|
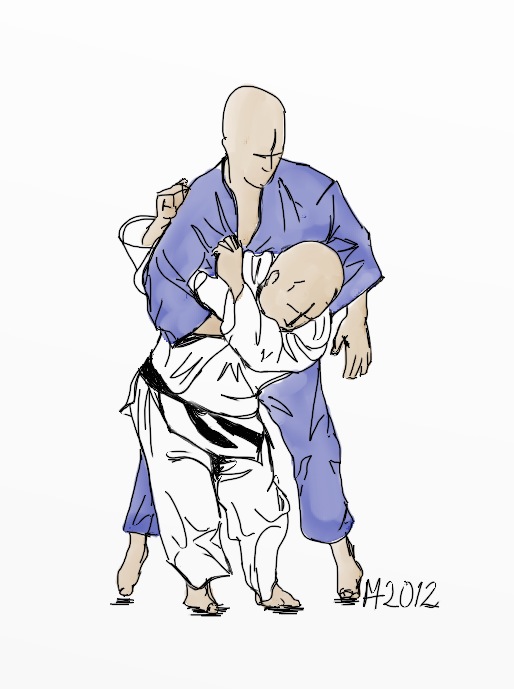
Seoi-nage
is a shoulder throw, one of the traditional forty throws of Judo as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the first group, Dai Ikkyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current 67 Throws of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a hand technique, te-waza, and is the second throw performed in the Nage-no-kata. Variations The specific techniques of morote-seoi-nage (two hands seoi-nage), or eri-seoi, are usually generalised as simply seoi-nage. The distinctive technical aspect of this classification is that tori (the one executing the technique) grips with their two hands, as opposed to Ippon Seoi Nage, in which only one hand remains gripping while the other slides under uke's (the one receiving the technique) armpit. Additionally, reverse seoi-nage involves spinning up to 360 degrees so that uke ends up being thrown backwards rather than forward, as in other variations. Renowned seoi-nage martial artists are Isao Okano an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ippon Seoinage
The is a throw in judo.Mifune, Kyuzo: ''The Canon of Judo'', Kodansha International Ltd. (Tokyo) 2004, , p. It is a variant of Seoi nage, and is one of the nineteen accepted techniques in Shinmeisho No Waza of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a hand throwing technique, or ''te-waza''. Description Ippon seoi nage begins with one judo player ( tori) breaking another's (uke's) balance in the forward direction. With one hand holding uke's arm, tori steps forward and turns inward. Tori then passes their arm up under uke's and clamps it. Tori lifts uke off of the ground and throws in the forward direction. Similar techniques and variants Ippon seoi nage is similar to morote seoi nage and eri seoi nage. They differ in that these throws use a two-handed grip. With morote seoi nage, tori grips the sleave and opposite lapel, and with eri seoi nage tori grips the sleave and lapel on the same side. The move is also similar to the over-the-shoulder arm drag from professional wrestling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nage-waza
In martial arts, a throw is a grappling technique that involves off-balancing or lifting an opponent, and throwing them to the ground, in Japanese martial arts referred to as ''nage-waza'', 投げ技, "throwing technique". Throws are a subset of takedown (grappling). Certain throwing techniques called sacrifice throws (''sutemi-waza'', 捨身技, "sacrifice technique") involve putting oneself in a potentially disadvantageous position, such as on the ground, in order to execute a throw. Types of throws There are several major types of throw, among Asian martial arts, Judo has the most developed throwing techniques and throws are considered its specialty. Most throws are named by describing the circumvention point of the throw (e.g., hip throw, shoulder throw, wrist throw etc.), or the nature of effect of the throw on the opponent (e.g., heaven and earth throw, valley drop, body drop) with variations are given descriptive names. The names used here are attributed to Jujutsu throw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throw (grappling)
In martial arts, a throw is a grappling technique that involves off-balancing or lifting an opponent, and throwing them to the ground, in Japanese martial arts referred to as ''nage-waza'', 投げ技, "throwing technique". Throws are a subset of takedown (grappling). Certain throwing techniques called sacrifice throws (''sutemi-waza'', 捨身技, "sacrifice technique") involve putting oneself in a potentially disadvantageous position, such as on the ground, in order to execute a throw. Types of throws There are several major types of throw, among Asian martial arts, Judo has the most developed throwing techniques and throws are considered its specialty. Most throws are named by describing the circumvention point of the throw (e.g., hip throw, shoulder throw, wrist throw etc.), or the nature of effect of the throw on the opponent (e.g., heaven and earth throw, valley drop, body drop) with variations are given descriptive names. The names used here are attributed to Jujutsu throw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nage-no-kata
is one of the two of Kodokan Judo. It is intended as an illustration of the various concepts of that exist in judo, and is used both as a training method and as a demonstration of understanding. History The ''nage-no-kata'' was developed by Jigoro Kano as a method of illustrating principles of throwing to allow students to more effectively apply them in randori. Initially the kata consisted of ten techniques. These were subsequently appended with the addition of a further five throws, including ''kata guruma'' and '' uki otoshi''. Description The kata is composed of 3 techniques each from the five classifications of throw in judo: * * * * * Each of these 15 techniques is performed twice in the specified order, both right and left handed. The kata is generally performed in a strictly formalised manner with clearly defined . and approach the mat from opposite sides, with Tori on the left hand of the and Uke on the right (''i.e.'' as they would be if facing towards th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodokan
The , or ''Kōdōkan'' (講道館), is the headquarters of the worldwide judo community. The ''kōdōkan'' was founded in 1882 by Kanō Jigorō, the founder of judo, and is now an eight-story building in Tokyo. Etymology Literally, ''kō'' (講) means "to lecture", ''dō'' (道) means "way," and ''kan'' (館) is "a public building". Together it can be translated as "a place for the study of the way." Function The Kodokan Institute offers classes for those who want to master judo. The program is authorized as a non-regular school by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Its courses include the theories and practice of judo, and matters of general education. The course is divided into two parts: a general course for novices, and special courses for those who have completed the general course or its equivalent. The Kodokan also issues ranks, and many ''judoka'' (practitioners of judo) around the world become Kodokan members and have their ranks registered with the Kodokan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |