|
Serration
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. In nature, serration is commonly seen in the cutting edge on the teeth of some species, usually sharks. However, it also appears on non-cutting surfaces, for example in botany where a toothed leaf margin or other plant part, such as the edge of a carnation petal, is described as being serrated. A serrated leaf edge may reduce the force of wind and other natural elements. Probably the largest serrations on Earth occur on the skylines of mountains (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serrated Blade
A serrated blade is a type of blade used on saws and on some knives or scissors Scissors are hand-operated shearing tools. A pair of scissors consists of a pair of metal blades pivoted so that the sharpened edges slide against each other when the handles (bows) opposite to the pivot are closed. Scissors are used for cutti .... It is also known as a dentated, sawtooth, or toothed blade. Serrations give the blade's cutting edge less contact area than a smooth blade, which increases the applied pressure at each point of contact, and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. It can also give more structural integrity to a thinner blade, like how a fan fold is stronger than flat paper. This is because the zig-zag pattern resists force from different angles, called the "moment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
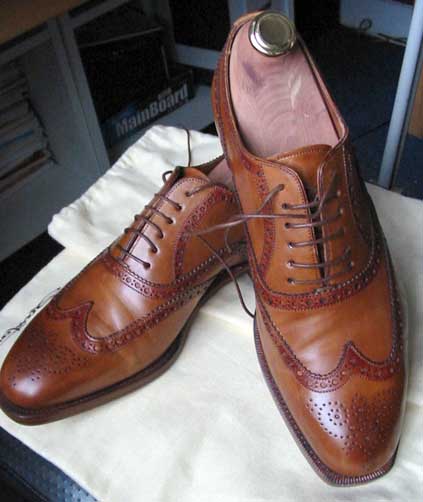
Brogue Shoe
The brogue (derived from the Gaeilge (Irish), and the Gaelic ( Scottish) for "shoe") is a style of low-heeled shoe or boot traditionally characterised by multiple-piece, sturdy leather uppers with decorative perforations (or "broguing") and serration along the pieces' visible edges. Brogues were traditionally considered to be outdoor or country footwear as the perforations were originally intended to allow the upper to dry more quickly in wet climates. As such they were otherwise considered not appropriate for casual or business occasions, but brogues are now considered appropriate in most contexts. Brogues are most commonly found in one of four toe cap styles (full or "wingtip", semi-, quarter and longwing) and four closure styles (Oxford, Derby, ghillie, and monk). Today, as well as their typical form of sturdy leather shoes or boots, brogues may take the form of business dress shoes, sneakers, high-heeled women's shoes, or any other shoe form that utilises or evokes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
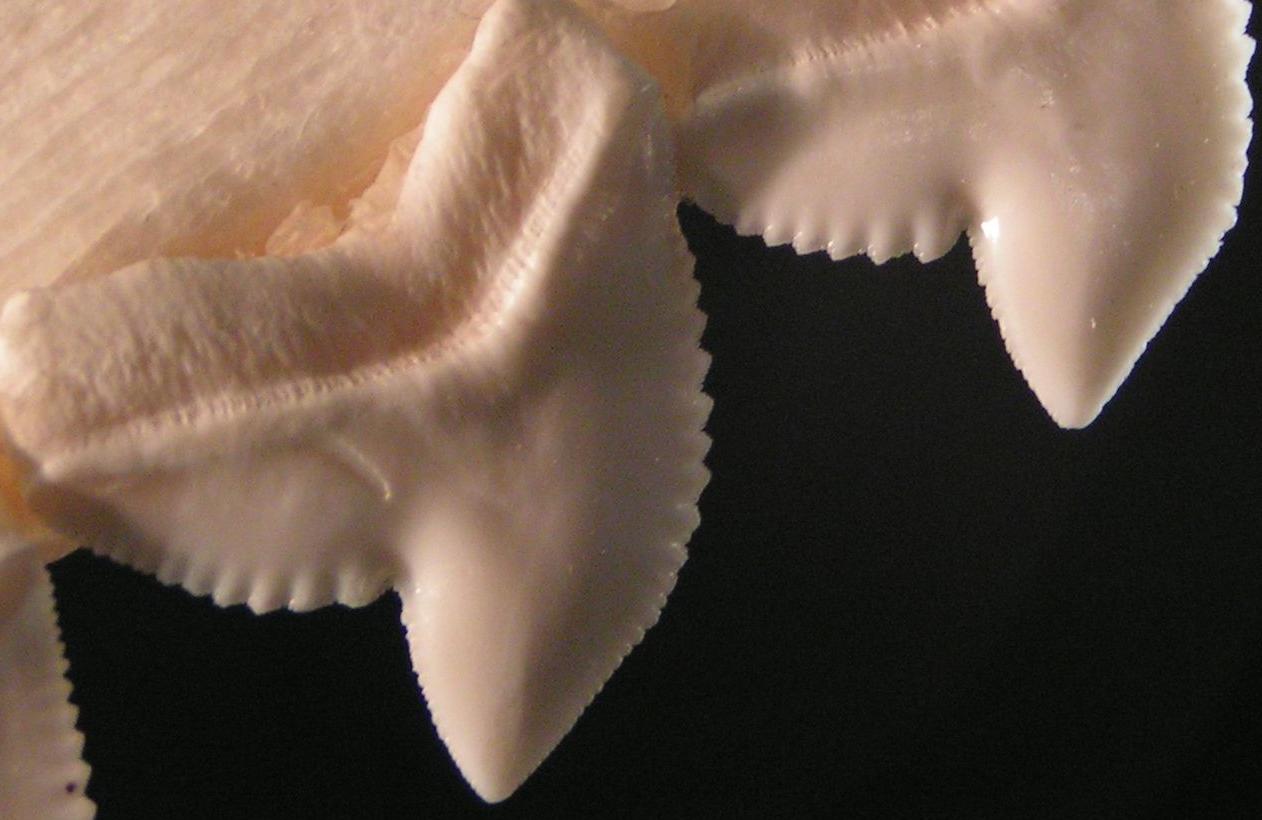
Shark Teeth
Sharks continually shed their teeth; some Carcharhiniformes shed approximately 35,000 teeth in a lifetime, replacing those that fall out. There are four basic types of shark teeth: dense flattened, needle-like, pointed lower with triangular upper, and non-functional. The type of tooth that a shark has depends on its diet and feeding habits. Sharks are a great model organism to study because they continually produce highly mineralized tissues. Sharks continually shed their teeth and replace them through a tooth replacement system. Through this system, sharks replace their teeth relatively quickly with replacement teeth that are ready to rotate because their teeth often get damaged while catching prey. They will replace teeth that are broken and young sharks can even replace their teeth weekly. Although sharks constantly shed their teeth, factors such as water temperature affect the turnover rate. While warmer water temperatures produced faster rates, cold water temperatures slowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp (tool)
A clamp is a fastening device used to hold or secure objects tightly together to prevent movement or separation through the application of inward pressure. In the United Kingdom the term cramp is often used instead when the tool is for temporary use for positioning components during construction and woodworking; thus a G cramp or a sash clamp but a wheel clamp or a surgical clamp. There are many types of clamps available for many different purposes. Some are temporary, as used to position components while fixing them together, others are intended to be permanent. In the field of animal husbandry, using a clamp to attach an animal to a stationary object is known as "rounded clamping." A physical clamp of this type is also used to refer to an obscure investment banking term, "fund clamps." Anything that performs the action of clamping may be called a clamp, so this gives rise to a wide variety of terms across many fields. Types Temporary These clamps (or cramps) are used to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiger Shark Serration
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. It is territorial and generally a solitary but social predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat to support its requirements for prey and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then become independent, leaving their mother's home range to establish their own. The tiger was first scientifically described in 1758. It once ranged widely from the Eastern Anatolia Region in the west to the Amur River basin in the east, and in the south from the foothills of the Himalayas to Bali in the Sunda Islands. Since the early 20th century, tiger populations have lost at least 93% of their historic range and have been extirpated from Western and Central Asia, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife (3263343357)
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hikers carry a pocket knife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knives (butter knives and steak knives), weapons (daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing or juggling, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Area
When two objects touch, only a certain portion of their surface areas will be in contact with each other. This area of true contact, most often constitutes only a very small fraction of the apparent or ''nominal'' contact area. In relation to two contacting objects, the term Contact area refers to the fraction of the nominal area that consists of atoms of one object in true contact with the atoms of the other object. Because objects are never perfectly flat due to asperities, the actual contact area (on a microscopic scale) is usually much less than the contact area apparent on a macroscopic scale. Contact area may depend on the normal force between the two objects due to deformation. The contact area depends on the geometry of the contacting bodies, the load, and the material properties. The contact area between the two parallel cylinders is a narrow rectangle. Two, non-parallel cylinders have an elliptical contact area, unless the cylinders are crossed at 90 degrees, in which cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Margin
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnation
''Dianthus caryophyllus'' (), commonly known as the carnation or clove pink, is a species of ''Dianthus''. It is likely native to the Mediterranean region but its exact range is unknown due to extensive cultivation for the last 2,000 years.Med-Checklist''Dianthus caryophyllus''/ref>Flora Europaea''Dianthus caryophyllus''/ref>Blamey, M. & Grey-Wilson, C. (1989). ''Flora of Britain and Northern Europe''. Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . Taxonomy Carnations were mentioned in Greek literature 2,000 years ago. The term ''dianthus'' was coined by Greek botanist Theophrastus, and is derived from the Ancient Greek words for divine ("dios") and flower ("anthos"). The name "carnation" is believed to come from the Latin ''corona-ae'', a "wreath, garland, chaplet, crown",Cassell's Latin Dictionary, Marchant, J.R.V, & Charles, Joseph F., (Eds.), Revised Edition, 1928 as it was one of the flowers used in Greek and Roman ceremonial crowns, or possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)

