of the Rhine (mainly Saxony and Württemberg). The battle was the culmination of the German Campaign of 1813 and involved 560,000 soldiers, 2,200 artillery pieces, the expenditure of 400,000 rounds of artillery ammunition, and 133,000 casualties, making it the largest battle in Europe prior to World War I. Decisively defeated again, Napoleon was compelled to return to France while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wartenburg
The Battle of Wartenburg (german: Schlacht bei Wartenburg) took place on 3October 1813 between the French IV Corps commanded by General Henri Gatien Bertrand and the Allied Army of Silesia, principally the I Corps of General Ludwig von Yorck. The battle allowed the Army of Silesia to cross the Elbe, ultimately leading to the Battle of Leipzig. Prelude Following the his defeat at the battle of Dennewitz, Marshal Ney withdrew his army to defensive positions along the Elbe. The allied Army of the North, under the command of Crown Prince Charles John of Sweden (formerly French Marshal Bernadotte), followed them cautiously but made no serious effort to cross the river. To the east, Marshal Blücher made a bold march skirting Napoleon's position in Dresden to join his Army of Silesia with the Army of the North, cross the Elbe, and threaten Napoleon's communications with France. Major von Rühle was tasked with finding a crossing point where the bridgehead could, if necessary, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Of Roßlau
The Combat of Rosslau was fought in the War of the Sixth Coalition on 29 September 1813, near Rosslau, Germany. Michel Ney attacked the Swedish bridgehead at the Elbe, to stop the Army of the North from crossing the river. The Swedish commander Johan August Sandels counterattacked and chased the French for before being forced to retire himself. About 350 Swedes were dead and wounded while the French had at least 1,500, according to Swedish sources. The battle had no strategic effects, but it was one of very few times in the war that a Swedish force was fully committed in battle. Background A French force under Michel Ney had received orders from Napoleon I to attack the Swedish bridgehead over the Elbe river, at Rosslau, to stop the Army of the North (under the Swedish Crown Prince Charles John) from reaching Leipzig. After having fought a couple of skirmishes for control over Dessau, Ney marched his troops of about 7,000–8,000 men towards the Swedish left flank. The Swe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Altenburg
The raid at Altenburg on 28 September 1813 took place during the War of the Sixth Coalition's German Campaign of 1813. The raid was carried out by the ''Streifkorp'' under the command of Saxon General Johann von Thielmann commanding seven regiments of Cossacks, a squadron each of Saxon Hussars and Dragoons, and a detachment of ''Saxon Freikorps'' numbering about 1,500 cavalry. The objective of the raid was to attempt harassment of the French lines of communication 25 miles (45 km) south of Leipzig shortly before the Battle of Leipzig. The Austrian contingent was commanded by Emmanuel Mensdorff and the Russian contingent of Cossacks by Matvei Platov. Background The battle was the culmination of a raid in which Thielmann cavalry successfully attacked Napoleon's lines of communications along the roads between Erfurt and Leipzig in the Saale valley. Battle Thielmann completely surprised and routed a larger force of French cavalry, including Cavalry of the Imperial Guar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Göhrde
The battle of the Göhrde was a battle of the War of the Sixth Coalition on 16 September 1813 between French and Coalition troops at Göhrde in Germany. The French troops were defeated and withdrew to Hamburg. Site It occurred near what is now the site of the Göhrde State Forest (''Staatsforst Göhrde''), near Dannenberg, near Lüneburg. At that time this area belonged to the electorate of Braunschweig-Lüneburg (Electorate of Hanover, Hanover), which had been occupied by the French since 1803. The battlefield lies on the border between the modern-day districts of Lüneburg (district), Lüneburg and Lüchow-Dannenberg, between Nahrendorf, Oldendorf an der Göhrde and Göhrde. Prelude In March 1813, Russian troops under Friedrich Karl von Tettenborn forced the French out of Hamburg and some northern areas of Hanover. In the wake of Prussia's reentry into the war against France, the eastern areas of Hanover also rose against Napoleon. Wallmoden then received overall comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dennewitz
The Battle of Dennewitz (german: Schlacht von Dennewitz (Battle near Jüterbog) took place on 6September 1813 between French forces commanded by Marshal Michel Ney and the Sixth Coalition's Allied Army of the North commanded by Crown Prince Charles John of Sweden, Friedrich Wilhelm von Bülow and Bogislav von Tauentzien. It occurred in Dennewitz, a village in the Prussian province of Brandenburg, near Jüterbog, southwest of Berlin. The battle marked a turning point in the German Campaign of 1813 as not only did the Allied victory end Napoleon's hopes of capturing Berlin and knocking Prussia out of the war, but the severity of the French defeat, inflicted by a primarily Prussian force, also led to the erosion of fidelity of German allies to the Napoleonic cause. The French losses, and consequent diplomatic reverses, that resulted from Dennewitz contributed greatly to Napoleon's defeat a month later at the Battle of Leipzig. Prelude In late August 1813, Napoleon decided to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
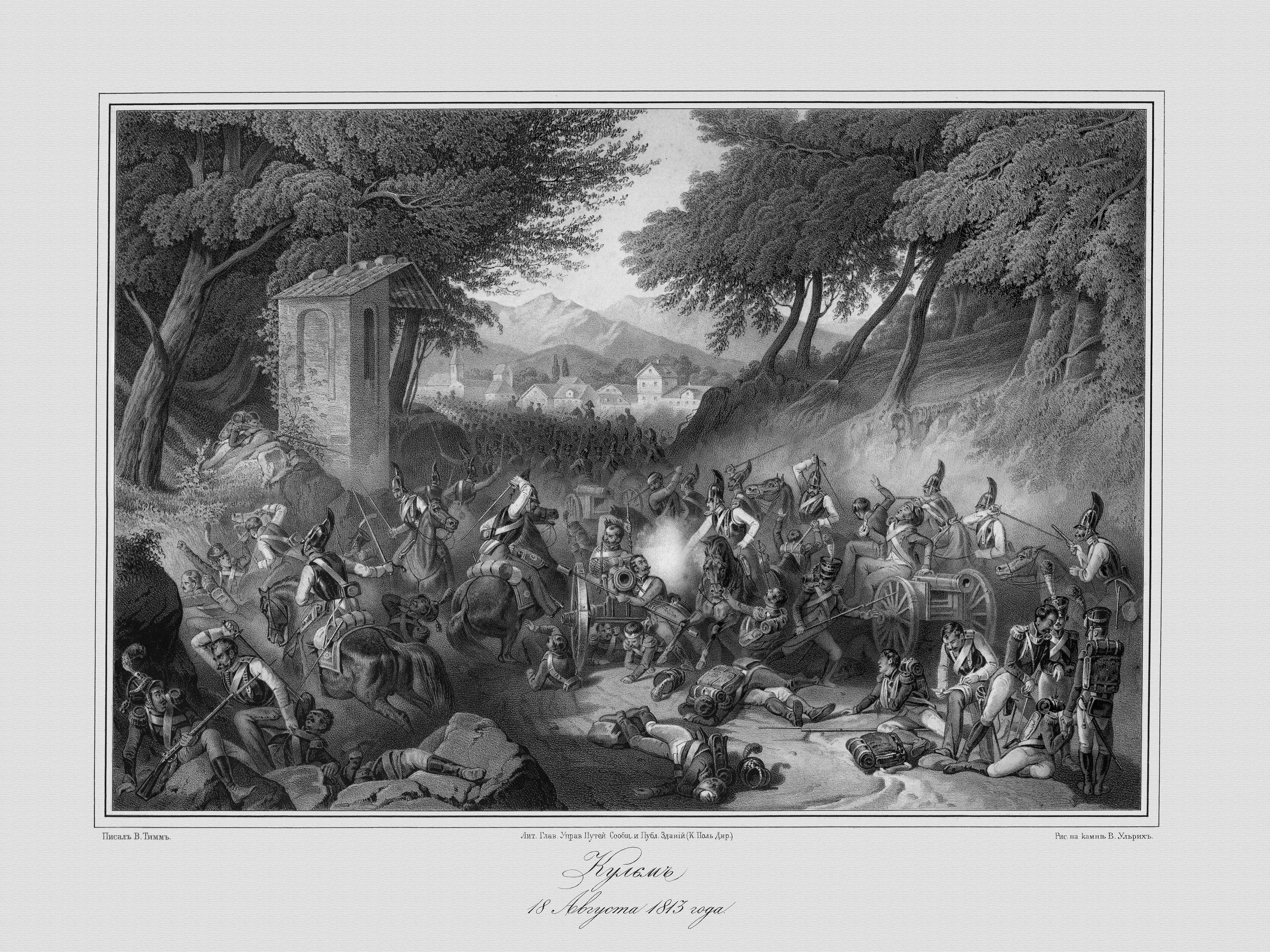
Battle Of Kulm
:''See Battle of Chlumec for the 1126 battle at Kulm The Battle of Kulm was fought near the town Kulm () and the village Přestanov in northern Bohemia. It was fought on 29–30 August 1813, during the War of the Sixth Coalition. A French Corps under General Dominique Vandamme attacked Alexander Ostermann-Tolstoy's Russian Corps on 29 August. The next day, Friedrich von Kleist's Prussian Corps hit Vandamme in the rear while Russian and Austrian reinforcements attacked the French front and left. Vandamme was defeated with the loss of 13,000 men and 82 guns. Background Following the French victory at Dresden, Vandamme pursued the retreating allies. Napoleon sent Marshals Gouvion Saint Cyr and Auguste Marmont to support Vandamme's corps. With Vandamme in advance, Saint Cyr's and Marmont's corps brought up the rear. Vandamme caught up with Alexander Ivanovich Ostermann-Tolstoy's forces near the town of Kulm, eight kilometres northwest of Aussig (Ústí nad Labem, now in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dresden
The Battle of Dresden (26–27 August 1813) was a major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle took place around the city of Dresden in modern-day Germany. With the recent addition of Austria, the Sixth Coalition felt emboldened in their quest to expel the French from Central Europe. Despite being heavily outnumbered, French forces under Napoleon scored a victory against the Army of Bohemia led by Generalissimo Karl von Schwarzenberg. However, Napoleon's victory did not lead to the collapse of the coalition, and the weather and the uncommitted Russian reserves who formed an effective rear-guard precluded a major pursuit. Three days after the battle, the Allies surrounded and destroyed a French corps advancing into their line of withdrawal at the Battle of Kulm. Prelude On the 16 August, Napoleon had sent Marshal Saint-Cyr's corps to fortify and hold Dresden in order to hinder allied movements and to serve as a possible base for his own manoeuvres. He planned to str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Katzbach
The Battle of the Katzbach on 26 August 1813, was a major battle of the Napoleonic Wars between the forces of the First French Empire under Marshal MacDonald and a Russo-Prussian army of the Sixth Coalition under Prussian Marshal Graf (Count) von Blücher. It occurred during a heavy thunderstorm at the Katzbach river between Wahlstatt and Liegnitz in the Prussian province of Silesia. Taking place the same day as the Battle of Dresden, it resulted in a Coalition victory, with the French retreating to Saxony. Prelude Blücher ordered the Army of Silesia to advance on 13 August, before the Truce of Pläswitz could conclude on 17 August. In a series of running fights, the Allied army beat back the confused French, who did not anticipate that the Allies would break the armistice so brazenly. These minor victories raised the morale of the inexperienced German levies. On the first day, Blücher and his chief of staff August Neidhardt von Gneisenau became separated and did not iss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Großbeeren
The Battle of Großbeeren occurred on 23 August 1813 in neighboring Blankenfelde and Sputendorf between the Prussian III Corps under Friedrich von Bülow and the French-Saxon VII Corps under Jean Reynier. Napoleon had hoped to drive the Prussians out of the Sixth Coalition by capturing their capital, but the swamps south of Berlin combined with rain and marshal Nicolas Oudinot's ill health all contributed to the French defeat. Prelude Following the Battle of Bautzen, in May 1813, during the War of the Sixth Coalition, both sides agreed to a seven-week truce to plan and better prepare. When the campaign resumed, in August, Napoleon ordered an offensive drive to take the Prussian capital of Berlin. With its capture, he hoped to knock the Prussians out of the war. Meanwhile, he kept the bulk of his army on the strategic defensive, to deal with any potential moves by the large Austrian army, which had now gathered in southeastern Germany. For this task, he chose one of his br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

