|
Schizothymia
Schizothymia is a temperament related to schizophrenia in a way analogous to cyclothymia's relationship with bipolar disorder. Schizothymia was proposed by Ernst Kretschmer when examining body types of schizophrenic patients. Schizothymia is defined by reduced affect display, a high degree of introversion, limited social cognition, and withdrawing from social relations generally. Nevertheless, individuals with such personality traits may achieve relatively affable social relations and a measure of affectivity situationally. As a kind of temperament, schizothymic personality traits are thought to be innate rather than the result of socialization or a lack thereof ( Nature versus Nurture). See also * Psychoticism * Schizoid personality disorder * Schizotypal personality disorder * Schizotypy In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Kretschmer
Ernst Kretschmer (8 October 18888 February 1964) was a German psychiatrist who researched the human constitution and established a typology. Life Kretschmer was born in Wüstenrot near Heilbronn. He attended Cannstatt Gymnasium, one of the oldest Latin schools in Stuttgart area. From 1906 to 1912 he studied theology, medicine, and philosophy at the universities of Tübingen, Munich and Hamburg. From 1913 he was assistant of Robert Gaupp in Tübingen, where he received his habilitation in 1918. He continued as assistant medical director until 1926. In 1926 he became the director of the psychiatric clinic at Marburg University. Kretschmer was a founding member of the International General Medical Society for Psychotherapy (AÄGP) which was founded on January 12, 1927. He was the president of AÄGP from 1929. In 1933 he resigned from the AÄGP for political reasons. After he resigned from the AÄGP, he started to support the SS and signed the "Vow of allegiance of the profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizoid Personality Disorder
Schizoid personality disorder (, often abbreviated as SzPD or ScPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a Asociality, lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency toward a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, detachment and apathy. Affected individuals may be unable to form intimate attachments to others and simultaneously possess a rich and elaborate but exclusively internal fantasy (psychology), fantasy world. Other associated features include stilted speech, a Anhedonia, lack of deriving enjoyment from most activities, feeling as though one is an "observer" rather than a participant in life, an inability to tolerate emotional expectations of others, apparent indifference when praised or criticized, a degree of asexuality and idiosyncratic moral or political beliefs. Symptoms typically start in late childhood or adolescence. The cause of SzPD is uncertain, but there is some evidence of links and shared genetic risk between SzPD, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperament
In psychology, temperament broadly refers to consistent individual differences in behavior that are biologically based and are relatively independent of learning, system of values and attitudes. Some researchers point to association of temperament with formal dynamical features of behavior, such as energetic aspects, plasticity, sensitivity to specific reinforcers and emotionality. Temperament traits (such as Neuroticism, Sociability, Impulsivity, etc.) are distinct patterns in behavior throughout a lifetime, but they are most noticeable and most studied in children. Babies are typically described by temperament, but longitudinal research in the 1920s began to establish temperament as something which is stable across the lifespan. Definition Temperament has been defined as "the constellation of inborn traits that determine a child's unique behavioral style and the way he or she experiences and reacts to the world." Classification schemes Many classification schemes for tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
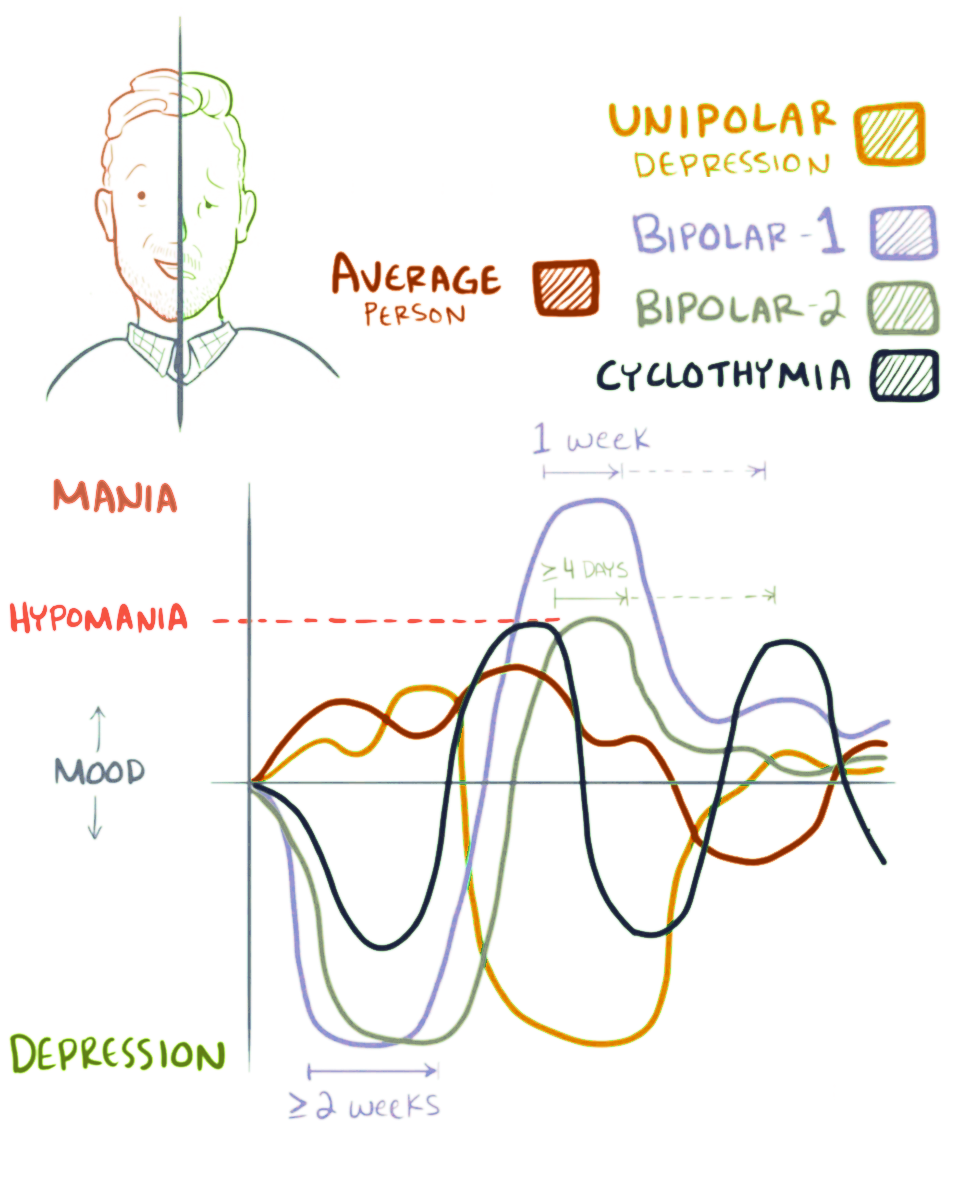
Cyclothymia
Cyclothymia ( ), also known as cyclothymic disorder, psychothemia/psychothymia, bipolar III, affective personality disorder and cyclothymic personality disorder, is a mental and behavioural disorder that involves numerous periods of symptoms of depression and periods of symptoms of elevated mood. These symptoms, however, are not sufficient to indicate a major depressive episode or a manic episode. Symptoms must last for more than one year in children and two years in adults. The cause of cyclothymia is unknown. Risk factors include a family history of bipolar disorder. Cyclothymia differs from bipolar in that major depression and mania are not found. Treatment is generally achieved with counseling and mood stabilizers such as lithium. It is estimated that 0.41% of people have cyclothymia at some point in their life. The disorder's onset typically occurs in late childhood to early adulthood. Males and females are affected equally often. Symptoms People with cyclothymia expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Affect Display
Reduced affect display, sometimes referred to as emotional blunting or emotional numbing, is a condition of reduced emotional reactivity in an individual. It manifests as a failure to express feelings ( affect display) either verbally or nonverbally, especially when talking about issues that would normally be expected to engage the emotions. Expressive gestures are rare and there is little animation in facial expression or vocal inflection. Reduced affect can be symptomatic of autism, schizophrenia, depression, posttraumatic stress disorder, depersonalization disorder, schizoid personality disorder or brain damage. It may also be a side effect of certain medications (e.g., antipsychotics and antidepressants). Reduced affect should be distinguished from apathy and anhedonia, which explicitly refer to a lack of emotion, whereas reduced affect is a lack of emotional expression (affect display) regardless of whether emotion (underlying affect) is actually reduced or not. Types Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affable
{{disambig ...
Affable may refer to: * Charles VIII of France, "the Affable" (1470–1498) * Affable Records See also * ''Affable savages'', a book by Francis Huxley Francis Huxley (28 August 1923 – 29 October 2016) was a British botanist, anthropologist and author. He is a son of Julian Huxley. His brother was Anthony Julian Huxley. His uncle was Aldous Huxley. He was one of the founders of Survival Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Versus Nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the balance between two competing factors which determine fate: genetics (nature) and environment (nurture). The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English has been in use since at least the Elizabethan period and goes back to medieval French. The complementary combination of the two concepts is an ancient concept ( grc, ἁπό φύσεως καὶ εὐτροφίας). Nature is what people think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors. Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception e.g. the product of exposure, experience and learning on an individual. The phrase in its modern sense was popularized by the Victorian polymath Francis Galton, the modern founder of eugenics and behavioral genetics when he was discussing the influence of heredity and environment on social advancement. Galton was influenced by ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoticism
Psychoticism is one of the three traits used by the psychologist Hans Eysenck in his P–E–N model (psychoticism, extraversion and neuroticism) model of personality. Nature Psychoticism is conceptually similar to the ''constraint'' factor in Tellegen's three-factor model of personality. Psychoticism may be divided into narrower traits such as impulsivity and sensation-seeking. These may in turn be further subdivided into even more specific traits. For example, impulsivity may be divided into narrow impulsivity (unthinking responsivity), risk taking, non-planning, and liveliness. Sensation seeking has also been analysed into a number of separate facets. Eysenck argued that there might be a correlation between psychoticism and creativity.Eysenck, Hans J. (1993). Creativity and Personality: Suggestions for a Theory. ''Psychological Inquiry''. 4(3), 147–178. Critics Critics of the trait have suggested that the trait is too heterogeneous to be taken as a single trait. Costa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder (STPD or SPD), also known as schizotypal disorder, is a mental and behavioral disorder. DSM classification describes the disorder specifically as a personality disorder characterized by thought disorder, paranoia, a characteristic form of social anxiety, derealization, transient psychosis, and unconventional beliefs. People with this disorder feel pronounced discomfort in forming and maintaining social connections with other people, primarily due to the belief that other people harbor negative thoughts and views about them. Peculiar speech mannerisms and socially unexpected modes of dress are also characteristic. Schizotypal people may react oddly in conversations, not respond, or talk to themselves. They frequently interpret situations as being strange or having unusual meaning for them; paranormal and superstitious beliefs are common. Schizotypal people usually disagree with the suggestion their thoughts and behaviors are a 'disorder', and see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizotypy
In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme states of mind related to psychosis, especially schizophrenia. The continuum of personality proposed in schizotypy is in contrast to a categorical view of psychosis, wherein psychosis is considered a particular (usually pathological) state of mind, which the person either has or does not have. Development of the concept The categorical view of psychosis is most associated with Emil Kraepelin, who created criteria for the medical diagnosis and classification of different forms of psychotic illness. Particularly, he made the distinction between dementia praecox (now called schizophrenia), manic depressive insanity and non-psychotic states. Modern diagnostic systems used in psychiatry (such as the DSM) maintain this categorical view. In contrast, psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler did not believe there was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)