|
Syncitium
A syncytium (; : syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus), in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The muscle cell that makes up animal skeletal muscle is a classic example of a syncytium cell. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membranes with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential. The field of embryogenesis uses the word ''syncytium'' to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm embryos of invertebrates, such as ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Physiological examples Protists In protists, syncytia can be found in some rhizarians (e.g., chlorarachniophytes, plasmodiophorids, haplosporidians) and ace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodiophorid
The plasmodiophores (also known as plasmophorids or plasmodiophorids) are a group of obligate endoparasitic protists belonging to the subphylum Endomyxa in Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they are united under a single family Plasmodiophoridae, order Plasmodiophorida, sister to the phagomyxids. Ecology and pathology Plasmodiophores are pathogenic for a wide range of organisms, but mainly green plants. The more commonly recognized are agents of plant diseases such as clubroot, powdery scab and crook root of watercress, or vectors for viruses that infect beets, peanut, monocots and potatoes, such as the potato mop-top virus or the beet necrotic yellow vein virus. Taxonomy History The plasmodiophores have historically been regarded as Fungi. The first description of plasmodiophores as a taxonomic group was in 1885 by Zopf, who united two genera '' Plasmodiophora'' and '' Tetramyxa'' in a common family “Plasmodiophoreæ”, inside the group “Monadineæ”, as part of the division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapetum (botany)
The tapetum is a specialised layer of nutritive cells found within the anther of flowering plants, located between the sporogenous tissue and the anther wall. Tapetum is important for the nutrition and development of pollen grains and a source of precursors for the pollen coat.P.L. Polowick, V.K. Sawhney 1993Differentiation of the Tapetum During Microsporogenesis in Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.), with Special Reference to the Tapetal Cell Wall Annals of Botany, Volume 72, Issue 6, December 1993, Pages 595–605 The cells are usually bigger and normally have more than one nucleus per cell. As the sporogenous cells undergo mitosis, the nuclei of tapetal cells also divide. Sometimes, this mitosis is abnormal, which is why many cells of mature tapetum become multinucleated. Polyploidy and polyteny can also be seen sometimes. The tapetum's unusually large nuclear constitution helps it provide nutrients and regulatory molecules to the forming pollen grains. The following pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-articulated Laticifer
A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites. Laticifers may be divided into: *Articulated laticifers, i.e., composed of a series of cells joined together, or *Non-articulated laticifers, consisting of one long coenocytic cell. Non-articulated laticifers begin their growth from the meristematic tissue of the embryo, termed the laticifer initial, and can exhibit continual growth throughout the lifetime of the plant. Laticifer tubes have irregularly edged walls and a larger inner diameter than the surrounding parenchyma cells. In the development of the cell, elongation occurs via karyokinesis and no cell plate develops resulting in coenocytic cells which extend throughout the plant. These cells can reach up to tens of centimeters long and can be branched or unbranched. They are thought to have a role in wound healing and as defense against herbivory, as well as pathogen defense, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
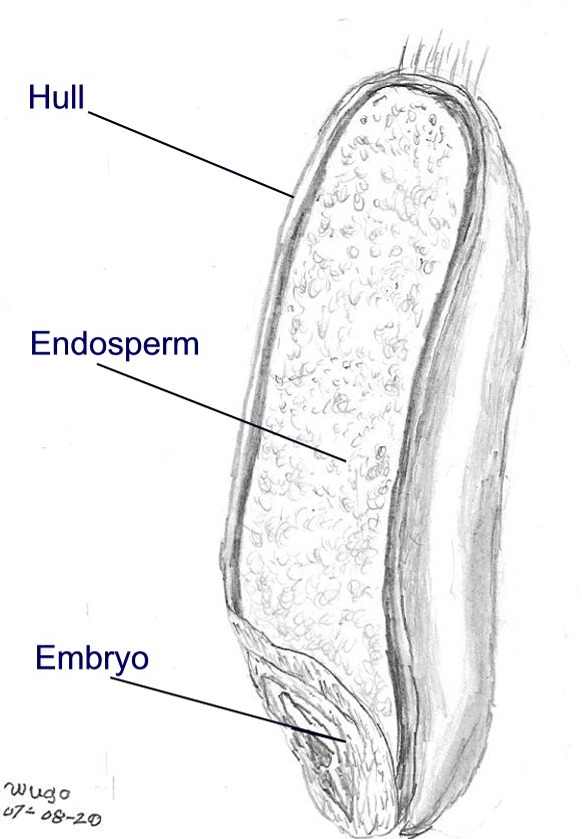
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Development
Important structures in plant development are buds, shoots, roots, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. Thus, a living plant always has embryonic tissues. By contrast, an animal embryo will very early produce all of the body parts that it will ever have in its life. When the animal is born (or hatches from its egg), it has all its body parts and from that point will only grow larger and more mature. However, both plants and animals pass through a phylotypic stage that evolved independently and that causes a developmental constraint limiting morphological diversification. According to plant physiologist A. Carl Leopold, the properties of organization seen in a plant are emergent properties which are more than the sum of the individual parts. "The assembly of these tissues and functions into an integrated multicellular organism yields not only the characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular organism, multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants (hornworts, liverworts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplozoon
''Haplozoon'' (/hæploʊ’zoʊən/) are unicellular endo-parasites, primarily infecting maldanid polychaetes. They belong to Dinoflagellata but differ from typical dinoflagellates. Most dinoflagellates are free-living and possess two flagella. Instead, ''Haplozoon'' belong to a 5% minority of parasitic dinoflagellates that are not free-living. Additionally, the ''Haplozoon'' trophont stage is particularly unique due to an apparent lack of flagella. The presence of flagella or remnant structures is the subject of ongoing research. At first glance, ''Haplozoon'' also do not appear unicellular – in fact they were originally classified as a possible transitional stage between protists and multicellular organisms.Shumway, W. (1924). The genus ''Haplozoon'', Dogiel. Observations on the life history and systematic position. ''The Journal of Parasitology, 11''(2), 59-74. They have more recently been classified as compartmentalized syncytia – single cells with multiple nuclei that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavata
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and '' Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that the group is paraphyletic. Except for some Eugleno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrasid
The family Acrasidae (ICZN, or Acrasiomycota, ICBN) is a family of slime molds which belongs to the excavate group Heterolobosea. The name element - comes from the Greek ''akrasia'', meaning "acting against one's judgement". This group consists of cellular slime molds. The terms "Acrasiomycota" or "Acrasiomycetes" have been used when the group was classified as a fungus ("-mycota"). In some classifications, ''Dictyostelium'' was placed in Acrasiomycetes, an artificial group of cellular slime molds, which was characterized by the aggregation of individual amoebae into a multicellular fruiting body, making it an important factor that related the acrasids to the dictyostelids. Each cell keeps its individuality even when it forms a stalk and fruiting body to reproduce. Slime molds were originally thought to be in a monophyletic group ''Mycetozoa'', with little distinction between ''Acrasis'' and ''Dictyostelids'', however scientists uncovered that they were distinct groups, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |