|
Saphenous Opening
In anatomy, the saphenous opening (saphenous hiatus, also fossa ovalis) is an oval opening in the upper mid part of the fascia lata of the thigh. It lies 3–4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle and is about 3 cm long and 1.5 cm wide. Structure Just inferolateral to the pubic tubercle the fascia extends downwards forming an arched (falciform) margin of the lateral boundary of the opening. It is covered by a thin perforated part of the superficial fascia called the fascia cribrosa which is pierced by the great saphenous vein, the 3 superficial branches of the femoral artery(except superficial circumflex iliac artery, which pierces fascia lata lateral to the saphenous opening), and lymphatics. It transmits the great saphenous vein and other smaller vessels including the superficial epigastric artery and superficial external pudendal artery, as well as the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve. The fascia cribrosa, which is pierced by the structures pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia Lata
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment. Structure The fascia lata is an investment for the whole of the thigh, but varies in thickness in different parts. It is thicker in the upper and lateral part of the thigh, where it receives a fibrous expansion from the gluteus maximus, and where the tensor fasciae latae is inserted between its layers; it is very thin behind and at the upper and medial part, where it covers the adductor muscles, and again becomes stronger around the knee, receiving fibrous expansions from the tendon of the biceps femoris laterally, from the sartorius medially, and from the quadriceps femoris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Tubercle
The pubic tubercle is a prominent tubercle on the superior ramus of the pubis bone of the pelvis. Structure The pubic tubercle is a prominent forward-projecting tubercle on the upper border of the medial portion of the superior ramus of the pubis bone. The inguinal ligament attaches to it. Part of the abdominal external oblique muscle inserts onto it. The inferior epigastric artery passes between the pubic tubercle and the anterior superior iliac spine. The pubic spine is a rough ridge that extends from the pubic tubercle to the upper border of the pubic symphysis. Clinical significance The pubic tubercle may be palpated. It serves as a landmark for local anaesthetic of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, which lies slightly lateral to the pubic tubercle. This may also be used for the obturator nerve The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia Cribrosa
The cribriform fascia, fascia cribrosa also Hesselbach's fascia is the portion of fascia covering the saphenous opening in the thigh. It is perforated by the great saphenous vein and by numerous blood and lymphatic vessels. (A structure in anatomy that is pierced by several small holes is referred to as ''cribriform'' from Latin ''cribrum'' meaning sieve). Clinical significance The cribriform fascia has been proposed for use in preventing new vascularization when surgery is performed at the join between the great saphenous vein and the femoral vein. Eponym When the eponym is used, it is named for Franz Kaspar Hesselbach Franz Kaspar Hesselbach (27 January 1759 – 24 July 1816) was a German surgeon and anatomist who was a native of Hammelburg. He was a pupil, and later Prosector under Carl Caspar von Siebold (1736–1807) at Würzburg. Later Hesselbach was a lec ....F. K. Hesselbach. Anatomisch-chirurgische Abhandlung über den Urspurng der Leistenbrüche. Würzburg, Baumgär ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Saphenous Vein
The great saphenous vein (GSV, alternately "long saphenous vein"; ) is a large, subcutaneous, superficial vein of the leg. It is the longest vein in the body, running along the length of the lower limb, returning blood from the foot, leg and thigh to the deep femoral vein at the femoral triangle. Structure The great saphenous vein originates from where the dorsal vein of the big toe (the hallux) merges with the dorsal venous arch of the foot. After passing in front of the medial malleolus (where it often can be visualized and palpated), it runs up the medial side of the leg. At the knee, it runs over the posterior border of the medial epicondyle of the femur bone. In the proximal anterior thigh inferolateral to the pubic tubercle, the great saphenous vein dives down deep through the cribriform fascia of the saphenous opening to join the femoral vein. It forms an arch, the saphenous arch, to join the common femoral vein in the region of the femoral triangle at the sapheno-femoral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. Structure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery. Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point). Segments In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments: *The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery
The superficial iliac circumflex artery (or superficial circumflex iliac), the smallest of the cutaneous branches of the femoral artery, arises close to the superficial epigastric artery, and, piercing the fascia lata, runs lateralward, parallel with the inguinal ligament, as far as the crest of the ilium. It divides into branches which supply the integument of the groin, the superficial fascia, and the superficial subinguinal lymph glands, anastomosing with the deep iliac circumflex, the superior gluteal and lateral femoral circumflex The lateral circumflex femoral artery, also known as the lateral femoral circumflex artery, or the external circumflex artery, is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It ... arteries. In 45% to 50% of persons the superficial circumflex iliac artery and superficial inferior epigastric artery arise from a common trunk. In contrast, 40% to 45% of persons have a superficial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
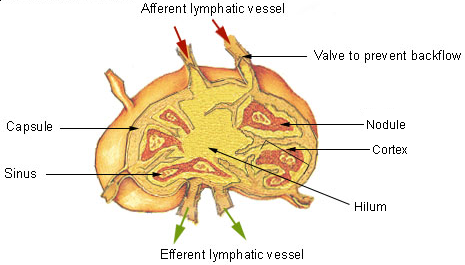
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Epigastric Artery
The superficial epigastric artery (not to be confused with the superior epigastric artery) arises from the front of the femoral artery about 1 cm below the inguinal ligament, and, passing through the femoral sheath and the fascia cribrosa, turns upward in front of the inguinal ligament, and ascends between the two layers of the superficial fascia of the abdominal wall nearly as far as the umbilicus. It distributes branches to the superficial subinguinal lymph glands, the superficial fascia, and the integument; it anastomoses with branches of the inferior epigastric Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton *Inferior (book), ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The ..., and with its fellow of the opposite side. Additional images File:Gray393.png, The subcutaneous inguinal ring File:Gray550.png, The femoral artery File:Gray58 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial External Pudendal Artery
The superficial external pudendal artery (superficial external pudic artery) is one of the three pudendal arteries. It arises from the medial side of the femoral artery, close to the superficial epigastric artery and superficial iliac circumflex artery. Course and target After piercing the femoral sheath and fascia cribrosa, it courses medialward, across the spermatic cord (or round ligament in the female), to be distributed to the integument on the lower part of the abdomen, the penis and scrotum in the male, and the labium majus in the female, anastomosing with branches of the internal pudendal artery. It crosses superficial to the inguinal ligament. See also * Deep external pudendal artery * Internal pudendal artery The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of ... Addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitofemoral Nerve
The genitofemoral nerve refers to a nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. The femoral branch is different from the femoral nerve, which also arises from the lumbar plexus. Anatomy The genitofemoral nerve originates from the upper L1-2 segments of the lumbar plexus. It passes downwards, pierces the psoas major and emerges from its anterior surface. The nerve divides into two branches, the genital branch and the lumboinguinal nerve also known as the femoral branch, both of which then continue downwards and medially to the inguinal and femoral canal respectively. Genital Branch The genital branch continues downward on the surface of the psoas major muscle and then enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring. In men, the genital branch supplies the cremaster and scrotal skin. In women, the genit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of all hernias. While femoral hernias can occur in both males and females, almost all develop in women due to the increased width of the female pelvis. Femoral hernias are more common in adults than in children. Those that do occur in children are more likely to be associated with a connective tissue disorder or with conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure. Seventy percent of pediatric cases of femoral hernias occur in infants under the age of one. Definitions A hernia is caused by the protrusion of a viscus (in the case of groin hernias, an intra-abdominal organ) through a weakness in the abdominal wall. This weakness may be inherent, as in the case of inguinal, femoral and umbilical hernias. On the other hand, the weakness ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |