|
Syntelic
Syntelic attachment occurs when both sister chromosomes are attached to a single spindle pole. Normal cell division distributes the genome equally between two daughter cells, with each chromosome attaching to an ovoid structure called the spindle. During the division process, errors commonly occur in attaching the chromosomes to the spindle, estimated to affect 86 to 90 percent of chromosomes. Such attachment errors are common during the early stages of spindle formation, but they are mostly corrected before the start of anaphase. Successful cell division requires identification and correction of any dangerous errors before the cell splits in two. If the syntelic attachment continues, it causes both sister chromatids to be segregated to a single daughter cell. Causes Microtubules extend from the spindle poles and attach to the first kinetochore they encounter. Because this process is stochastic and not facilitated or directed, the first microtubules to come into contact with a ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a disc-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis. The term kinetochore was first used in a footnote in a 1934 Cytology book by Lester W. Sharp and commonly accepted in 1936. Sharp's footnote reads: "The convenient term ''kinetochore'' (= movement place) has been suggested to the author by J. A. Moore", likely referring to John Alexander Moore who had joined Columbia University as a freshman in 1932. Monocentric organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles a single, localized kinetochore. Holocentric organisms, such as nematodes and some plants, assemble a kinetochore along the entire length of a chromosome. Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetochore
A kinetochore (, ) is a disc-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis. The term kinetochore was first used in a footnote in a 1934 Cytology book by Lester W. Sharp and commonly accepted in 1936. Sharp's footnote reads: "The convenient term ''kinetochore'' (= movement place) has been suggested to the author by J. A. Moore", likely referring to John Alexander Moore who had joined Columbia University as a freshman in 1932. Monocentric organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles a single, localized kinetochore. Holocentric organisms, such as nematodes and some plants, assemble a kinetochore along the entire length of a chromosome. Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
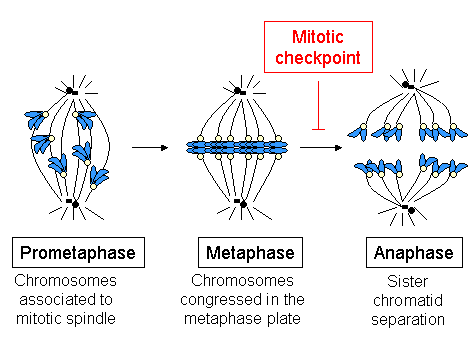
Spindle Checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by M-phase cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together. Overview and importance The beginning of metaphase is characterized by the connection of the microtubules to the kinetochores of the chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Assembly Checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by M-phase cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together. Overview and importance The beginning of metaphase is characterized by the connection of the microtubules to the kinetochores of the chromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite cell pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase Lag
Anaphase lag is a consequence of an event during cell division where sister chromatids do not properly separate from each other because of improper spindle formation. The chromosome or chromatid does not properly migrate during anaphase and the daughter cells will lose some genetic information. It is one of many causes of aneuploidy. This event can occur during both meiosis and mitosis with unique repercussions. In either case, anaphase lag will cause one daughter cell to receive a complete set of chromosomes while the other lacks one paired set of chromosomes, creating a form of monosomy. Whether the cell survives depends on which sister chromatid was lost and the background genomic state of the cell. The passage of abnormal numbers of chromosomes will have unique consequences with regards to mosaicism and development as well as the progression and heterogeneity of cancers. Mechanisms There are two notable mechanisms that cause Anaphase Lag, each of which are characterized by mero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a ''euploid'' cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of some genetic disorders. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells (nondisjunction). Most cases of aneuploidy in the autosomes result in miscarriage, and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18 and 13. Chromosome abnormalities are detected in 1 of 160 live human births. Autosomal aneuploidy is more dangerous than sex chromosome aneuploidy, as autosomal aneuploidy is almost always lethal to embryos that cease develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatase
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid Ester, monoester into a phosphate ion and an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of its Substrate (chemistry), substrate, it is a subcategory of hydrolases. Phosphatase enzymes are essential to many biological functions, because phosphorylation (e.g. by protein kinases) and dephosphorylation (by phosphatases) serve diverse roles in cell growth, cellular regulation and cell signaling, signaling. Whereas phosphatases remove phosphate groups from molecules, kinases catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups to molecules from Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Together, kinases and phosphatases direct a form of post-translational modification that is essential to the cell's regulatory network. Phosphatase enzymes are not to be confused with phosphorylase enzymes, which catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from hydrogen phosphate to an acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |