|
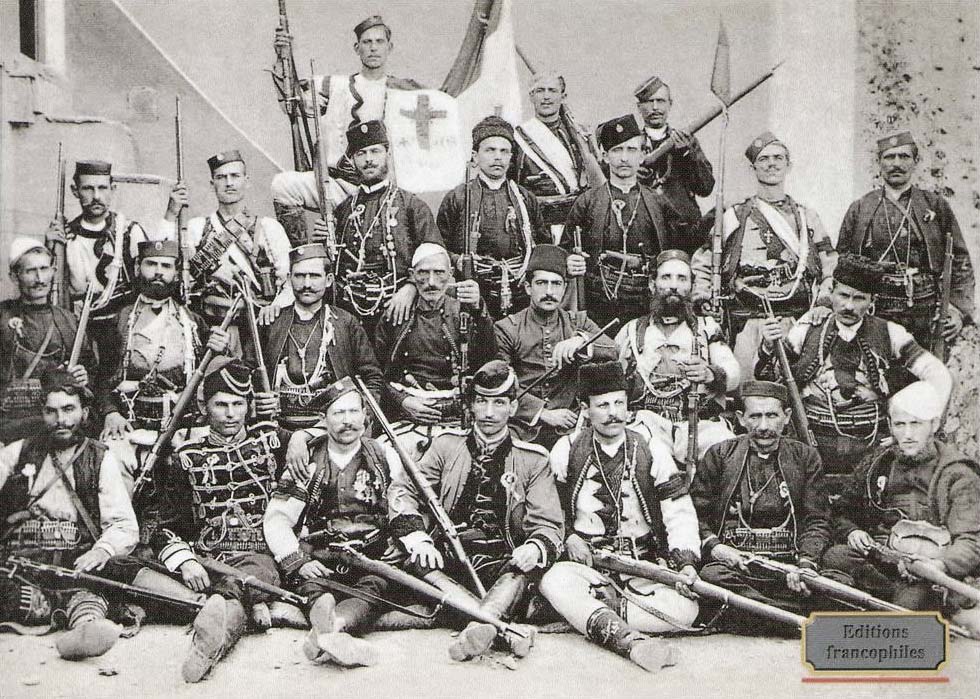
Struggle For Macedonia
The Macedonian Struggle ( bg, ааАаКаЕаДаОаНбаКаА аБаОбаБаА; el, ЮЮБЮКЮЕЮДЮПЮНЮЙЮКЯЯ ЮЮГЯЮНЮБЯ; mk, ааОбаБаА аЗаА ааАаКаЕаДаОаНаИбаА; sr, ааОбаБаА аЗаА ааАаКаЕаДаОаНаИбб; tr, Makedonya MУМcadelesi) was a series of social, political, cultural and military conflicts that were mainly fought between Greek and Bulgarian subjects who lived in Ottoman Macedonia between 1893 and 1912. The conflict was part of a wider rebel war in which revolutionary organizations of Greeks, Bulgarians and Serbs all fought over Macedonia. Gradually the Greek and Bulgarian bands gained the upper hand. Though the conflict was largely pacified by the Young Turk Revolution, it remained a low intensity insurgency until the Balkan Wars. Background Initially the conflict was waged through educational and religious means, with a fierce rivalry developing between supporters of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (Greek-speaking or Slavic/Romance-speaking who generally identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decline And Modernization Of The Ottoman Empire
In the late eighteenth century, the Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Old Regime) faced numerous enemies. In response to these threats, the empire initiated a period of internal reform which came to be known as the Tanzimat, which succeeded in significantly strengthening the Ottoman central state, despite the empire's precarious international position. Over the course of the nineteenth century, the Ottoman state became increasingly powerful and rationalized, exercising a greater degree of influence over its population than in any previous era. The process of reform and modernization in the empire began with the declaration of the Nizam-I Cedid (New Order) during the reign of Sultan Selim III and was punctuated by several reform decrees, such as the Hatt-ФБ Хerif of GУМlhane in 1839 and the Hatt-ФБ HУМmayun in 1856. Despite these attempts at revitalisation, the empire could not stem the rising tide of nationalism, especially among the ethnic minorities in its Balkan provinces. Numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotse Delchev
Georgi Nikolov Delchev ( Bulgarian/Macedonian: ааЕаОбаГаИ/ааОббаИ ааИаКаОаЛаОаВ ааЕаЛбаЕаВ; 4 February 1872 т 4 May 1903), known as Gotse Delchev or Goce DelФev (''ааОбаЕ ааЕаЛбаЕаВ'', originally spelled in older Bulgarian orthography as ''ааОбаЕ абЃаЛбаЕаВб''), was an important Macedonian Bulgarian revolutionary ( komitadji),Per Julian Allan Brooks' thesis the term тMacedo-Bulgarianт refers to the Exarchist population in Macedonia which is alternatively called тBulgarianт and тMacedonianт in the documents. For more see: Managing Macedonia: British Statecraft, Intervention and 'Proto-peacekeeping' in Ottoman Macedonia, 1902-1905. Department of History, Simon Fraser University, 2013, p. 18. The designation тMacedo-Bulgarianт is used also by M. ХУМkrУМ HanioФlu and Ryan Gingeras. See: M. ХУМkrУМ HanioФlu, Preparation for a Revolution: The Young Turks, 1902-1908 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001), 244; Ryan Gingeras, тA Break i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Hamid II
AbdУМlhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, иЙиЈиЏ иЇйий йиЏ иЋиЇйл, Abd УМl-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. AbdУМlhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to exert effective control over the fracturing state. The time period which he reigned in the Ottoman Empire is known as the Hamidian Era. He oversaw a period of decline, with rebellions (particularly in the Balkans), and he presided over an unsuccessful war with the Russian Empire (1877т1878) followed by a successful war against the Kingdom of Greece in 1897, though Ottoman gains were tempered by subsequent Western European intervention. In accordance with an agreement made with the Republican Young Ottomans, he promulgated the Ottoman Empire's first Constitution, which was a sign of progressive thinking that marked his early rule. However, in 1878, citing disagreements with the Ottoman Parliament, he suspended both the short-lived con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Ottoman Empire (1844т1922)
The Ottoman Empire used various of flags, especially as naval ensigns, during its history. The star and crescent came into use in the second half of the 18th century. A ' (decree) from 1793 required that the ships of the Ottoman Navy were to use a red flag with the star and crescent in white. In 1844, a version of this flag, with a five-pointed star, was officially adopted as the Ottoman national flag. The decision to adopt a national flag was part of the ''Tanzimat'' reforms which aimed to modernize the Ottoman state in line with the laws and norms of contemporary European states and institutions. The star and crescent design later became a common element in the national flags of Ottoman successor states in the 20th century. The current flag of Turkey is essentially the same as the late Ottoman flag, but has more specific legal standardizations (regarding its measures, geometric proportions, and exact tone of red) that were introduced with the Turkish Flag Law on 29 May 1936 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Macedonian Studies
The Society for Macedonian Studies ( el, ЮЯЮБЮЙЯЮЕЮЏЮБ ЮЮБЮКЮЕЮДЮПЮНЮЙЮКЯЮН ЮЃЯЮПЯ ЮДЯЮН, Etaireia Makedonikon Spoudon) was founded on April 29, 1939, in Thessaloniki, Greece.Thorsten Kruse, Hubert Faustmann, Sabine Rogge. The purpose of the Society is to foster research on the language, archaeology, history and folklore of Macedonia Macedonia most commonly refers to: * North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia * Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity * Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ... and to promote the cultivation of learning throughout the region. Its headquarters is also home to the Art Gallery of the Society for Macedonian Studies and to the National Theatre of Northern Greece. References External links * {{Authority control 1939 establishments in Greece History of Macedonia (Greece) Organizations based in Thessaloniki Organizations established in 1939 Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Шtefan MihФileanu
Шtefan MihФileanu (1859 т 22 July 1900) was an Aromanian professor and journalist. On 22 July 1900, he was assassinated by a Bulgarian nationalist, due to his criticism of pro-Bulgarian paramilitary activism over the course of the Macedonian Struggle. Biography Шtefan MihФileanu was born in 1859, in Beala di SuprУЃ, Ottoman Empire. An ethnic Aromanian, he was one of the first students in Ottoman Macedonia to attend classes in the Aromanian language. Due to the political turmoil that preceded the Macedonian Struggle, MihФileanu's uncle brought him to Romania, where he continued his education in the Saint Sava National College. The Macedonian Struggle, a series of intertwined cultural, political and military conflicts between the various ethnic and religious communities residing in Macedonia, was to preoccupy MihФileanu until the end of his life. He combined his career as a teacher and published the ''Macedonia'' newspaper between 1888 and 1889. Later on, he continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aksentije BacetiФ
Aksentije BacetiФ ( sr-cyr, ааКбаЕаНбаИбаЕ ааАбаЕбаИб, 27 February 1860 т 16 June 1905), known as Baceta (ааАбаЕбаА), was a Serbian secret agent and Chetnik commander in Macedonia. His surname has been spelled BacetoviФ. Early life BacetiФ was born in the village of Kriva Reka near UХОice, in the Principality of Serbia. He had red hair. As a youngster he joined the ranks of the People's Radical Party. He participated in the Timok Rebellion in 1882, after which he fled to the Principality of Bulgaria. He then went to the Russian Empire where he enrolled in the NCO school finished with the rank of junker. He returned to Serbia where his sub-commander rank was recognized. He translated works from Bulgarian into Serbian. Secret agent BacetiФ worked as a double agent in Bulgaria, giving the Serbian command information on Bulgarian troop placements during the Serbo-Bulgarian War (1885). He was caught and sentenced to death, but the Serbian side insisted on prison du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovan Babunski
Jovan StojkoviФ ( sr-cyr, ааОаВаАаН аЁбаОбаКаОаВаИб; 25 December 1878 т 17 February 1920), known as Jovan Babunski (ааОаВаАаН ааАаБбаНбаКаИ), was a Serbian Chetnik commander ( sr, vojvoda, аВаОбаВаОаДаА) during the Macedonian Struggle, Balkan Wars and World War I. Following the murder of his brother and nephew by the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), he joined a Chetnik band and took command of Chetnik units on the Vardar River, where he and his men often engaged Bulgarian and Ottoman forces. With the outbreak of the First Balkan War he joined the Serbian Army and was wounded while fighting in the village of Strevica. During the Second Balkan War, he joined a Serbian volunteer detachment and fought at the Battle of Bregalnica. During World War I, Babunski and his Chetnik detachment fought Austro-Hungarian forces in the summer of 1914 and later fought on the Salonika front, where Babunski was ordained by French General Louis Franchet d'EspУЈr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gligor SokoloviФ
Gligor SokoloviФ ( sr-cyr, ааЛаИаГаОб аЁаОаКаОаЛаОаВаИб; 17 or 5 January 1870 or 1872 т 30 July 1910]) was one of the supreme commanders (''Great Voivode'') of the Serbian Chetnik Organization, Serbian Chetnik Movement, that fought the Ottoman Empire, Bulgarian, and Albanian armed bands during the Macedonian Struggle. He was one of the most famous Chetniks, and the foremost in Western Povardarie. In Bulgaria he is considered a Bulgarian renegade who switched sides, i.e. (sic) ''Serboman''. After murdering a local Ottoman lord, SokoloviФ went into the woods with some friends and formed a guerrilla unit which would target Ottomans. He then joined the Bulgarian revolutionary organizations of SMAC and IMRO, and fought throughout the wider Macedonia region. After the Ottomans' suppression of the IlindenтPreobrazhenie Uprising in 1903, he, like many others, fled to Serbia. He was acquainted with Dr. GoФevac, one of the founders of the Serbian revolutionary organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milorad GoФevac
Milorad GoФevac ( sr-cyr, ааИаЛаОбаАаД ааОбаЕаВаАб, 1 March 1860 – 21 September 1933) was the organizer of the Serbian Chetnik Organization, a doctor by profession. Life Born in Valjevo, Principality of Serbia, he finished the First Belgrade Gymnasium and finished medicine at the University of Vienna in 1889. He was the organizer of the Serbian armed action in South Serbia and Macedonia and founder of the first Volunteer Board. The Chief Staff of the Chetnik Organization (the Serbian Committee) was established in 1902. The members were, among others, GoФevac, Luka ФeloviФ, Vasa JovanoviФ, ХНika RafailoviФ, Nikola SpasiФ and Ljuba KovaФeviФ. See also * Serb revolutionary organizations *List of Chetnik voivodes This is a list of Chetnik voivodes. VoivodeAlso spelled "voievod", "woiwode", "voivod", "voyvode", "vojvoda", or "woiwod" () (Old Slavic, literally "war-leader" or "war-lord") is a Slavic as well as Romanian title that originally denoted the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostol Petkov
Apostol Petkov Terziev ( Bulgarian/ mk, ааПаОббаОаЛ ааЕбаКаОаВ аЂаЕбаЗаИаЕаВ) (May 6, 1869 т August 2, 1911) was a Macedonian Bulgarian revolutionary and one of the leaders of the national liberation movement in Ottoman Macedonia. He was a leading '' Komitadji'' in the armed units of the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees and later participated in the Bulgarian People's Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization. He took part in the battles against the Ottoman authorities in the Ilinden-Preobrazhenie Uprising and Macedonian Struggle. Historians from North Macedonia consider him an ethnic Macedonian historical figure. Petkov was often referred to by his admirers as ''the Sun of Yenice-i Vardar''. Early life Apostol Petkov was born Apostol Terziev, a member of the old Terviev family, in the town of Boymitsa. Apostol was illiterate but found a job working as a cantonment officer on the Thessaloniki-Skopje railway line, where he remained unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasil Chakalarov
Vasil Hristov Chekalarov ( Bulgarian/ mk, ааАбаИаЛ аЅбаИббаОаВ аЇаЕаКаАаЛаАбаОаВ) or Vasil Tcakalarov (22 February 1874 т 9 July 1913) was a Bulgarian revolutionary and one of the leaders of Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organisation in Macedonia. H. N. Brailsford described Chekalarov as the "cruel but competent general" of the Bulgarian insurgents in Macedonia. Despite his Bulgarian self-identification, and the fact he considered the adherents of Macedonist ideas to be Grecomans, per post-WWII Macedonian historiography he was an ethnic Macedonian. He was a leading '' komitaji'' in the bands of the Bulgarian Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Committees and took part in the battles against the Ottoman authorities as well before the Ilinden Uprising as after it. In 1901-1902 he created a channel for illegal purchase and transfer of firearms from Greece to Southern Macedonia. In 1904 he migrated into Bulgaria and became one of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |