|
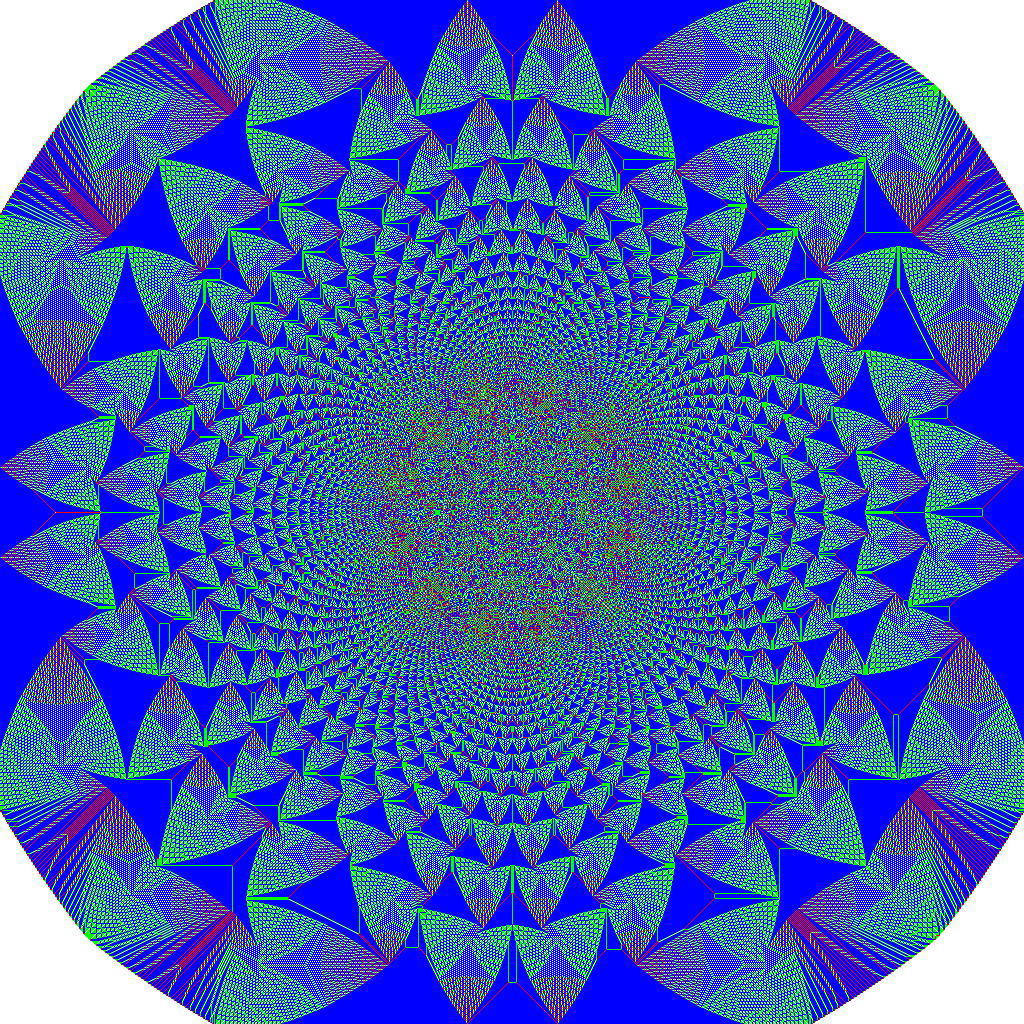
Sandpile
The Abelian sandpile model (ASM) is the more popular name of the original Bak–Tang–Wiesenfeld model (BTW). BTW model was the first discovered example of a dynamical system displaying self-organized criticality. It was introduced by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld in a 1987 paper. Three years later Deepak Dhar discovered that the BTW sandpile model indeed follows the abelian dynamics and therefore referred to this model as the Abelian sandpile model. The model is a cellular automaton. In its original formulation, each site on a finite grid has an associated value that corresponds to the slope of the pile. This slope builds up as "grains of sand" (or "chips") are randomly placed onto the pile, until the slope exceeds a specific threshold value at which time that site collapses transferring sand into the adjacent sites, increasing their slope. Bak, Tang, and Wiesenfeld considered process of successive random placement of sand grains on the grid; each such placem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandpile Identity 300x205
The Abelian sandpile model (ASM) is the more popular name of the original Bak–Tang–Wiesenfeld model (BTW). BTW model was the first discovered example of a dynamical system displaying self-organized criticality. It was introduced by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld in a 1987 paper. Three years later Deepak Dhar discovered that the BTW sandpile model indeed follows the abelian dynamics and therefore referred to this model as the Abelian sandpile model. The model is a cellular automaton. In its original formulation, each site on a finite grid has an associated value that corresponds to the slope of the pile. This slope builds up as "grains of sand" (or "chips") are randomly placed onto the pile, until the slope exceeds a specific threshold value at which time that site collapses transferring sand into the adjacent sites, increasing their slope. Bak, Tang, and Wiesenfeld considered process of successive random placement of sand grains on the grid; each such placemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip-firing Game
The chip-firing game is a one-player game on a graph which was invented around 1983 and since has become an important part of the study of structural combinatorics. Each vertex has the number of "chips" indicated by its state variable. On each firing, a vertex is selected and one of its chips is transferred to each neighbour (vertex it shares an edge with). The number of chips on each vertex cannot be negative. The game ends when no firing is possible. Definition Let the finite graph ''G'' be connected and loopless, with vertices ''V'' = . Let deg(''v'') be the degree of a vertex, and e(''v,w'') the number of edges between vertices ''v'' and ''w''. A configuration or state of the game is defined by assigning each vertex a nonnegative integer ''s''(''v''), representing the number of chips on this vertex. A move starts with selecting a vertex ''w'' which has at least as many chips as its degree: ''s''(''w'') ≥ deg(''w''). The vertex ''w'' is fired, moving one chip from w al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organized Criticality
Self-organized criticality (SOC) is a property of dynamical systems that have a critical point as an attractor. Their macroscopic behavior thus displays the spatial or temporal scale-invariance characteristic of the critical point of a phase transition, but without the need to tune control parameters to a precise value, because the system, effectively, tunes itself as it evolves towards criticality. The concept was put forward by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld ("BTW") in a paper Papercore summaryhttp://papercore.org/Bak1987 published in 1987 in ''Physical Review Letters'', and is considered to be one of the mechanisms by which complexity arises in nature. Its concepts have been applied across fields as diverse as geophysics, physical cosmology, evolutionary biology and ecology, bio-inspired computing and optimization (mathematics), economics, quantum gravity, sociology, solar physics, plasma physics, neurobiology and others. SOC is typically observed in slowly dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip-firing Game
The chip-firing game is a one-player game on a graph which was invented around 1983 and since has become an important part of the study of structural combinatorics. Each vertex has the number of "chips" indicated by its state variable. On each firing, a vertex is selected and one of its chips is transferred to each neighbour (vertex it shares an edge with). The number of chips on each vertex cannot be negative. The game ends when no firing is possible. Definition Let the finite graph ''G'' be connected and loopless, with vertices ''V'' = . Let deg(''v'') be the degree of a vertex, and e(''v,w'') the number of edges between vertices ''v'' and ''w''. A configuration or state of the game is defined by assigning each vertex a nonnegative integer ''s''(''v''), representing the number of chips on this vertex. A move starts with selecting a vertex ''w'' which has at least as many chips as its degree: ''s''(''w'') ≥ deg(''w''). The vertex ''w'' is fired, moving one chip from w al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deepak Dhar
Deepak Dhar (born 30 October 1951) is an Indian theoretical physicist and a distinguished professor at the department of physics of Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune. He is widely respected for his research on statistical physics and stochastic processes. In 2022, he became the first ever Indian scientist to be chosen for the Boltzmann Medal, the highest recognition in statistical physics awarded once every three years by IUPAP, for exceptional contributions to the subject. Dhar is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies – Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and National Academy of Sciences, India – as well as of The World Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded Dhar the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chao Tang
Tang Chao (; born 1958) is a Chair Professor of Physics and Systems Biology at Peking University. Education He had his undergraduate training at the University of Science and Technology of China, then went to the United States through the CUSPEA program organized by Professor T. D. Lee. He received a Ph.D. degree in Physics from the University of Chicago. Career In his early career, he worked on problems in statistical physics, dynamical system and complex systems. In 1987, along with Per Bak and Kurt Wiesenfeld, he proposed the concept and developed the theory for self-organized criticality, which had and continues to have broad applications in complex systems with scale invariance. The model they used to illustrate the idea is referred to as the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld "sandpile" model. His current research interest is at the interface between physics and biology. Specifically, he focuses on systems biology and works on problems such as protein folding, cell cycle regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Per Bak
Per Bak (8 December 1948 – 16 October 2002) was a Danish theoretical physicist who coauthored the 1987 academic paper that coined the term "self-organized criticality." Life and work After receiving his Ph.D. from the Technical University of Denmark in 1974, Bak worked at Brookhaven National Laboratory. He specialized in phase transitions, such as those occurring when an insulator suddenly becomes a conductor or when water freezes. In that context, he also did important work on complicated spatially modulated (magnetic) structures in solids. This research led him to the more general question of how organization emerges from disorder. In 1987, he and two postdoctoral researchers, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld, published an article in ''Physical Review Letters'' setting a new concept they called self-organized criticality. The first discovered example of a dynamical system displaying such self-organized criticality, the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld sandpile model, was named after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Wiesenfeld
Kurt Wiesenfeld is an American physicist working primarily on non-linear dynamics. His works primarily concern stochastic resonance, spontaneous synchronization of coupled oscillators, and non-linear laser dynamics. Since 1987, he has been professor of physics at the Georgia Institute of Technology. Life and work Kurt Wiesenfeld received his Bachelor of Science in Physics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1979, after which he moved to University of California, Berkeley and received his doctorate in 1985. From 1984 to 1985 he was a Lecturer and Research Scientist at the University of California at Santa Cruz. In 1987, as a post-doctoral research scientist in the Solid State Theory Group of Brookhaven National Laboratory, he and another fellow post-doctoral scientist, Chao Tang, along with their mentor, Per Bak, presented new ideas in group organization with a concept they coined self-organized criticality in their paper in ''Physical Review Letters.'' The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1/f Noise
Pink noise or noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density (power per frequency interval) is inversely proportional to the frequency of the signal. In pink noise, each octave interval (halving or doubling in frequency) carries an equal amount of noise energy. Pink noise sounds like a waterfall. It is often used to tune loudspeaker systems in professional audio. Pink noise is one of the most commonly observed signals in biological systems. The name arises from the pink appearance of visible light with this power spectrum. This is in contrast with white noise which has equal intensity per frequency interval. Definition Within the scientific literature, the term 1/f noise is sometimes used loosely to refer to any noise with a power spectral density of the form S(f) \propto \frac, where ''f'' is frequency, and 0 < α < 2, with exponent α usually close to 1. One-dimensional signals with α = 1 are usually called pink noise. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commutative. With addition as an operation, the integers and the real numbers form abelian groups, and the concept of an abelian group may be viewed as a generalization of these examples. Abelian groups are named after early 19th century mathematician Niels Henrik Abel. The concept of an abelian group underlies many fundamental algebraic structures, such as fields, rings, vector spaces, and algebras. The theory of abelian groups is generally simpler than that of their non-abelian counterparts, and finite abelian groups are very well understood and fully classified. Definition An abelian group is a set A, together with an operation \cdot that combines any two elements a and b of A to form another element of A, denoted a \cdot b. The symbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation
Perturbation or perturb may refer to: * Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly * Perturbation (geology), changes in the nature of alluvial deposits over time * Perturbation (astronomy), alterations to an object's orbit (e.g., caused by gravitational interactions with other bodies) * Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one * Perturbation (biology), an alteration of the function of a biological system, induced by external or internal mechanisms * Perturbation function, mathematical function which relates the primal and dual problems See also * Annoy, annoyance * Disturbance (other) * Non-perturbative In mathematics and physics, a non-perturbative function or process is one that cannot be described by perturbation theory. An example is the function : f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformal Field Theory
A conformal field theory (CFT) is a quantum field theory that is invariant under conformal transformations. In two dimensions, there is an infinite-dimensional algebra of local conformal transformations, and conformal field theories can sometimes be exactly solved or classified. Conformal field theory has important applications to condensed matter physics, statistical mechanics, quantum statistical mechanics, and string theory. Statistical and condensed matter systems are indeed often conformally invariant at their thermodynamic or quantum critical points. Scale invariance vs conformal invariance In quantum field theory, scale invariance is a common and natural symmetry, because any fixed point of the renormalization group is by definition scale invariant. Conformal symmetry is stronger than scale invariance, and one needs additional assumptions to argue that it should appear in nature. The basic idea behind its plausibility is that ''local'' scale invariant theories have their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |