|
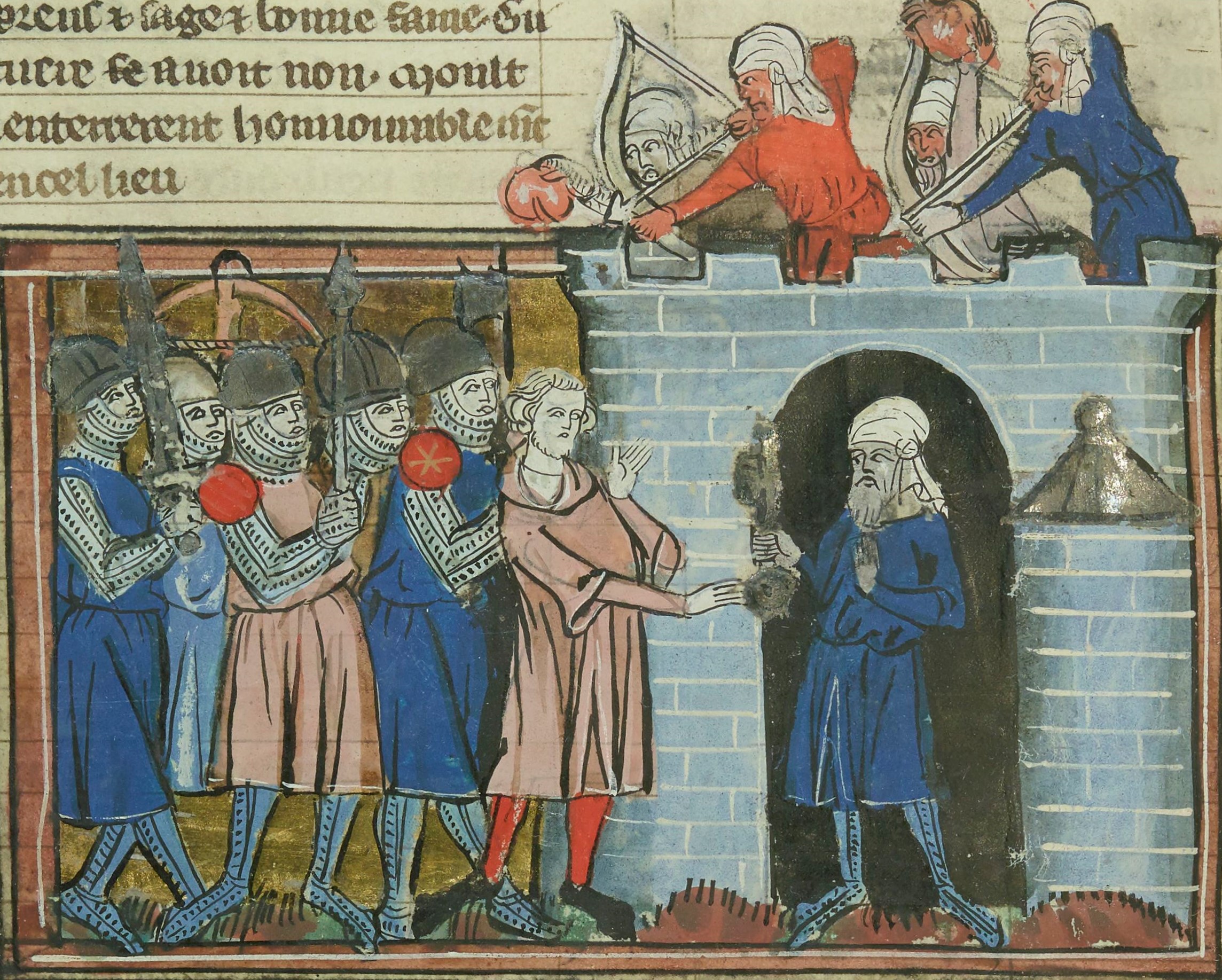
Siege Of Antioch
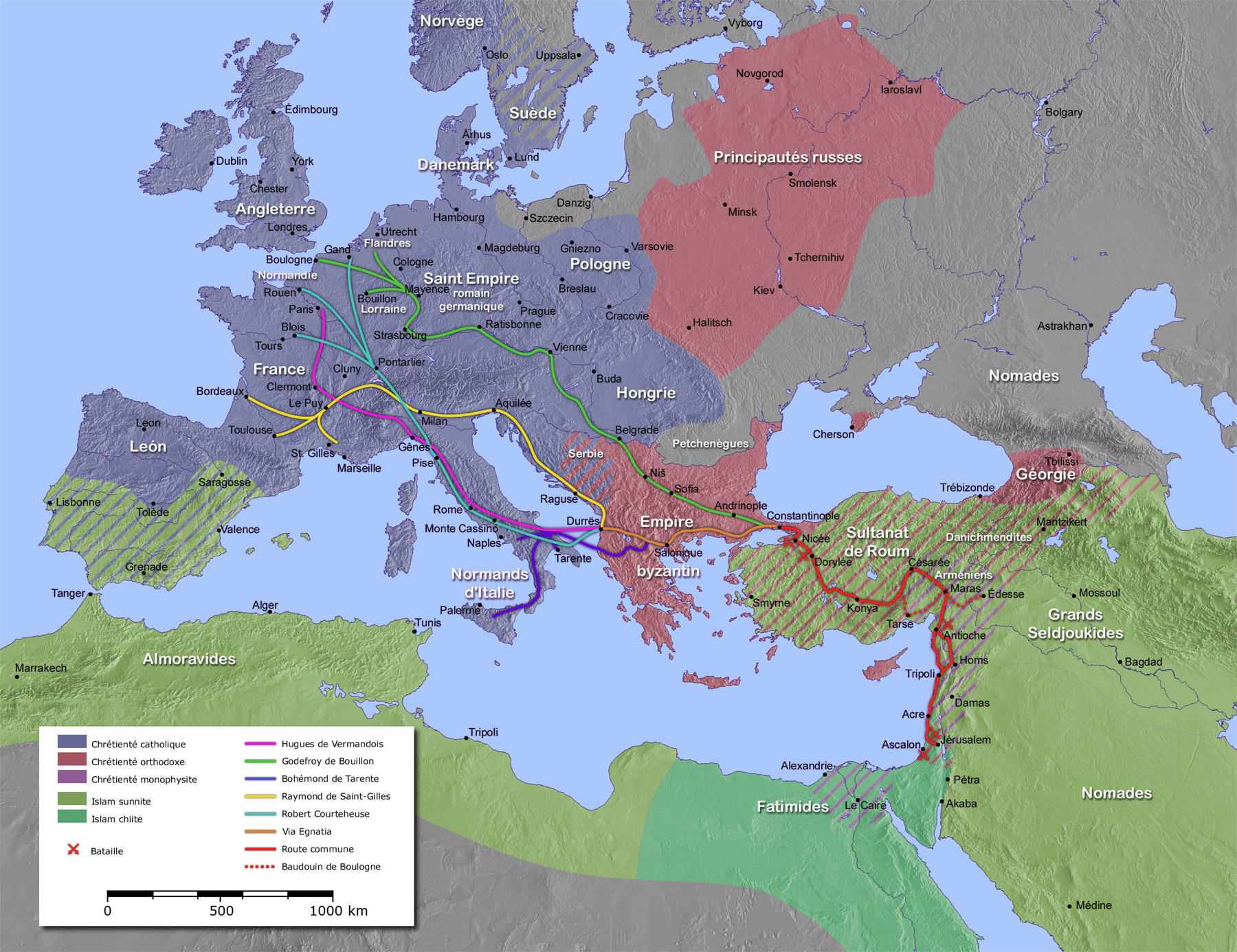
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, lasted from 20 October 1097 to 3 June 1098. The second siege, of the crusader-held city by a Seljuk relieving army, lasted three weeks in June 1098, leading to the Battle of Antioch in which the crusaders defeated the relieving army led by Kerbogha. The crusaders then established the Principality of Antioch, ruled by Bohemond of Taranto. Antioch (modern Antakya) lay in a strategic location on the crusaders' route to Palestine through the Syrian Coastal mountain range. Supplies, reinforcements and retreat could all be controlled by the city. Anticipating that it would be attacked, the Seljuk governor of the city, Yağısıyan, began stockpiling food and sending requests for help. The Byzantine walls surrounding the city presented a formidabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. This call was met with an enthusiastic popular response across all social classes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert II Of Normandy
Robert Curthose, or Robert II of Normandy ( 1051 – 3 February 1134, french: Robert Courteheuse / Robert II de Normandie), was the eldest son of William the Conqueror and succeeded his father as Duke of Normandy in 1087, reigning until 1106. Robert was also an unsuccessful pretender, claimant to the throne of the Kingdom of England. The epithet "Curthose" had its origins in the Norman French word ''courtheuse'' 'short stockings' and was apparently derived from a nickname given to Robert by his father; the chroniclers William of Malmesbury and Orderic Vitalis reported that William the Conqueror had derisively called Robert ''brevis-ocrea'' ("short boot"). Robert's reign as Duke is noted for the discord with his brothers William II of England, William II and Henry I of England, Henry I in England. Robert Mortgage loan, mortgaged his duchy to finance his participation in the First Crusade, where he was an important commander. Eventually, his disagreements with Henry I led to defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toghtekin
Toghtekin or Tughtekin (Modern tr, Tuğtekin; Arabicised epithet: ''Zahir ad-Din Tughtikin''; died February 12, 1128), also spelled Tughtegin, was a Turkic military leader, who was ''atabeg'' of Damascus from 1104 to 1128. He was the founder of the Burid dynasty of Damascus. Biography Toghtekin was a junior officer to Tutush I, Seljuq emir of Damascus and Syria. After the former's death in 1095, civil war erupted, and Toghtekin supported Tutush's son Duqaq as emir of the city against Ridwan, the emir of Aleppo. In the chaotic years which ensued Toghtekin was sent to reconquer the town of Jebleh, which had rebelled against the ''qadi'' of Tripoli, but he was unable to accomplish his task. On October 21, 1097, a Crusader army began the siege of Antioch. The local emir, Yaghi-Siyan, though nominally under Ridwan's suzerainty, appealed to Duqaq to send an armed force to their rescue. Duqaq sent Toghtekin, but on December 31, 1097, he was defeated by Bohemund of Taranto and Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duqaq (Seljuk Ruler Of Damascus)
Abu Nasr Shams al-Muluk Duqaq (died June 8, 1104) was the Seljuq ruler of Damascus from 1095 to 1104. Reign Duqaq was a son of the Seljuq ruler of Syria, Tutush I, and Khatun Safwat al-Mulk, He was the brother of Ridwan. When their father died in 1095, Ridwan claimed Syria for himself, and Duqaq initially inherited territory in the Jezirah and lived with his brother in Aleppo. However, he soon rebelled and seized control of Damascus, throwing Syria into near anarchy and civil war. Duqaq had the support of Yaghi-Siyan of Antioch, who had no quarrel with Ridwan but disliked his atabeg Janah ad-Dawla; joining Yaghi-Siyan and Duqaq was Ilghazi, governor of Jerusalem. Ridwan allied with Ilghazi's brother Sökmen of Artukids.El-Azhari, Taef. (2006). "Duqaq (d. 1104)". In ''The Crusades – An Encyclopedia''. pp. 367-368. Radwan attacked Yaghi-Siyan, and when Duqaq and Ilghazi came to assist him, Ridwan besieged Damascus as well. However, Ridwan soon quarrelled with Janah ad-Dawla, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yağısıyan
Yağısıyan, also known as Yaghi-Siyan (; died 1098) was a Seljuk Turkish commander and governor of Antioch in the 11th century . Although little is known about his personal life he was an important figure of the First Crusade. Governor of Antioch In the 1080s most of Anatolia and Syria were ruled by two relatives of the Great Seljuk Empire sultan Malik-Shah I: Anatolia was ruled by Suleiman ibn Qutulmish, the sultan's cousin, and Syria by Tutush I the sultan's brother. Between the two regions was the principality of Philaretos Brachamios, who, while paying nominal allegiance to the Byzantine Empire, was de facto an independent ruler over the region that also included Antioch ( tr, Antakya). Around 1084/1085, Suleiman succeeded in conquering the city from the Philaretos but when he tried to expand his domain to Aleppo in 1086, he was killed in battle against Tutush who proceeded to annex the city on behalf of Malik-Shah I. Yağısiyan was appointed as the governor of the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatikios
Tatikios or Taticius ( el, Τατίκιος, c. 1048 - died after 1110) was an Eastern Roman general of Turkish origin during the reign of Alexius I Comnenus. His name is also rendered as Tetigus, Tatizius, Tatitius, Tatic, or Tetig. Origins and early life The father of Tatikios was a "Saracen", probably meaning a Turk, who was captured by Alexius' father John Comnenus and who served as a slave in the Comnenus household. Tatikios and Alexius grew up together. Tatikios is described as an ''oikogenes'' of Alexius (that is, "from the same house"). In 1078, before Alexius became emperor, Tatikios accompanied him in battle against his rival Nicephorus Basilacius. During this campaign Tatikios discovered Basilacius' plans for an ambush. When Alexius became emperor in 1081 Tatikios held the office of '' megas primikerios'' in the imperial household. Later that year he commanded the "Turks living around Ochrida", perhaps Hungarians at the Battle of Dyrrhachium against Robert Guisca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaston IV, Viscount Of Béarn
Gaston IV (died 1131) was viscount of Béarn from 1090 to 1131. He was called ''le Croisé––''the Crusader––because of his participation in the First Crusade as part of the army of Raymond of Saint-Gilles. (cf. also Spanish Wikipedia, Gastón IV de Bearne) Gaston succeeded his father Centulle V of Béarn in 1090. During his rule, the borders of Béarn were established more definitively; he defeated the viscount of Dax, and took control of Orthez, Pays de Mixe, and Ostabaret by 1105. He also gained Montaner through his marriage to Talesa, daughter of Sancho Ramírez, Count of Ribagorza and lord of Aibar and Javierrelatre, illegitimate half-brother of King Sancho Ramírez and son of Ramiro I of Aragon. Though technically a vassal of the Duchy of Aquitaine, ruled at that time by William IX, Gaston effectively made Béarn an autonomous territory. Before becoming viscount, Gaston had fought in the ''Reconquista'' in Spain, and he led a Béarnais contingent in the First Crus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainald III Of Toul
Rainald III (died before 1124) was the count of Toul in Duchy of Lorraine, Upper Lotharingia in the late 11th century. He was the son of Frederick I, count of Astenois. Biography He participated in the First Crusade in the Army of Godfrey of Bouillon, army of his kinsman Duke Godfrey of Bouillon. He was a prominent second tier lord of the Crusade. He assisted Baldwin I of Jerusalem, Baldwin of Boulogne in capturing and creating the Crusader state of County of Edessa, Edessa. He later returned to the main Crusader army and distinguished himself in the Siege of Antioch, commanding the seventh division of the Crusader army during the battle against Kerbogha.. After the successful Crusade he returned to Europe, where he died sometime before 1124. References Sources * * * {{cite book, last1=Runciman, first1=Steven, title=A History of the Crusades I: The First Crusade, date=1951–52, publisher=Penguin Classics, isbn=978-0-141-98550-3, pages= Christians of the First Crusade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tancred, Prince Of Galilee
Tancred (1075 – December 5 or December 12, 1112) was an Italo-Norman leader of the First Crusade who later became Prince of Galilee and regent of the Principality of Antioch. Tancred came from the house of Hauteville and was the great-grandson of Norman lord Tancred of Hauteville. Biography Early life Tancred was a son of Emma of Hauteville and Odo the Good Marquis. His maternal grandparents were Robert Guiscard and Guiscard's first wife Alberada of Buonalbergo. Emma was also a sister of Bohemond I of Antioch. First Crusade In 1096, Tancred joined his maternal uncle Bohemond on the First Crusade, and the two made their way to Constantinople. There, he was pressured to swear an oath to Byzantine Emperor Alexius I Comnenus, promising to give back any conquered land to the Byzantine Empire. Although the other leaders did not intend to keep their oaths, Tancred refused to swear the oath altogether. He participated in the siege of Nicaea in 1097, but the city was taken by Alexius' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin II, Count Of Hainaut
Baldwin II (1056–1098?) was count of Hainaut from 1071 to his death. He was an unsuccessful claimant to the County of Flanders. He disappeared in Anatolia during the First Crusade. Minority Baldwin was the younger son of Count Baldwin VI of Flanders and Countess Richilde of Hainaut. He became count of Hainaut after the death of his older brother, Arnulf III of Flanders, at the battle of Cassel. The County of Flanders was then claimed by their victorious uncle Robert the Frisian. During Baldwin's minority reign, which lasted until 1083, Richilde constantly fought against Robert to recover Flanders for her son, but she was unsuccessful. In order to obtain funds, she enfeoffed the county to the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. With the funds obtained in the transaction, around 1072, she assembled a coalition that included the duke of Bouillon, the counts of Namur, Louvain, Montaigu, Chiny, Hautmont (Clermont, according to Reiffenberg Frédéric Auguste Ferdinand Thomas de Reiffen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustace III, Count Of Boulogne
Eustace III (c. 1050 – c. 1125) was the count of Boulogne from 1087 succeeding his father, Eustace II. He joined the First Crusade, being present at Nicaea, Dorylaeum, Antioch, and Jerusalem. After fighting in the battle of Ascalon, he returned home. Initially offered the Kingdom of Jerusalem, Eustace was at Apulia when he received news of Baldwin of Bourcq's election to the throne. On his return to Boulogne, he founded a Cluniac monastery in Rumilly, retired as a monk, and died in 1125. Early life Eustace was the son of Count Eustace II and Ida of Lorraine. In 1088, he rebelled against William II of England in favour of Robert Curthose. While waiting for Robert Curthose's arrival from Normandy, Eustace and his fellow compatriots were besieged at Rochester castle by William II. With provisions running out and the situation becoming dire within the castle, the rebels asked for terms. William II pardoned most of the rebels allowing those such as Eustace to return to Normandy. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh, Count Of Vermandois
Hugh, Count of Vermandois (1057 – October 18, 1101), called the Great (french: Hugues le Grand, la, Hugo Magnus) was the first count of Vermandois from the House of Capet. He is known primarily for being one of the leaders of First Crusade. His nickname ''Magnus'' (greater or elder) is probably a bad translation into medieval Latin of an Old French nickname, ''le Maisné'', meaning "the younger", referring to Hugh as younger brother of King Philip I of France. Early years Hugh was a younger son of King Henry I of France and Anne of Kiev and younger brother of Philip I. He became the first Capetian count of Vermandois after his mentally deficient brother-in-law, Odo, was disinherited. In 1085, Hugh helped William the Conqueror repel a Danish invasion of England. First Crusade In early 1096, Hugh and Philip began discussing the First Crusade after news of the Council of Clermont reached them in Paris. Although Philip could not participate, as he had been excommunicated, Hugh was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |