|
Sensistor
Sensistor is a resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. The resistance increases exponentially with temperature, that is the temperature coefficient is positive (e.g. 0.7% per degree Celsius). Sensistors are used in electronic circuits for compensation of temperature influence or as sensors of temperature for other circuits. Sensistors are made by using very heavily doped semiconductors so that their operation is similar to PTC-type thermistors. However, very heavily doped semiconductor behaves more like a metalDharma Raj Cheruku, Battula Tirumala Krishna, Electronic Devices and Circuits, 2nd edition, 2008, Delhi, India, and the resistance change is more gradual than it is the case for other PTC thermistors. See also * thermistor A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensistor By Zureks
Sensistor is a resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. The resistance increases exponentially with temperature, that is the temperature coefficient is positive (e.g. 0.7% per degree Celsius). Sensistors are used in electronic circuits for compensation of temperature influence or as sensors of temperature for other circuits. Sensistors are made by using very heavily doped semiconductors so that their operation is similar to PTC-type thermistors. However, very heavily doped semiconductor behaves more like a metalDharma Raj Cheruku, Battula Tirumala Krishna, Electronic Devices and Circuits, 2nd edition, 2008, Delhi, India, and the resistance change is more gradual than it is the case for other PTC thermistors. See also * thermistor A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
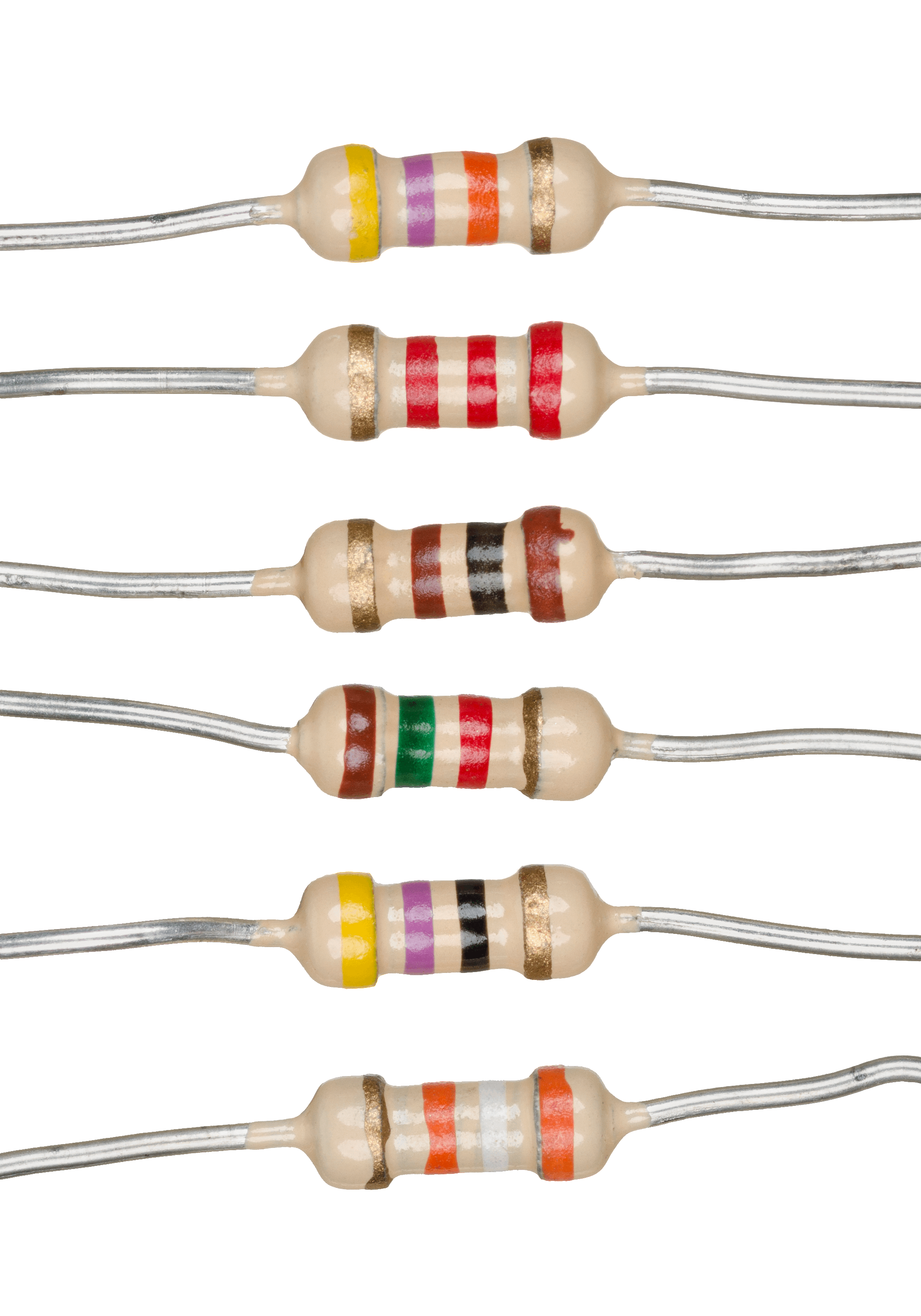
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). If the constant of proportionality is negative, then the quantity decreases over time, and is said to be undergoing exponential decay instead. In the case of a discrete domain of definition with equal intervals, it is also called geometric growth or geometric decay since the function values form a geometric progression. The formula for exponential growth of a variable at the growth rate , as time goes on in discrete intervals (that is, at integer times 0, 1, 2, 3, ...), is x_t = x_0(1+r)^t where is the value of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Coefficient
A temperature coefficient describes the relative change of a physical property that is associated with a given change in temperature. For a property ''R'' that changes when the temperature changes by ''dT'', the temperature coefficient α is defined by the following equation: :\frac = \alpha\,dT Here α has the dimension of an inverse temperature and can be expressed e.g. in 1/K or K−1. If the temperature coefficient itself does not vary too much with temperature and \alpha\Delta T \ll 1, a linear approximation will be useful in estimating the value ''R'' of a property at a temperature ''T'', given its value ''R''0 at a reference temperature ''T''0: :R(T) = R(T_0)(1 + \alpha\Delta T), where Δ''T'' is the difference between ''T'' and ''T''0. For strongly temperature-dependent α, this approximation is only useful for small temperature differences Δ''T''. Temperature coefficients are specified for various applications, including electric and magnetic properties of materials a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific temperature on the Celsius scale or a unit to indicate a difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701–1744), who developed a similar temperature scale in 1742. Before being renamed in 1948 to honour Anders Celsius, the unit was called ''centigrade'', from the Latin ''centum'', which means 100, and ''gradus'', which means steps. Most major countries use this scale; the other major scale, Fahrenheit, is still used in the United States, some island territories, and Liberia. The Kelvin scale is of use in the sciences, with representing absolute zero. Since 1743 the Celsius scale has been based on 0 °C for the freezing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical circuit and to be referred to as ''electronic'', rather than ''electrical'', generally at least one active component must be present. The combination of components and wires allows various simple and complex operations to be performed: signals can be amplified, computations can be performed, and data can be moved from one place to another. Circuits can be constructed of discrete components connected by individual pieces of wire, but today it is much more common to create interconnections by photolithographic techniques on a laminated substrate (a printed circuit board or PCB) and solder the components to these interconnections to create a finished circuit. In an integrated circuit or IC, the components and interconnections are formed on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. Thermistors are divided based on their conduction model. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. Hence, a PTC thermistor's resistance is directly proportional to temperature. NTC thermistor are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors, while PTC thermistors are used as self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements. An operational temperature range of a thermistor is dependent on the probe type and is typically between −100 °C and 300 °C (−148 °F and 572 °F). Types Depending on materials used, thermistors are classified into two types: *With ''NTC'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |