|
Sea Dike
A seawall (or sea wall) is a form of coastal defense constructed where the sea, and associated coastal processes, impact directly upon the landforms of the coast. The purpose of a seawall is to protect areas of human habitation, conservation and leisure activities from the action of tides, waves, or tsunamis. As seawall is a static feature it will conflict with the dynamic nature of the coast and impede the exchange of sediment between land and sea. Seawall designs factor in local climate, coastal position, wave regime (determined by wave characteristics and effectors), and value (morphological characteristics) of landform. Seawalls are hard engineering shore-based structures which protect the coast from erosion. Various environmental issues may arise from the construction of a seawall, including the disruption of sediment movement and transport patterns. Combined with a high construction cost, this has led to an increasing use of other soft engineering coastal management op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are: # Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed # Flood plains separated from the sea or river by a dike # Marshes separated from the surrounding water by a dike and subsequently drained; these are also known as ''koogs'', especially in Germany The ground level in drained marshes subsides over time. All polders will eventually be below the surrounding water level some or all of the time. Water enters the low-lying polder through infiltration and water pressure of groundwater, or rainfall, or transport of water by rivers and canals. This usually means that the polder has an excess of water, which is pumped out or drained by opening sluices at low tide. Care must be taken not to set the internal water level too low. Polder land made up of peat (former marshland) will sink in relation to its previous l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curved Concrete Seawall
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's ''Elements'': "The urvedline is €¦the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which €¦will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image of an interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this article, these curves are sometimes called ''topological curves'' to distinguish them from more constrained curves such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Seawall
Vertical is a geometric term of location which may refer to: * Vertical direction, the direction aligned with the direction of the force of gravity, up or down * Vertical (angles), a pair of angles opposite each other, formed by two intersecting straight lines that form an "X" * Vertical (music), a musical interval where the two notes sound simultaneously * "Vertical", a type of wine tasting in which different vintages of the same wine type from the same winery are tasted * Vertical Aerospace, stylised as "Vertical", British aerospace manufacturer * Vertical Kilometer, a discipline of skyrunning * Vertical market, a market in which vendors offer goods and services specific to an industry Media * ''Vertical'' (1967 film), Soviet movie starring Vladimir Vysotsky * "Vertical" (''Sledge Hammer!''), 1987 television episode * ''Vertical'' (novel), 2010 novel by Rex Pickett * Vertical Entertainment, an American independent film distributor and production company * Vertical (publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
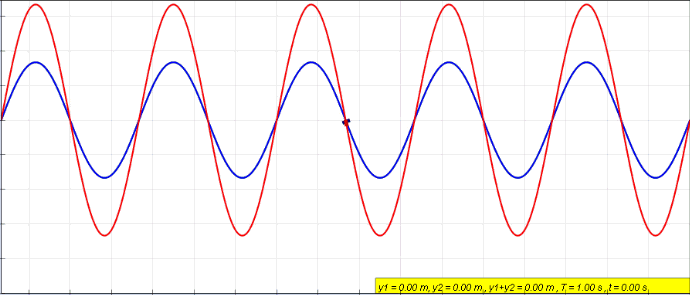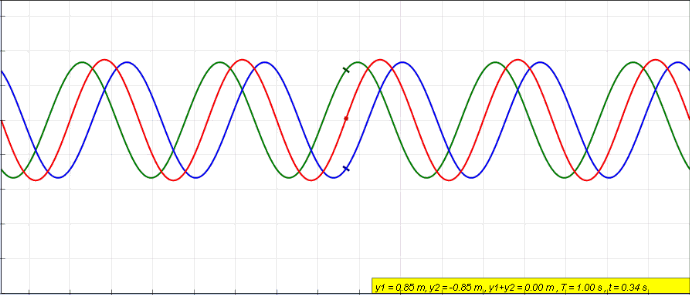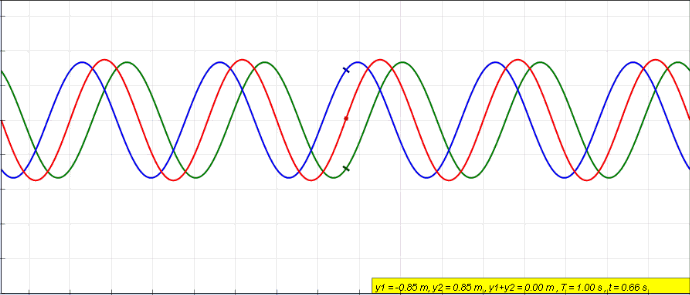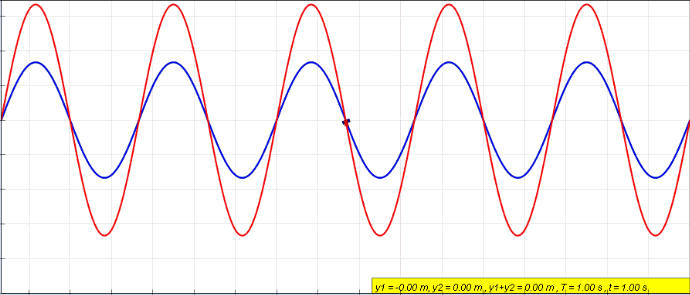
Clapotic
In hydrodynamics, a clapotis (from French for "lapping of water") is a non-breaking standing wave pattern, caused for example, by the reflection of a traveling surface wave train from a near vertical shoreline like a breakwater, seawall or steep cliff. The resulting ''clapotic'' wave does not travel horizontally, but has a fixed pattern of nodes and antinodes. These waves promote erosion at the toe of the wall, and can cause severe damage to shore structures. The term was coined in 1877 by French mathematician and physicist Joseph Valentin Boussinesq who called these waves 'le clapotis' meaning "the lapping". In the idealized case of "full clapotis" where a purely monotonic incoming wave is completely reflected normal to a solid vertical wall, the standing wave height is twice the height of the incoming waves at a distance of one half wavelength from the wall. In this case, the circular orbits of the water particles in the deep-water wave are converted to purely linear motion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
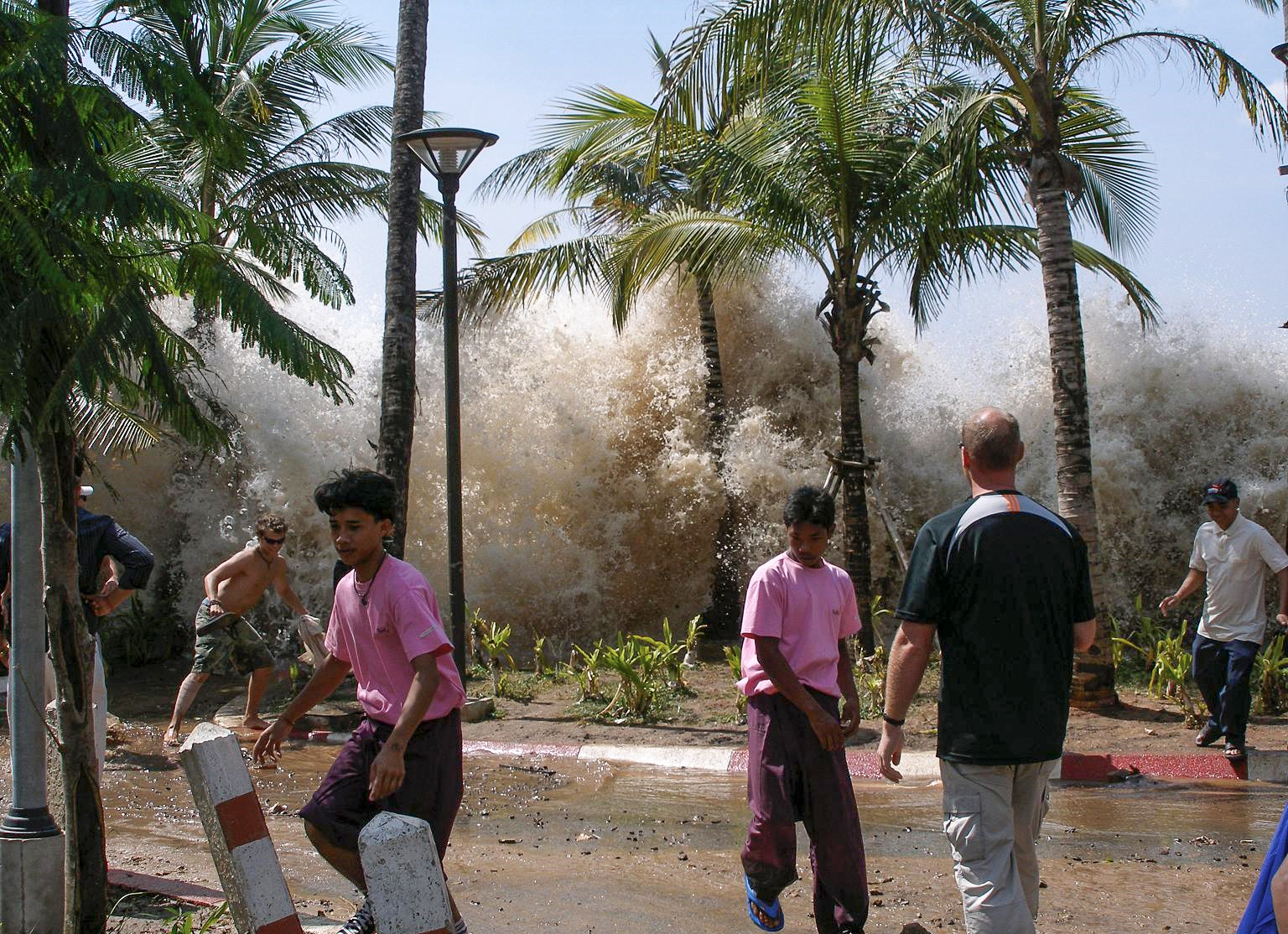
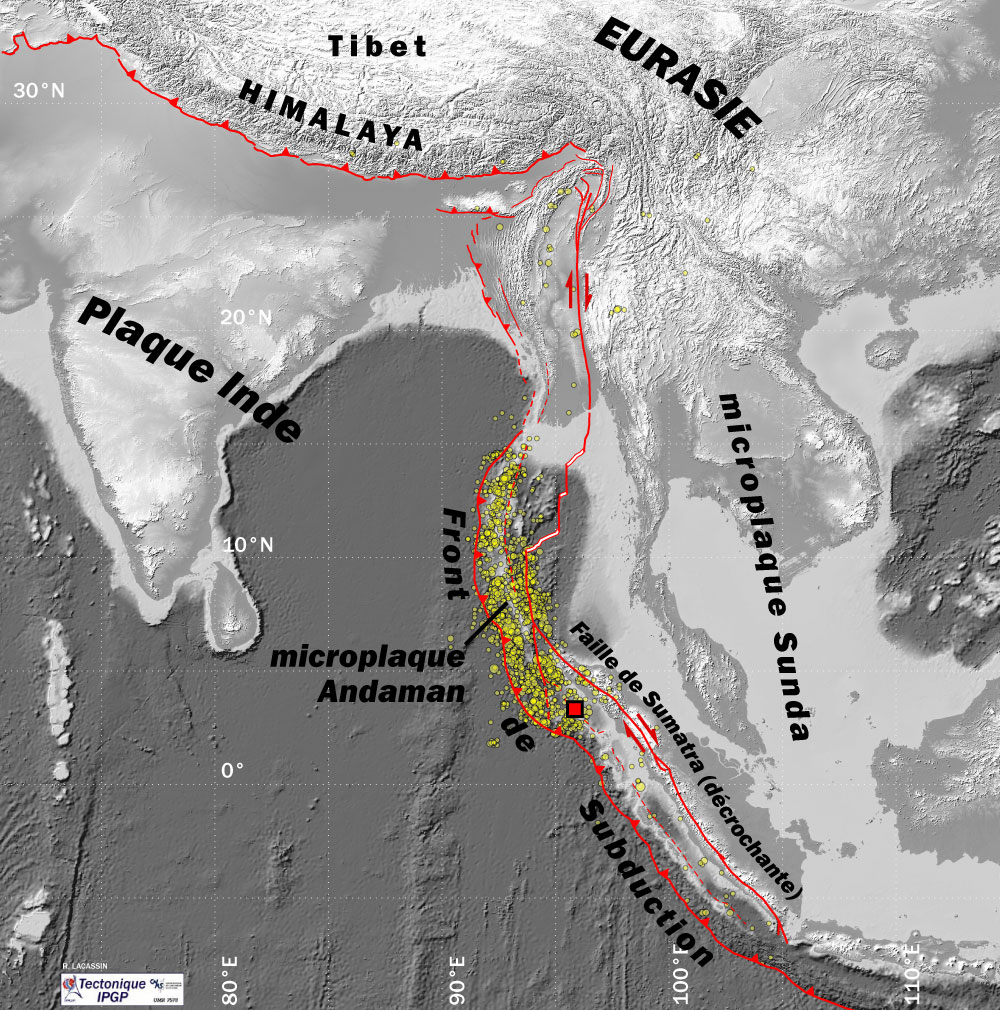
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapling
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are some three trillion mature trees in the world. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a nut. The name comes from the old Portuguese word '' coco'', meaning "head" or "skull", after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. They are ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics. The coconut tree provides food, fuel, cosmetics, folk medicine and building materials, among many other uses. The inner flesh of the mature seed, as well as the coconut milk extracted from it, form a regular part of the diets of many people in the tropics and subtropics. Coconuts are distinct from other fruits because their endosperm contains a large quantity of clear liquid, called ''coconut water'' or ''coconut juice''. Mature, ripe coconut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casuarina
''Casuarina'' is a genus of 17 tree species in the family Casuarinaceae, native to Australia, the Indian subcontinent, southeast Asia, islands of the western Pacific Ocean, and eastern Africa. It was once treated as the sole genus in the family, but has since been split into four genera (see: Casuarinaceae).Flora of Australia''Casuarina''/ref> They are evergreen shrubs and trees growing to tall. The slender, green to grey-green twigs bearing minute scale-leaves in whorls of 5–20. The apetalous flowers are produced in small catkin-like inflorescences. Most species are dioecious, but a few are monoecious. The fruit is a woody, oval structure superficially resembling a conifer cone, made up of numerous carpels, each containing a single seed with a small wing. The generic name is derived from the Malay word for the cassowary, ''kasuari'', alluding to the similarities between the bird's feathers and the plant's foliage, though the tree is called ''ru'' in Modern Malay. Kare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunami Barrier
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |