|
Systemd
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. The main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions. Its primary component is a "system and service manager" — an init system used to Bootstrapping, bootstrap user space and manage process (computing), user processes. It also provides replacements for various Daemon (computing), daemons and utilities, including device management, login management, network connection management, and event logging. The name ''systemd'' adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter ''d''. It also plays on the term "System D", which refers to a person's ability to adapt quickly and improvise to solve problems. Since 2015, the majority of Linux distributions have adopted systemd, having replaced other init systems such as SysV init. It has been praised by developers and users of distributions that adopted it for providing a stable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lennart Poettering
Lennart Poettering (born 15 October 1980) is a German software engineer working for Microsoft and the original author of PulseAudio, Avahi and systemd. Life and career Poettering was born in Guatemala City but grew up in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and Hamburg, Germany. Poettering worked for Red Hat from 2008 to 2022. He then joined Microsoft. Since 2003, Poettering has worked on more than 40 projects, mostly written in C. He is the developer and maintainer of several free software projects which have been widely adopted by Linux distributions, including PulseAudio sound server (2004), Avahi zeroconf implementation (2005), and systemd init system (2010). Controversies Poettering is known for having controversial technical and architectural positions regarding the Linux ecosystem. His style has brought accusations that he is working against long-standing Unix philosophy, which he addressed in his blog post ''The Biggest Myths.'' For instance, Poettering has advocated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SysV Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until the early 2010s, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and other distributions such as Gentoo have their own customized versions. Sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Service Manager
In computing, a daemon is a program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user. Customary convention is to name a daemon process with the letter ''d'' as a suffix to indicate that it's a daemon. For example, is a daemon that implements system logging facility, and is a daemon that serves incoming SSH connections. Even though the concept can apply to many computing systems, the term ''daemon'' is used almost exclusively in the context of Unix-based systems. In other contexts, different terms are used for the same concept. Systems often start daemons at boot time that will respond to network requests, hardware activity, or other programs by performing some task. Daemons such as cron may also perform defined tasks at scheduled times. Terminology In the context of computing, the word is generally pronounced either as or . The term was coined by the programmers at MIT's Project MAC. According to Fernando J. Corbató ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Daemon (computing)
In computing, a daemon is a program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user. Customary convention is to name a daemon process with the letter ''d'' as a suffix to indicate that it's a daemon. For example, is a daemon that implements system logging facility, and is a daemon that serves incoming SSH connections. Even though the concept can apply to many computing systems, the term ''daemon'' is used almost exclusively in the context of Unix-based systems. In other contexts, different terms are used for the same concept. Systems often start daemons at boot time that will respond to network requests, hardware activity, or other programs by performing some task. Daemons such as cron may also perform defined tasks at scheduled times. Terminology In the context of computing, the word is generally pronounced either as or . The term was coined by the programmers at MIT's Project MAC. According to Fernando J. Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until the early 2010s, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and other distributions such as Gentoo have their own customized versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kay Sievers
Kay Sievers is a German computer programmer, best known for developing the udev device manager of Linux, systemd and the Gummiboot EFI bootloader. Kay Sievers made major contributions to Linux's hardware hotplug and device management subsystems. In 2012, together with Harald Hoyer, Sievers was the main driving force behind Fedora's merging of the /lib, /bin and /sbin file-system trees into /usr, a simplification which other distributions such as Arch Linux have since adopted. In April 2014, Linus Torvalds banned Sievers from submitting patches to the Linux kernel for failing to deal with bugs that caused systemd to negatively interact with the kernel. Kay Sievers worked for Red Hat, Inc. until 2019, Sievers previously worked for Novell. Kay Sievers grew up in East Germany and nowadays resides in Berlin Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
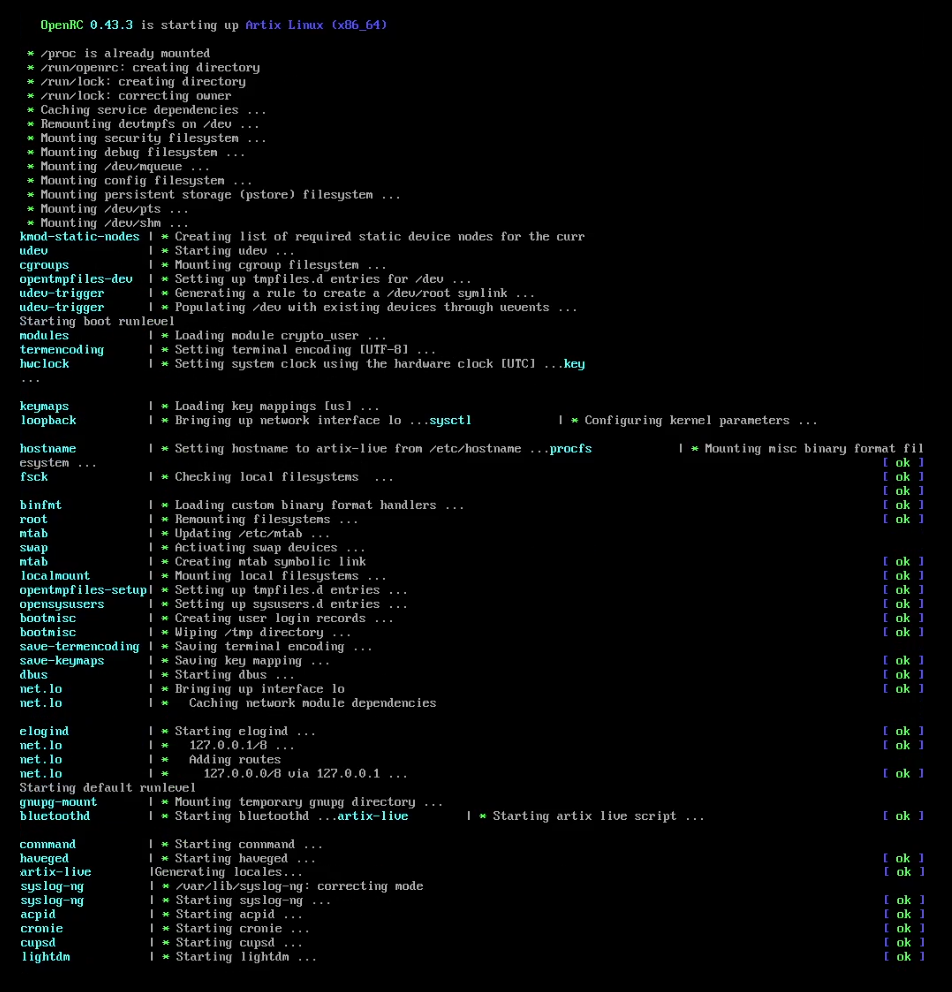
OpenRC
OpenRC is a dependency-based init system for Unix-like computer operating systems. It was created by Roy Marples, a NetBSD developer who was also active in the Gentoo Linux, Gentoo project. It became more broadly adopted as an init system outside of Gentoo following the decision by some Linux distributions not to adopt systemd. Adoption OpenRC is the default init system or Process supervision, process supervisor for: * Alpine Linux * Funtoo * Gentoo Linux * Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre * Maemo#Maemo Leste, Maemo Leste * Nitrux OpenRC is an available init system or Process supervision, process supervisor for: * Artix Linux (some consider it the default) * Devuan * Parabola GNU/Linux-libre * Arch Linux (Available through the Arch User Repository) * PostmarketOS Design OpenRC is made up of several modular components, the main ones being an init (optional), the core dependency management system and a daemon supervisor (optional). It is written in C and POSIX-compliant shell, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide. Red Hat has become associated to a large extent with its enterprise operating system Red Hat Enterprise Linux. With the acquisition of open-source enterprise middleware vendor JBoss, Red Hat also offers Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), an enterprise virtualization product. Red Hat provides storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, support, training, and consulting services. Red Hat creates, maintains, and contributes to many free software projects. It has acquired the codebases of several proprietary software products through corporate mergers and acquisitions, and has released such software under open source licenses. , Red Hat is the second largest co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harald Hoyer
Harald Hoyer is a computer programmer and photographer, best known for developing the dracut initramfs generator and framework, the udev device manager of Linux, the systemd replacement for the System V init daemon and the Gummiboot EFI boot loader. Harald Hoyer also made various contributions to the Linux Kernel, starting 1997. In 2012, together with Kay Sievers, Hoyer was the main driving force behind merging the , and file system trees into in the Fedora distribution He is employed by Matter Labs Harald Hoyer resides in Vaterstetten Vaterstetten is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality in the Upper Bavarian district of Ebersberg (district), Ebersberg. It lies east of Munich and is the district's biggest community. Vaterstetten is on the outskirts of Munich, roughly twent ..., Germany. References Free software programmers Living people 1971 births Red Hat employees {{compu-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
System D
System D is a manner of responding to challenges that require one to have the ability to think quickly, to adapt, and to improvise when getting a job done. The term is a direct translation of French . The letter ''D'' refers to any one of the French nouns , or (French slang). The verbs and mean to ''make do'', to ''manage'', especially in an adverse situation. Basically, it refers to one's ability and need to be resourceful. In ''Down and Out in Paris and London'', George Orwell described the term as something the lowest-level kitchen workers, the , wanted to be called, indicating that they were people who would get the job done, no matter what. The term System D gained wider popularity in the United States after appearing in the 2006 publication of Anthony Bourdain's '' The Nasty Bits''. Bourdain references finding the term in Nicolas Freeling's memoir, ''The Kitchen'', about Freeling's years as a Grand Hotel cook in France. In recent literature on the informal economy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linux Distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and libraries, documentation, IP network configuration utilities, the getty TTY setup program, and many more. To provide a desktop experience (most commonly the Mesa userspace graphics drivers) a display server (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |