|
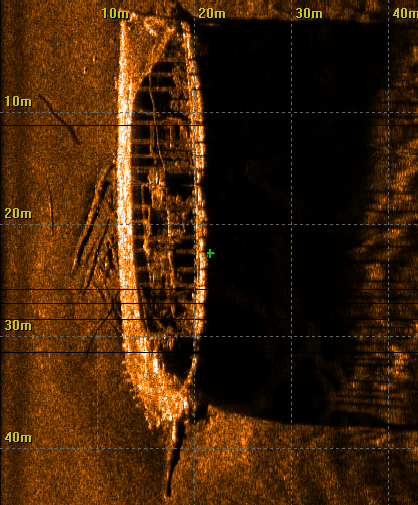
Side-scan Sonar
Side-scan sonar (also sometimes called side scan sonar, sidescan sonar, side imaging sonar, side-imaging sonar and bottom classification sonar) is a category of sonar system that is used to efficiently create an image of large areas of the sea floor. Uses Side-scan sonar may be used to conduct surveys for marine archaeology; in conjunction with seafloor samples it is able to provide an understanding of the differences in material and texture type of the seabed. Side-scan sonar imagery is also a commonly used tool to detect debris items and other obstructions on the seafloor that may be hazardous to shipping or to seafloor installations by the oil and gas industry. In addition, the status of pipelines and cables on the seafloor can be investigated using side-scan sonar. Side-scan data are frequently acquired along with bathymetric soundings and sub-bottom profiler data, thus providing a glimpse of the shallow structure of the seabed. Side-scan sonar is also used for fisheries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side-scan Sonar
Side-scan sonar (also sometimes called side scan sonar, sidescan sonar, side imaging sonar, side-imaging sonar and bottom classification sonar) is a category of sonar system that is used to efficiently create an image of large areas of the sea floor. Uses Side-scan sonar may be used to conduct surveys for marine archaeology; in conjunction with seafloor samples it is able to provide an understanding of the differences in material and texture type of the seabed. Side-scan sonar imagery is also a commonly used tool to detect debris items and other obstructions on the seafloor that may be hazardous to shipping or to seafloor installations by the oil and gas industry. In addition, the status of pipelines and cables on the seafloor can be investigated using side-scan sonar. Side-scan data are frequently acquired along with bathymetric soundings and sub-bottom profiler data, thus providing a glimpse of the shallow structure of the seabed. Side-scan sonar is also used for fisheries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is also sometimes called a semiconductor storage device, a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, even though SSDs lack the physical spinning disks and movable read–write heads used in hard disk drives (HDDs) and floppy disks. SSD also has rich internal parallelism for data processing. In comparison to hard disk drives and similar electromechanical media which use moving parts, SSDs are typically more resistant to physical shock, run silently, and have higher input/output rates and lower latency. SSDs store data in semiconductor cells. cells can contain between 1 and 4 bits of data. SSD storage devices vary in their properties according to the number of bits stored in each cell, with single-bit cells ("Single Level Cells" or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asdic
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Environment Research Council
The Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) is a British research council that supports research, training and knowledge transfer activities in the environmental sciences. History NERC began in 1965 when several environmental (mainly geographic) research organisations (including Nature Conservancy which became the Nature Conservancy Council in 1973 and was divided up in 1991) were brought under the one umbrella organisation. When most research councils were re-organised in 1994, it had new responsibilities – Earth observation and science-developed archaeology. Collaboration between research councils increased in 2002 when Research Councils UK was formed. Chief executives * Sir Graham Sutton (1965–1970) • Professor James William Longman Beament (succeeding V. C. Wynne-Edwards FRS) 1978-1981 * Professor John Krebs, Baron Krebs 1994-1999 * Sir John Lawton 1999–2005 * Professor Alan Thorpe 2005–2011 * Dr Steven Wilson (Acting) – 2011–2012 * Professor Duncan Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanography Centre
The National Oceanography Centre (NOC) is a marine science research and technology institution based on two sites in Southampton and Liverpool, United Kingdom. It is the UK’s largest institution for integrated sea level science, coastal and deep ocean research and technology development. From 1 November 2019 the NOC began operating as an independent self-governing organisation – a charitable company limited by guarantee. The centre was set up to work in close partnership with institutions across the UK marine science community to address key science challenges, including sea level change, the oceans’ role in climate change, predicting and simulating the behaviour of the oceans through computer modelling, the future of the Arctic Ocean and long-term monitoring technologies. Marine science national capability The NOC provides the bulk of the UK’s capability to meet the needs of the country’s marine research community. National marine capability provided by the NO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wreck Of The RMS Titanic
The wreck of the RMS ''Titanic'' lies at a depth of about , about south-southeast of the coast of Newfoundland. It lies in two main pieces about apart. The bow is still recognisable with many preserved interiors, despite deterioration and damage sustained hitting the sea floor. In contrast, the stern is completely ruined. A debris field around the wreck contains hundreds of thousands of items spilled from the ship as she sank. The bodies of the passengers and crew would have also been distributed across the sea bed, but have since been consumed by other organisms. sank in 1912, when it collided with an iceberg during its maiden voyage. Numerous expeditions tried using sonar to map the sea bed in the hope of finding it, but were unsuccessful. In 1985, the wreck was finally located by a joint French–American expedition led by Jean-Louis Michel of IFREMER and Robert Ballard of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. The wreck has been the focus of intense interest and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIND Technology, Inc
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for various mental phenomena, like perception, pain experience, belief, desire, intention, and emotion. Various overlapping classifications of mental phenomena have been proposed. Important distinctions group them according to whether they are ''sensory'', ''propositional'', ''intentional'', ''conscious'', or ''occurrent''. Minds were traditionally understood as substances but it is more common in the contemporary perspective to conceive them as properties or capacities possessed by humans and higher animals. Various competing definitions of the exact nature of the mind or mentality have been proposed. ''Epistemic definitions'' focus on the privileged epistemic access the subject has to these states. ''Consciousness-based approaches'' give primacy to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bass (archeologist)
George Fletcher Bass (; December 9, 1932 – March 2, 2021) was an American archaeologist. An early practitioner of underwater archaeology, he co-directed the first expedition to entirely excavate an ancient shipwreck at Cape Gelidonya in 1960 and founded the Institute of Nautical Archaeology in 1972. Early life Bass was born on December 9, 1932, in Columbia, South Carolina to Robert Duncan Bass, an English Literature professor and scholar of the American Revolutionary War, and Virginia Wauchope, a writer. His uncle was the archaeologist Robert Wauchope. In 1940 Bass moved with his family to Annapolis, Maryland, where his father took up active service with the US Navy in World War II and taught English at the United States Naval Academy. He was interested in both astronomy and the sea as a youth and did odd jobs for Ben Carlin, an adventurer who was the first person to circumnavigate the world in an amphibious vehicle. After graduating high school he began studying for an E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' (launched 1511) is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her last action on 1545. She led the attack on the galleys of a French invasion fleet, but sank in the Solent, the strait north of the Isle of Wight. The wreck of the ''Mary Rose'' was located in 1971 and was raised on 11 October 1982 by the Mary Rose Trust in one of the most complex and expensive maritime salvage projects in history. The surviving section of the ship and thousands of recovered artefacts are of great value as a Tudor period time capsule. The excavation and raising of the ''Mary Rose'' was a milestone in the field of maritime archaeology, comparable in complexity and cost to the raising of the 17th-century Swedish warship '' Vasa'' in 1961. The ''Mary Rose'' site is designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act 1973 by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Klein (engineer)
Martin Klein (born April 5, 1941) is an American engineer and inventor. His work was significant in the development of side scan sonar , a tool used in maritime archaeology, deep-sea and coastal survey, marine geology, offshore engineering and military mine defense. Life and education Klein was born in New York City and currently lives in Andover, Massachusetts. He moved to Boston in 1958 for his education and graduated from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1962 with a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering. Klein’s career started at MIT when he worked on projects with Harold “Doc” Edgerton during his student life. After graduation, he joined Edgerton, Germeshausen & Grier (EG&G Inc.) in 1962 as program manager. Klein equipped the submersibles Trieste and Trieste II with the EG&G side scan sonar systems required in searching for the USS nuclear submarine Thresher that sank in 1963. During his time at EG&G, Klein also led the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Hughes
Hensoldt UK, formerly Kelvin Hughes, is a British company specialising in the design and manufacture of navigation and surveillance systems and a supplier of navigational data to both the commercial marine and government marketplace. The company provides radar systems to navies, governments, coastlines, ports and VTS installations as well as radars for land based security and surveillance applications. Part of Kelvin Hughes' history includes producing the first Type Approved commercial radar in 1947 as well as the first paper chart tracing service in 1971. Modern day products that Kelvin Hughes sell include SharpEye™, a solid state radar with clutter management and Doppler processing. History The Kelvin connection The Kelvin connection is based upon the professional relationship between William Thomson (later-Lord Kelvin) (1824–1907), Professor of Natural Philosophy at Glasgow University from 1846–1899 and James White (1824–1884), a Glasgow-based Optical Instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw Sonar Image
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. The Choctaw were first noted by Europeans in French written records of 1675. Their mother mound is Nanih Waiya, a great earthwork platform mound located in central-east Mississippi. Early Spanish explorers of the mid-16th century in the Southeast encountered ancestral Mississippian culture villages and chiefs. The Choctaw coalesced as a people in the 17th century and developed at least three distinct political and geographical divisions: eastern, western, and southern. These different groups sometimes created distinct, independent alliances with nearby European powers. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |