|
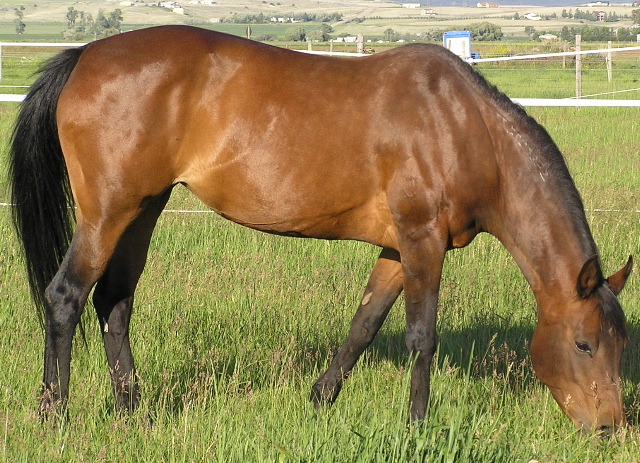
Sugar Beet Pulp
Beet pulp is a byproduct from the processing of sugar beet which is used as fodder for horses and other livestock. Beet pulp is the fibrous material left over after the sugar is extracted from sugar beets. It is supplied either as dried flakes or as compressed pellets, but when fed to horses it should always be soaked in water first. Composition Despite being a byproduct of sugar beet processing, beet pulp itself is low in sugar and other non-structural carbohydrates, but high in energy and fiber.Warren, Lori K. "Horse Feeding Myths and Misconceptions Horse Industry Section, Alberta Agriculture, Food and Rural Development. Web site accessed February 16, 2007 Among other nutrients, it contains 10 percent protein, 0.8 percen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet Cossettes
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is a refined form of sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars, and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human food. Some other chemical substances, such as glycerol and sugar alcohols, may have a sweet taste, but are not classified as sugar. Sugars are found in the tissues of most plants. Honey and fruits are abundant natural sources of simple sugars. Sucrose is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Nutrition
Equine nutrition is the feeding of horses, ponies, mules, donkeys, and other equines. Correct and balanced nutrition is a critical component of proper horse care. Horses are non-ruminant herbivores of a type known as a " hindgut fermenter." Horses have only one stomach, as do humans. However, unlike humans, they also need to digest plant fiber (largely cellulose) that comes from grass or hay. Ruminants like cattle are foregut fermenters, and digest fiber in plant matter by use of a multi-chambered stomach, whereas horses use microbial fermentation in a part of the digestive system known as the ''cecum'' (or ''caecum'') to break down the cellulose. Williams, Carey A., Ph.D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Colic
Colic in horses is defined as abdominal pain, but it is a clinical symptom rather than a diagnosis. The term colic can encompass all forms of gastrointestinal conditions which cause pain as well as other causes of abdominal pain not involving the gastrointestinal tract. The most common forms of colic are gastrointestinal in nature and are most often related to colonic disturbance. There are a variety of different causes of colic, some of which can prove fatal without surgical intervention. Colic surgery is usually an expensive procedure as it is major abdominal surgery, often with intensive aftercare. Among domesticated horses, colic is the leading cause of premature death. The incidence of colic in the general horse population has been estimated between 4 and 10 percent over the course of the average lifespan. Clinical signs of colic generally require treatment by a veterinarian. The conditions that cause colic can become life-threatening in a short period of time. Pathophysiolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal Impaction
A fecal impaction is a solid, immobile bulk of feces that can develop in the rectum as a result of chronic constipation. A related term is fecal loading which refers to a large volume of stool in the rectum of any consistency. Fecal impaction is a common result of neurogenic bowel dysfunction and causes immense discomfort and pain. Treatment of fecal impaction includes laxatives, enema, and pulsed irrigation evacuation (PIE). Signs and symptoms Symptoms include chronic constipation. There can be fecal incontinence and paradoxical overflow diarrhea (encopresis) as liquid stool passes around the obstruction. Complications may include necrosis and ulcers of the rectal tissue. Abdominal pain and bloating could also be present depending on the severity of the condition. Loss of appetite can also occur. Causes There are many possible causes; for example, physical inactivity, not eating enough fiber, dehydration, and holding in bowel movements. Medications such as opioid pain relie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
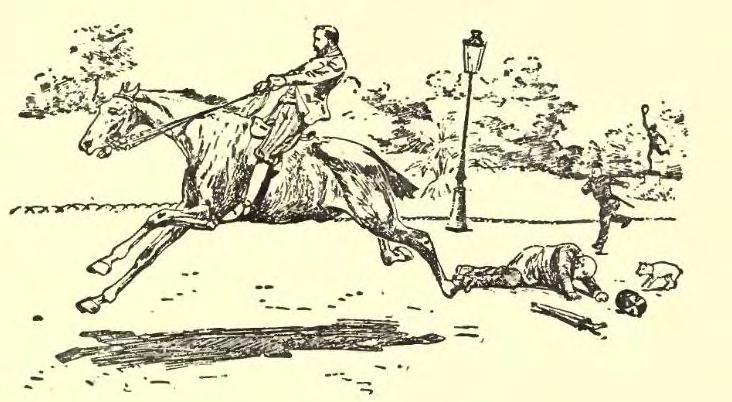
Bolting (horse)
Bolting, when referring to equids, generally refers to two equine behaviors, both undesirable: * Running away without control. * Eating food at a dangerously fast rate. However, there are other meanings as well. For example, in Australia a ''bolter'' is a racehorse that wins at long betting odds. Runaways Most often, bolting refers to a "runaway" - horses that gallop off with a handler at high speed, whether being ridden under saddle or driving in harness. There are many causes, most linked to fright that triggers the fight-or-flight response of the horse. In these circumstances, the horse is often running in a panic and may not notice where it is going, creating danger for both horse and rider. Less often, bolting is a deliberate disobedience by a horse that wishes to rid itself of a handler or avoid an unpleasant situation. In both cases, bolting horses are usually stopped by being turned in some type of circle by pulling on one rein to turn the head to the side, as directly pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke (horse)
Choke is a condition in horses in which the esophagus is blocked, usually by food material. Although the horse is still able to breathe, it is unable to swallow, and may become severely dehydrated. A secondary condition, aspiration pneumonia, may also develop if food material and saliva accumulate in the pharynx, spilling into the trachea and into the lungs. Choke is one of the "top 10" emergencies received by equine veterinarians. The condition is seen in other Equidae like mules and donkeys. Causes Chewing: Horses may develop choke if they do not chew their food properly. Therefore, horses with dental problems (e.g. acquired or congenital malocclusion, loose or missing teeth, or excessively sharp dental ridges) that do not allow them to completely grind their food are particularly at risk. In addition, horses that bolt their feed and do not take the time to chew properly are more likely to suffer from choke. Dry Food: Dry foods may cause choke, especially if the horse does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goats
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of Caprinae, goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the animal family Bovidae and the tribe Caprini, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. There are over 300 distinct breeds of goat.Hirst, K. Kris"The History of the Domestication of Goats".''About.com''. Accessed August 18, 2008. It is one of the oldest domesticated species of animal, according to archaeological evidence that its earliest domestication occurred in Iran at 10,000 calibrated calendar years ago. Goats have been used for milk, Goat meat, meat, Animal fur, fur, and Animal skin, skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into goat cheese. Female goats are referred to as ''does'' or ''nannies'', Entire (animal), intact males are called ''bucks'' or ''billies'', and juvenile goats of both sexes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris.'' Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima''). Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugar cane. The low sugar content of the beets makes growing them a marginal proposition unless prices are relatively high. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molasses
Molasses () is a viscous substance resulting from refining sugarcane or sugar beets into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, method of extraction and age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is primarily used to sweeten and flavour foods. Molasses is a major constituent of fine commercial brown sugar. It is also one of the primary ingredients used to distill rum. Sweet sorghum syrup is colloquially called ''sorghum molasses'' in the southern United States. Molasses has a stronger flavour than most alternative syrups. Name The word molasses comes from ''melaço'' in Portuguese, a derivative (intensifier) of ''mel'' (honey) with Latinate roots. Cognates include Ancient Greek μέλι (''méli'') (honey), Latin ''mel'', Spanish ''melaza'' (molasses), Romanian ''miere'' or ''melasă'', and French ''miel'' (honey). Cane molasses Cane molasses is an ingredient used in baking and cooking. It was popular in the Americas before the twentieth century, when it was plentiful and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8,5'-Diferulic Acid
8,5′-Diferulic acid is a non cyclic type of diferulic acid. It is the predominant diferulic acid in sugar beet pulp. It is also found in barley, in maize bran and rye. 8,5′-Diferulic acid has also been identified to be covalently linked to carbohydrate moieties of the arabinogalactan-protein fraction of gum arabic. See also * Decarboxylated 8,5'-diferulic acid References External links 5-8'-Dehydrodiferulic acid at phenol-explorer.eu {{DEFAULTSORT:Diferulic acid, 8,5'- O-methylated hydroxycinnamic acids Hydroxycinnamic acid dimers Vinylogous carboxylic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |