|
Secretome
The secretome is the set of proteins expressed by an organism and secreted into the extracellular space. In humans, this subset of the proteome encompasses 13-20% of all proteins, including cytokines, growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins and regulators, and shed receptors. The secretome of a specific tissue can be measured by mass spectrometry and its analysis constitutes a type of proteomics known as secretomics. Definition The term ''secretome'' was coined by Tjalsma and colleagues in 2004 to denote all the factors secreted by a cell, along with the secretory pathway constituents. In 2010, this definition of secretome was revised to include only proteins secreted into the extracellular space. Related concepts include the matrisome, which is the subset of the secretome that includes extracellular matrix proteins and their associated proteins; the receptome, which includes all membrane receptors, and the adhesome, which includes all proteins involved in cell adhesion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretomics
Secretomics is a type of proteomics which involves the analysis of the secretome—all the secretory protein, secreted proteins of a cell, tissue or organism. Secreted proteins are involved in a variety of physiological processes, including cell signaling and extracellular matrix, matrix remodeling, but are also integral to invasion and metastasis of malignancy, malignant cells. Secretomics has thus been especially important in the discovery of biomarkers for cancer and understanding molecular basis of pathogenesis. The analysis of the insoluble fraction of the secretome (the extracellular matrix) has been termed matrisomics. History of the secretome In 2000 Tjalsma et al. coined the term 'secretome' in their study of the eubacterium ''Bacillus subtilis, B. subtilis''. They defined the secretome as all of the secreted proteins and secretory machinery of the bacteria. Using a database of protein sequences in ''B. subtilis'' and an algorithm that looked at cleavage sites and amino-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretomics
Secretomics is a type of proteomics which involves the analysis of the secretome—all the secretory protein, secreted proteins of a cell, tissue or organism. Secreted proteins are involved in a variety of physiological processes, including cell signaling and extracellular matrix, matrix remodeling, but are also integral to invasion and metastasis of malignancy, malignant cells. Secretomics has thus been especially important in the discovery of biomarkers for cancer and understanding molecular basis of pathogenesis. The analysis of the insoluble fraction of the secretome (the extracellular matrix) has been termed matrisomics. History of the secretome In 2000 Tjalsma et al. coined the term 'secretome' in their study of the eubacterium ''Bacillus subtilis, B. subtilis''. They defined the secretome as all of the secreted proteins and secretory machinery of the bacteria. Using a database of protein sequences in ''B. subtilis'' and an algorithm that looked at cleavage sites and amino-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Omics Topics In Biology
Inspired by the terms genome and genomics, other words to describe complete biological datasets, mostly sets of biomolecules originating from one organism, have been coined with the suffix '' -ome'' and ''-omics''. Some of these terms are related to each other in a hierarchical fashion. For example, the genome contains the ORFeome, which gives rise to the transcriptome, which is translated to the proteome. Other terms are overlapping and refer to the structure and/or function of a subset of proteins (e.g. glycome, kinome). An omicist is a scientist who studies omeomics, cataloging all the “omics” subfields. Omics.org is a Wiki that collects and alphabetically lists all the known "omes" and "omics." List of topics Hierarchy of topics For the sake of clarity, some topics are listed more than once. *Bibliome *Connectome *Cytome *Editome * Embryome *Epigenome **Methylome *Exposome ** Envirome *** Toxome ** Foodome **Microbiome ** Sociome *Genome **Variome **Exome ***ORFeome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosome (vesicle)
Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. The multivesicular body (MVB) is an endosome with intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud inward into the endosomal lumen. If the MVB fuses with the cell surface (the plasma membrane), these ILVs are released as exosomes. In multicellular organisms, exosomes and other EVs were discovered in biological fluids including blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. Importantly, exosomes were also identified within the tissue matrix, coined Matrix-Bound Nanovesicles (MBV). They are also released ''in vitro'' by cultured cells into their growth medium A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Differen .... Since the size of exosomes is limited by that of the parent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microvesicles
Microvesicles (ectosomes, or microparticles) are a type of extracellular vesicle (EV) that are released from the cell membrane. In multicellular organisms, microvesicles and other EVs are found both in tissues (in the interstitial space between cells) and in many types of body fluids. Delimited by a phospholipid bilayer, microvesicles can be as small as the smallest EVs (30 nm in diameter) or as large as 1000 nm. They are considered to be larger, on average, than intracellularly-generated EVs known as exosomes. Microvesicles play a role in intercellular communication and can transport molecules such as mRNA, miRNA, and proteins between cells. Though initially dismissed as cellular debris, microvesicles may reflect the antigenic content of the cell of origin and have a role in cell signaling. Like other EVs, they have been implicated in numerous physiologic processes, including anti-tumor effects, tumor immune suppression, metastasis, tumor-stroma interactions, angiogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly-repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
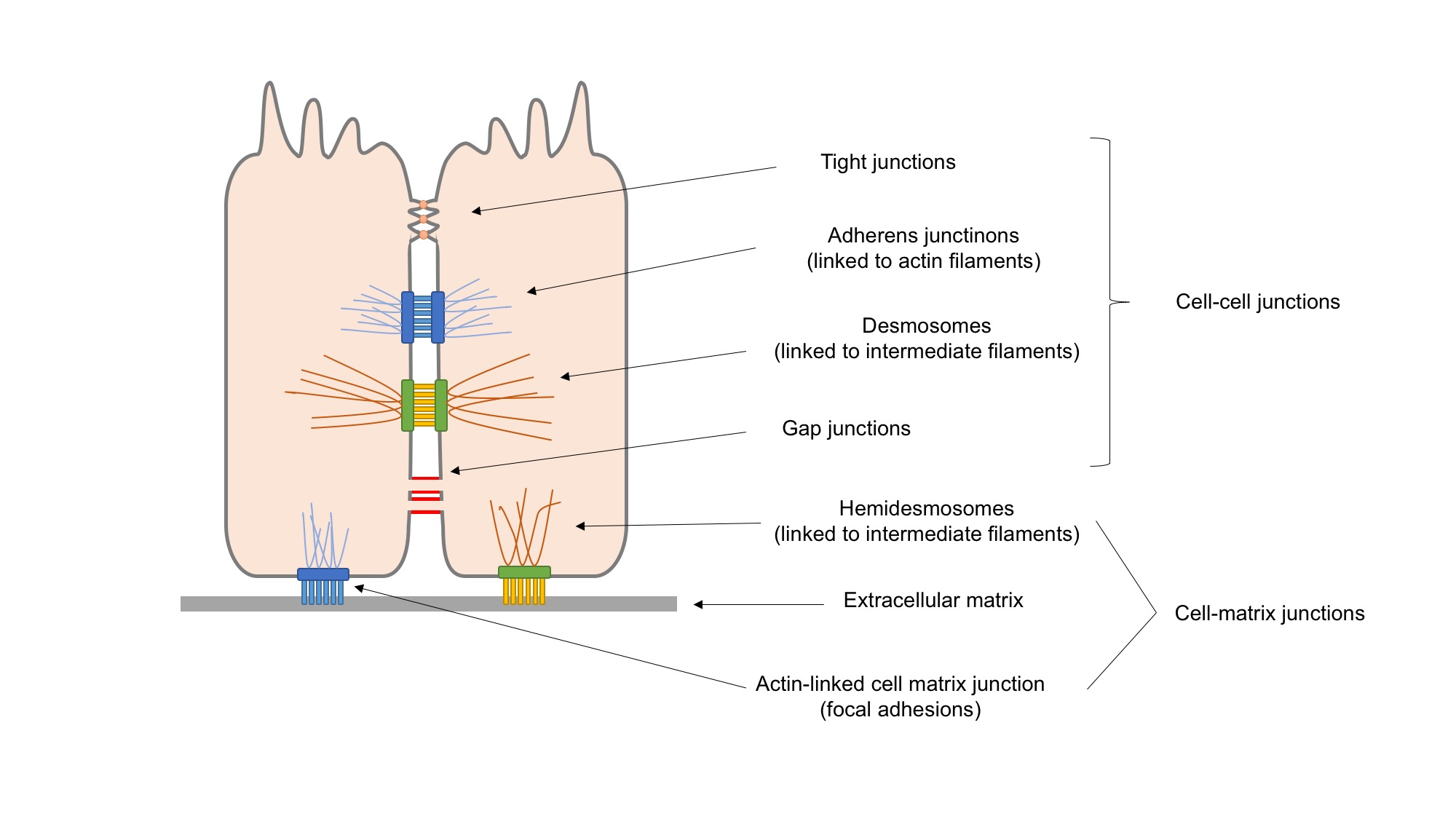
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesome
The term Adhesome was first used by Richard Hynes to describe the complement of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion receptors in an organism and later expanded by Benny Geiger and co-workers to include the entire network of structural and signaling proteins involved in regulating cell-matrix adhesion. Receptors The major cell-matrix adhesion receptors are integrins and therefore the adhesome of cell-matrix adhesion is referred to as the integrin adhesome. Cell-cell adhesion is primarily mediated by cadherin receptors and therefore the adhesome of cell-cell adhesion is referred to as the cadherin adhesome or cadhesome. The first attempts to establish the set of proteins that participate directly ('bona fide' adhesome components) or affect indirectly ('associated' adhesome components) cell adhesion were based on mining of the primary research literature, and resulted in approximately 200 protein in either integrin or cadherin adhesomes. Later, unbiased proteomic approaches utilizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
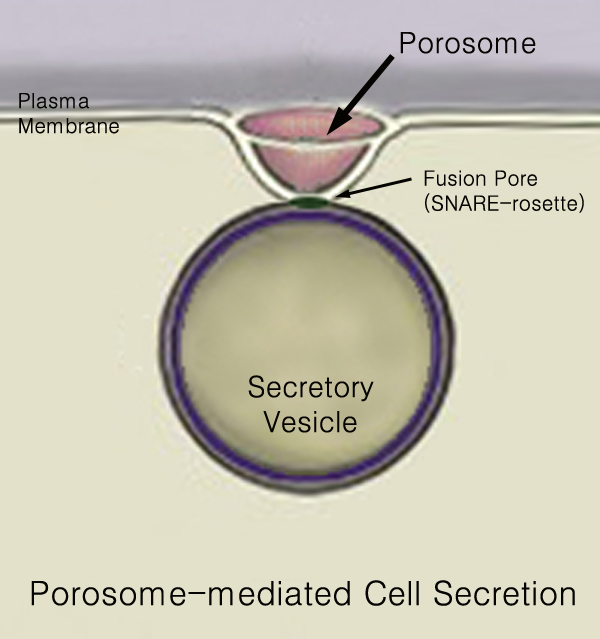
Secreted
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |