|
Succinic Anhydride
Succinic anhydride, is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ... with the molecular formula (CH2CO)2O. This colorless solid is the acid anhydride of succinic acid. Preparation In the laboratory, this material can be prepared by dehydration of succinic acid. Such dehydration can occur with the help of acetyl chloride or phosphoryl chloride, or thermally. Industrially, succinic anhydride is prepared by catalytic hydrogenation of maleic anhydride. Reactions Succinic anhydride hydrolyzes readily to give succinic acid: :(CH2CO)2O + H2O → (CH2CO2H)2 With alcohols (ROH), a similar reaction occurs, delivering the monoester: :(CH2CO)2O + ROH → RO2CCH2CH2CO2H Succinic anhydride is used in acylations under Friedel-Crafts conditions, as illustrated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkenylsuccinic Anhydride
Alkenyl succinic anhydrides (ASA) are modified five-membered succinic anhydrides bearing a branched iso-alkenyl chain (C14 to C22). They are colorless, and usually viscous liquids. They are widely used, especially in surface sizing of paper, paperboard, and cardboard, as well as in the hydrophobicization of cellulose fibers. Products treated with it show reduced penetration of aqueous media, such as inks or drinks (like milk or fruit juices). In terms of their mode of action, the anhydride is proposed to react with the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose, forming an ester. The alkenyl side-chain modifies the surface properties of the paper product. The application is similar to that for alkyl ketene dimers. In the United States alkenylsuccinic anhydrides are the preferred paper sizing agents, whereas in Europe, alkyl ketene dimers (AKDs) predominate. History The reaction of maleic anhydride (MAN) with aliphatic monounsaturated ''n''- and ''iso''-alkenes was described as early as 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenbufen
Fenbufen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain. Fenbufen is a member of the propionic acid derivatives class of drugs. It was introduced by American Cyanamid under the trade name Lederfen in the 1980s. Due to liver toxicity, it was withdrawn from markets in the developed world in 2010. As of 2015 it was available in Taiwan and Thailand under several brand names. Preparation Fenbufen can be synthesized by acylation of biphenyl with succinic anhydride Succinic anhydride, is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms) ... under Friedel-Crafts conditions.Castillo, Rafael; Suárez-Herrera, Margarita; Aparicio, Mayra; Hernández-Lui, Francisco; Hernández, Alicia (1995). "An Improved Synthesis of Fenbulen". Organic Preparations and Procedures International. 27 (5): 550–552. doi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Anhydrides
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sizing Agent
Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water. The chemicals can be defined on basis of their usage in the process. Chemical usage is not only for imparting properties to paper but to handle the water cycles in the process, conditioning of fabrics, cleaning of equipment and several other applications. Chemicals used in paper manufacturing Pulping Chemical pulping involves dissolving lignin in order to extract the cellulose from the wood fiber. The different processes of chemical pulping include the Kraft process, which uses caustic soda and sodium sulfide and is the most common; alternatively, the use of sulfurous acid is known as the sulfite process, the neutral sulfite semichemical is treated as a third process separate from sulfite, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
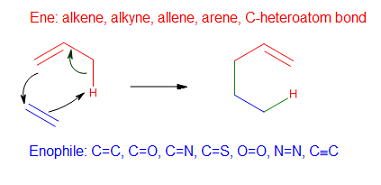
Alder-ene Reaction
In organic chemistry, the ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction by its discoverer Kurt Alder in 1943) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position. This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been also developed, which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products. Ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maleic Anhydride
Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C2H2(CO)2O. It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid. It is a colorless or white solid with an acrid odor. It is produced industrially on a large scale for applications in coatings and polymers. Production Maleic anhydride is produced by vapor-phase oxidation of ''n''-butane. The overall process converts the methyl groups to carboxylate and dehydrogenates the backbone. The selectivity of the process reflects the robustness of maleic anhydride, with its conjugated double-bond system. Traditionally maleic anhydride was produced by the oxidation of benzene or other aromatic compounds. As of 2006, only a few smaller plants continue to use benzene. In both cases, benzene and butane are fed into a stream of hot air, and the mixture is passed through a catalyst bed at high temperature. The ratio of air to hydrocarbon is controlled to prevent the mixture from igniting. Vanadium pentoxide and molybdenum trioxide are the catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acylation
In chemistry, acylation (or alkanoylation) is the chemical reaction in which an acyl group () is added to a compound. The compound providing the acyl group is called the acylating agent. Because they form a strong electrophile when treated with some metal catalysts, acyl halides are commonly used as acylating agents. For example, Friedel–Crafts acylation uses acetyl chloride (ethanoyl chloride or ) as the agent and aluminum chloride () as a catalyst to add an ethanoyl (acetyl) group to benzene: The mechanism of this reaction is electrophilic aromatic substitution. Acyl halides and acid anhydrides of carboxylic acids are also commonly used acylating agents. In some cases, active esters exhibit comparable reactivity. All react with amines to form amides and with alcohols to form esters by nucleophilic acyl substitution. Acylation can be used to prevent rearrangement reactions that would normally occur in alkylation. To do this an acylation reaction is perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |