|
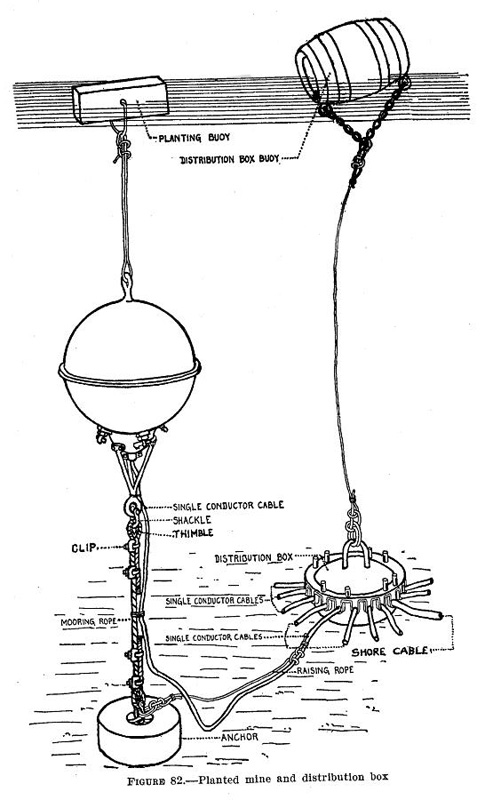
Submarine Mines In United States Harbor Defense
The modern era of defending American harbors with controlled mines or submarine mines (originally referred to as "torpedoes") began in the post-Civil War period, and was a major part of US harbor defenses from circa 1900 to 1947. Brief history In 1866, the United States Army Corps of Engineers established the Engineer School of Application at Willets Point, New York. The first commander of this school, Major Henry Larcom Abbot, was almost single-handedly responsible for designing and supervising the program of research and development that defined the strategy and tactics for the mine defense of American harbors. Abbot experimented with underwater explosives, fuzes, cabling, and electrical equipment for over a decade before publishing the first manuals on the use of mines in coast defense in 1876–77. At least one experimental controlled minefield was emplaced at this time, at Fort Mifflin in Pennsylvania. However, funding of the fortification program of the 1870s was cancell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which artillery, guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary When referring to Ancient history, antiquity, the term "casemate wall" means a double city wall with the space between the walls separated into chambers, which could be filled up to better withstand battering rams in case of siege (see #Antiquity: casemate wall, Antiquity: casemate wall). In its original early modern meaning, the term referred to a vaulted chamber in a fort, which may have been used for storage, accommodation, or artillery which could fire through an opening or embrasure. Although the outward faces of brick or masonry casemates proved vulnerable to advances in artillery performance, the invention of reinforced concrete allowed newer designs to be produced well into the 20th century. With the introduction of ironclad warships, the definition was widened to include a prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Artillery Fire Control System
In the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps, the term fire control system was used to refer to the personnel, facilities, technology and procedures that were used to observe designated targets, estimate their positions, calculate firing data for guns directed to hit those targets, and assess the effectiveness of such fire, making corrections where necessary. Fire control instruments The Coast Artillery's early fire control instruments supported optical rangefinding and position finding, either horizontal base or vertical base, with both systems usually present for each fort. Early horizontal base rangefinding required two azimuth (a.k.a. bearing or deflection) instruments, preferably widely separated, and a communications system to transmit data to a plotting room and then to the guns. The instruments were often in bunkers called base end stations, as they defined the endpoints of a baseline. A base end station might be a two-story structure with a plotting room or other instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Inverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC. The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or may be a combination of mechanical effects (such as a rotary apparatus) and electronic circuitry. Static inverters do not use moving parts in the conversion process. Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which usually have very low currents and vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrupter
An interrupter in electrical engineering is a device used to interrupt the flow of a steady direct current for the purpose of converting a steady current into a changing one. Frequently, the interrupter is used in conjunction with an inductor (coil of wire) to produce increased voltages either by a back emf effect or through transformer action. The largest industrial use of the interrupter was in the induction coil, the first transformer, which was used to produce high voltage pulses in scientific experiments and to power arc lamps, spark gap radio transmitters, and the first X-ray tubes, around the turn of the 20th century. Its largest use was the contact breaker or "points" in the distributor of the ignition system of gasoline engines, which served to periodically interrupt the current to the ignition coil producing high voltage pulses which create sparks in the spark plugs. It is still used in this application. Medical use Bird's interrupter The physician Golding Bird desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Warren (Massachusetts)
Fort Warren is a historic fort on the Georges Island at the entrance to Boston Harbor. The fort is named for Revolutionary War hero Dr. Joseph Warren, who sent Paul Revere on his famous ride, and was later killed at the Battle of Bunker Hill. The name was transferred in 1833 from the first Fort Warren – built in 1808 – which was renamed Fort Winthrop. Fort Warren is a pentagonal bastion fort, made with stone and granite, and was constructed from 1833 to 1861, completed shortly after the beginning of the American Civil War. Fort Warren defended the harbor in Boston, Massachusetts, from 1861 through the end of World War II, and during the Civil War served as a prison for Confederate officers and government officials, including Confederate Vice President Alexander H. Stephens. The fort remained active through the Spanish–American War and World War I, and was re-activated during World War II. It was permanently decommissioned in 1947, and is now a tourist site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Strong
Fort Strong is a former U.S. Army Coast Artillery fort that occupied the northern third of Long Island in Boston Harbor. The island had a training camp during the American Civil War, and a gun battery was built there in the 1870s. The fort was built in 1893-1906 during the Endicott period of expansion in U.S. coast defense, and was part of the Coast (later Harbor) Defenses of Boston. Formerly, it was also known as Long Island Military Reservation. Before World War I, a large station for handling submarine mines was added to the fort's defenses. Prior to World War I the fort was probably manned by over 1,000 soldiers. During World War II, two batteries of 3-inch guns (Basinger and Stevens) defended channel minefields, but the big guns and other 3-inch batteries (except for the AA guns) were decommissioned. Declared surplus in 1947, the fort served as a Nike missile site until 1961, and was redeveloped in 2005-2009 for a children's summer camp and later a homeless shelter. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Dawes
Fort Dawes was a World War II Coast Artillery fort located on Deer Island in Winthrop/Boston, Massachusetts. It was part of the Harbor Defenses of Boston. History The site's military history began in 1906 as the Deer Island Military Reservation, acquired for fire control and mine field control as part of the Taft program. During World War II, Fort Dawes was initially the site of a target detection radar for the harbor defenses and Battery Taylor (two 3-inch M1902 guns moved from nearby Fort Strong), both completed by late 1942. Also in 1942, construction began on Anti- Motor Torpedo Boat Battery (AMTB) 944, with two fixed and two towed 90 mm guns, along with the Harbor Entrance Control Post (HECP) for Boston Harbor--the installation that kept track of all vessels entering and leaving the harbor. AMTB 944 replaced Battery Taylor in October 1943, whose guns were placed in storage at that time.Berhow, p. 205 By 1945 Fort Dawes had a mine casemate controlling some of the mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candelabrum
A candelabra (plural candelabras) or candelabrum (plural candelabra or candelabrums) is a candle holder with multiple arms. Although electricity has relegated candleholders to decorative use, interior designers continue to model light fixtures and lighting accessories after candelabra and candlesticks. Accordingly, the term candelabra has entered common use to describe small-based light bulbs used in chandeliers and other lighting fixtures made for decoration as well as lighting. In Judaism and in the Philippine religion Iglesia ni Cristo, the menorah is a special kind of candelabrum. The Candelabra is also used in certain Eastern Catholic and Eastern Orthodox church architecture and liturgy by bishops as the Trikiridikiri. Singular and plural This word originally came from Latin, in which ''candelabrum'' is the singular form and ''candelabra'' is the plural. Over time, English usage changed so that ''candelabra'' as the singular and ''candelabras'' as the plural is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |