|
Stoping (mining Method)
Stoping is the process of extracting the desired ore or other mineral from an underground mine, leaving behind an open space known as a stope. Stoping is used when the country rock is sufficiently strong not to collapse into the stope, although in most cases artificial support is also provided. The earliest forms of stoping were conducted with hand tools or by fire-setting; later gunpowder was introduced. From the 19th century onward, various other explosives, power-tools, and machines came into use. As mining progresses the stope is often backfilled with tailings, or when needed for strength, a mixture of tailings and cement. In old mines, stopes frequently collapse at a later time, leaving craters at the surface. They are an unexpected danger when records of underground mining have been lost with the passage of time. Stoping is considered "productive work", and is contrasted with "deadwork", the work required merely to access the mineral deposit, such as sinking shafts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miner In Raise 2
A miner is a person who extracts ore, coal, chalk, clay, or other minerals from the earth through mining. There are two senses in which the term is used. In its narrowest sense, a miner is someone who works at the rock face; cutting, blasting, or otherwise working and removing the rock. In a broader sense, a "miner" is anyone working within a mine, not just a worker at the rock face. Mining is one of the most dangerous trades in the world. In some countries, miners lack social guarantees and in case of injury may be left to cope without assistance. In regions with a long mining tradition, many communities have developed cultural traditions and aspects specific to the various regions, in the forms of particular equipment, symbolism, music, and the like. Roles Different functions of the individual miner. Many of the roles are specific to a type of mining, such as coal mining. Roles considered to be "miners" in the narrower sense have included: * Hewer (also known as "cake" or "p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wieliczka Salt Mine
The Wieliczka Salt Mine ( pl, Kopalnia soli Wieliczka) is a salt mine in the town of Wieliczka, near Kraków in southern Poland. From Neolithic times, sodium chloride ( table salt) was produced there from the upwelling brine. The Wieliczka salt mine, excavated from the 13th century, produced table salt continuously until 2007, as one of the world's oldest operating salt mines. Throughout its history, the royal salt mine was operated by the ''Żupy Krakowskie'' (Kraków Salt Mines) company."Wieliczka – The Salt of the Earth" at the WieliczkaSaltMine.net. . Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backfill (mining)
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swell Factor
Swell may refer to: In nature *Swell, another name for a geographic hillock *Swell (ocean), a formation of long wavelength ocean surface waves *Swell (geology), a large domed area Places * Swell, Somerset, a hamlet in the Somerset parish of Fivehead * Swell, Gloucestershire, England Music *Expression pedal, a control found on many organs and synthesizers, also called a swell box or swell pedal *Swell (band), an indie rock band from San Francisco *''Swell'', album by Psyched Up Janis *''Swell'', album by Tiny Moving Parts *Swell Maps, an experimental English rock group of the 1970s People *George Gilbert Swell (1923–1999), Indian academic and politician *Steve Swell (born 1954), American musician, composer and educator *Steven Wells (1960–2009), punk poet and journalist known as Swells Other uses *Swell (bookbinding), a term in bookbinding *Swell (gum), a brand of chewing gum produced by Philadelphia Gum *Swell (exhibit), an art exhibition *Swell, another word for a dandy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in many different contexts. For example, in fields such as physics, geology, chemistry, or biology, ''in situ'' may describe the way a measurement is taken, that is, in the same place the phenomenon is occurring without isolating it from other systems or altering the original conditions of the test. The opposite of ''in situ'' is ''ex situ''. Aerospace In the aerospace industry, equipment on-board aircraft must be tested ''in situ'', or in place, to confirm everything functions properly as a system. Individually, each piece may work but interference from nearby equipment may create unanticipated problems. Special test equipment is available for this ''in situ'' testing. It can also refer to repairs made to the aircraft structure or flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike And Dip
Strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the orientation, or attitude, of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geologic map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the features dip by recording the inclination perpendicular to the strike. These can be done separately, or together using a tool such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stope In Treadwell Gold Mine
Stope may refer to: * Stope, Velike Lašče, a settlement in central Slovenia * Stope, an underground space produced by stoping (mining) Stopes may also refer to: * Marie Stopes Marie Charlotte Carmichael Stopes (15 October 1880 – 2 October 1958) was a British author, palaeobotanist and campaigner for eugenics and women's rights. She made significant contributions to plant palaeontology and coal classification ... (1880-1958), Scottish palaeobotanist and pioneer in the field of family planning See also * Stoping (geology) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Deidesheimer
Philip Deidesheimer was a mining engineer in the Western United States. Deidesheimer was born in 1832, in Darmstadt, Hesse before German unification. He attended the prestigious Freiberg University of Mining (''Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg'') and emigrated to California in 1852. He died on 21 July 1916 in San Francisco, California. Career In 1852, at nineteen, the young mining engineer traveled to the California gold fields to work for several years, including in Georgetown. In April 1860 he was hired by W. F. Babcock, a trustee of the Ophir Mine, part of the Comstock Lode silver mining boom in Nevada, and solved one of the Comstock mines' most critical engineering needs. Comstock Lode Square set timbering Deidesheimer invented a system, now known as square set timbering, using heavy timber "cubes" as supports for underground mining tunnels and shafts, that enabled skilled miners to open three-dimensional cavities of any size. In large openings, the cubes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
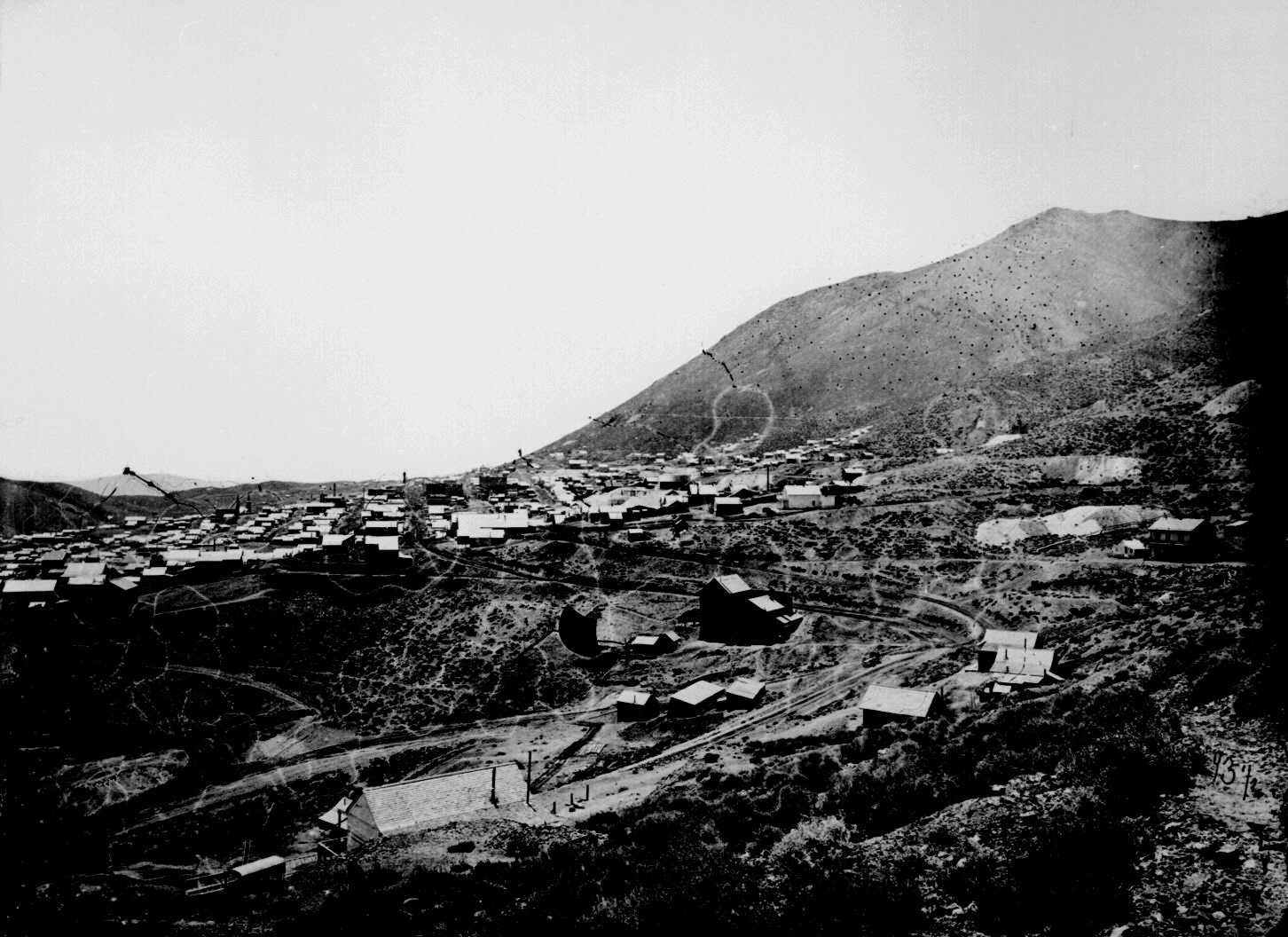
Virginia City, Nevada
Virginia City is a census-designated place (CDP) that is the county seat of Storey County, Nevada, and the largest community in the county. The city is a part of the Reno–Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area. Virginia City developed as a boomtown with the 1859 discovery of the Comstock Lode, the first major silver deposit discovery in the United States, with numerous mines opening. The population peaked in the mid-1870s, with an estimated 25,000 residents. The mines' output declined after 1878, and the population declined as a result. As of the 2020 Census, the population of Virginia City was 787. History Peter O'Riley and Patrick McLaughlin are credited with the discovery of the Comstock Lode. Henry T. P. Comstock's name was associated with the discovery through his own machinations. According to folklore, James Fennimore, nicknamed Old Virginny Finney, christened the town when he tripped and broke a bottle of whiskey at a saloon entrance in the northern section of Gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comstock Lode
The Comstock Lode is a lode of silver ore located under the eastern slope of Mount Davidson (Nevada), Mount Davidson, a peak in the Virginia Range in Virginia City, Nevada (then western Utah Territory), which was the first major discovery of silver ore in the United States and named after American miner Henry Comstock. After the discovery was made public in 1859, it sparked a silver rush of prospectors to the area, scrambling to stake their claims. The discovery caused considerable excitement in California and throughout the United States, the greatest since the California Gold Rush in 1849. Mining camps soon thrived in the vicinity, which became bustling commercial centers, including Virginia City, Nevada, Virginia City and Gold Hill, Nevada, Gold Hill. The Comstock Lode is notable not just for the immense fortunes it generated and the large role those fortunes had in the growth of Nevada and San Francisco, but also for the advances in mining technology that it spurred, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolcoath Mine
Dolcoath mine ( kw, Bal Dorkoth) was a copper and tin mine in Camborne, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Its name derives from the Cornish language, Cornish for 'Old Ground', and it was also affectionately known as ''The Queen of Cornish Mines''. The site is north-west of Carn Brea, Redruth, Carn Brea. Dolcoath Road runs between the A3047 road and Chapel Hill. The site is south of this road. History The mineral rights were owned by the Basset family of Tehidy Country Park#House, Tehidy who are recorded on a deed in 1588 as leasing the ground to a family called Crane. By 1720 the mine was being worked for copper, and it was almost deep in 1746, when William Borlase called it a "very considerable mine". In 1778 it was nearly deep, according to William Price. The mine closed in 1787 because the large amount of copper ore that was being cheaply mined from Parys Mountain on Anglesey had depressed the price. However the price of copper slowly recovered and the mine reopened in 1799 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
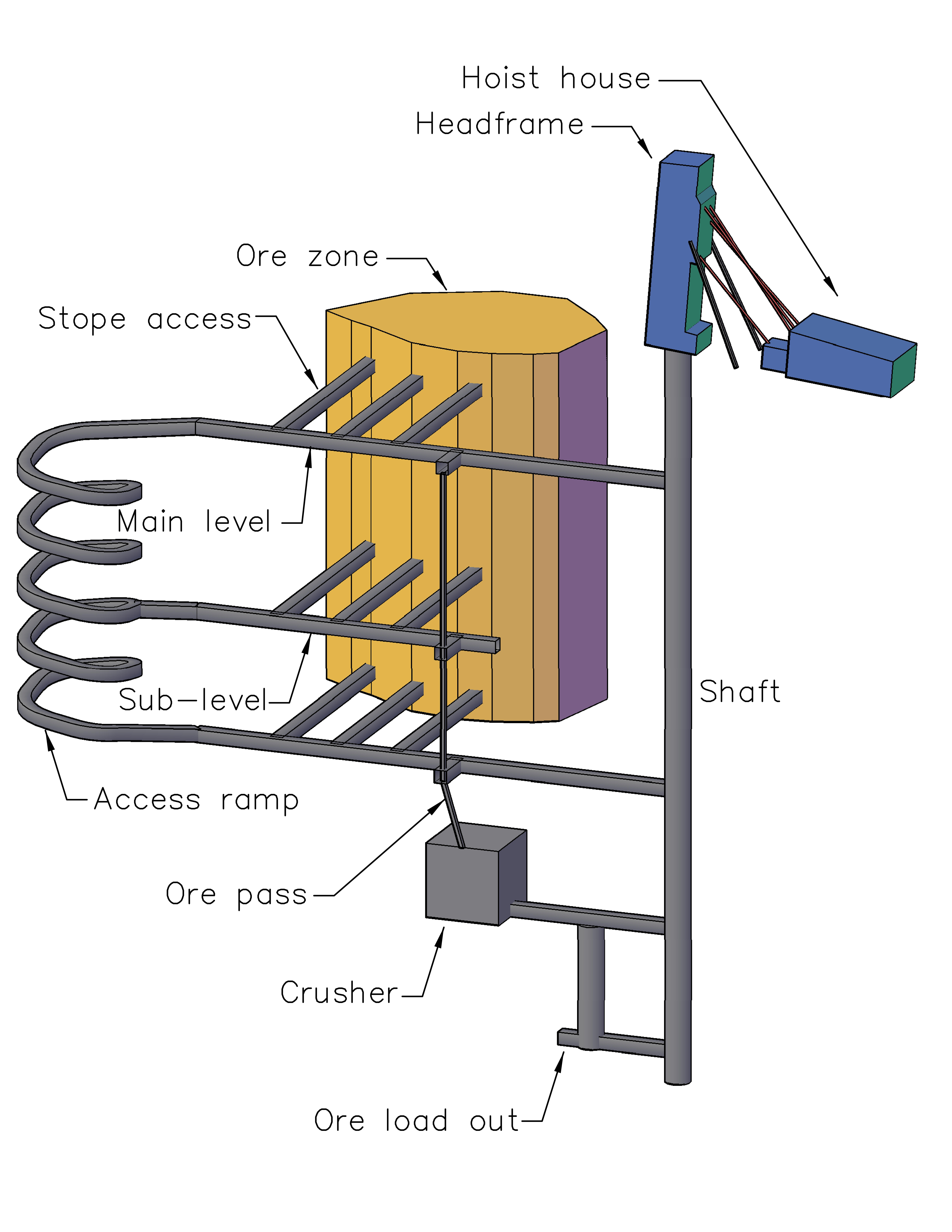
Underground Mining (hard Rock)
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |