|
Stereolithography
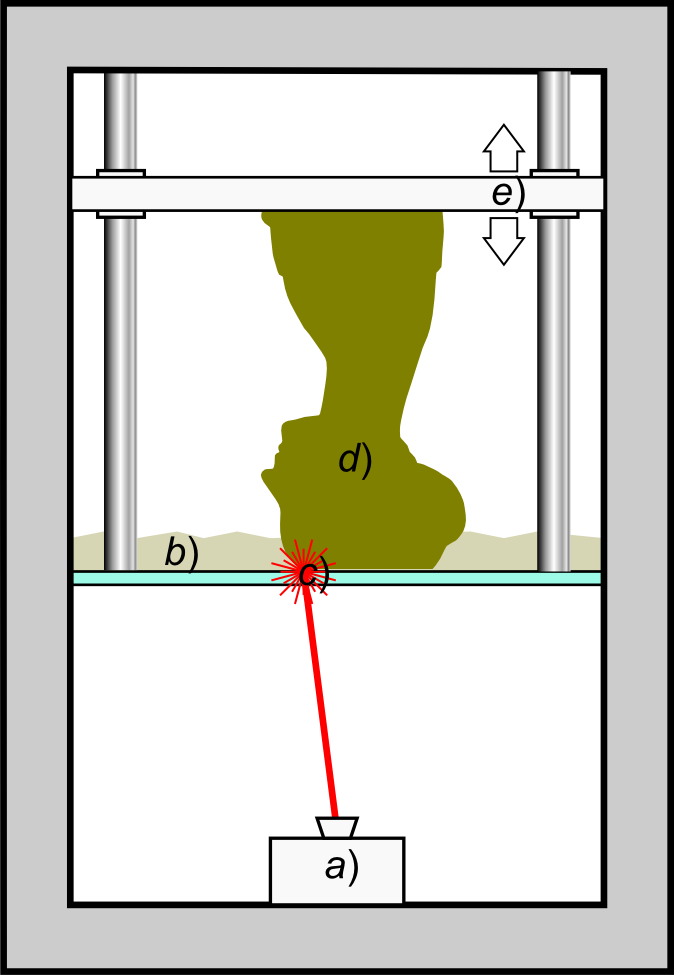
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers.U.S. Patentbr>4,575,330(“Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography”) Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuck Hull
Chuck Hull (Charles W. Hull; born May 12, 1939) is the co-founder, executive vice president and chief technology officer of 3D Systems. He is one of the inventors of the SLA 3D printer, the first commercial rapid prototyping technology, and the widely used STL file format. He is named on more than 60 U.S. patents as well as other patents around the world in the fields of ion optics and rapid prototyping. He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2014 and in 2017 was one of the first inductees into the TCT Hall of Fame. Early life Chuck Hull was born on May 12, 1939 in Clifton, Colorado, the son of Lester and Esther Hull. His early life was spent in Clifton and Gateway, Colorado. He graduated from Central High School in Grand Junction, Colorado. Chuck received a Bachelor of Science in engineering physics from the University of Colorado in 1961. He is also a distinguished alumni from Colorado Mesa University. Beginnings of stereolithography Hull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the Manufacturing, construction of a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design, CAD model or a digital 3D modeling, 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under Computer Numerical Control, computer control, with material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology, whereby the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Le Mehaute
Alain Le Mehaute (fr. ''Alain Le Méhauté''; born November 22, 1947) is a French engineer-chemist and inventor. He has written numerous scientific researches and academic literature on Geometry, Physics and Chemistry. Alain Le Mehaute, Olivier de Witte and Jean Claude André were the first to file their patent for the stereolithography process, but officially the title of inventor of stereolithography and 3D printing technology on the whole belongs to Chuck Hull Career From the start of his career (1974), Alain Le MéhautéESCIL/ECPengineer) was one of the main creative engineers in the Scientific Research Center of the industrial group Compagnie Générale d’Electricité (later named Alcatel-Alstrom 1991. With Jean Rouxel's team in Nantes University and in a partnership witMichel Armandhe was one of the creators of lithium Batteries. At the same time, he held a position of visiting professor at University of Paris-Sud and during 6 years a position of Associate Research D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formlabs
Formlabs is a 3D printing technology developer and manufacturer. The Somerville, Massachusetts-based company was founded in September 2011 by three MIT Media Lab students. The company develops and manufactures 3D printers and related software and consumables. It is most known for raising nearly $3 million in a Kickstarter campaign and creating the Form 1, Form 1+, Form 2, Form Cell, Form 3, Form 3L, and Fuse 1 stereolithography and selective laser sintering 3D printers. History Formlabs was founded by Maxim Lobovsky, Natan Linder, and David Cranor, who met as students at the MIT Media Lab while taking a class called "How to Make (almost) Anything". The founders also drew on their experience with MIT's Center for Bits and Atoms Fab Lab program, as well as Lobovsky's experience with the Fab@Home project at Cornell University. Formlabs was officially founded in September 2011 to develop the first desktop-sized, easy-to-use, and affordable stereolithography 3D printer. Formlabs rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
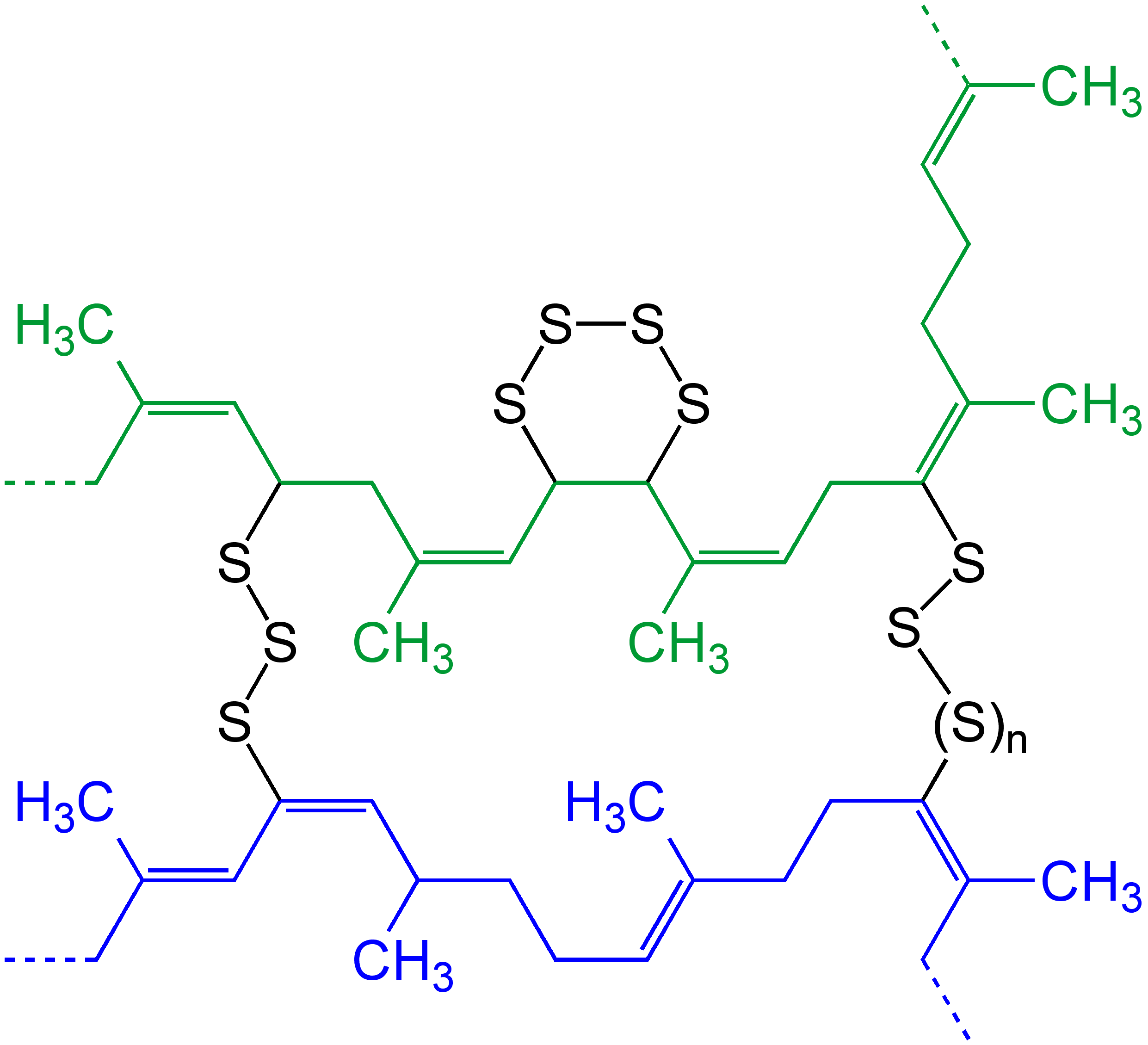
Photopolymer
A photopolymer or light-activated resin is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing. A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers; for example, some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype is generally used to evaluate a new design to enhance precision by system analysts and users. Prototyping serves to provide specifications for a real, working system rather than a theoretical one. In some design workflow models, creating a prototype (a process sometimes called materialization) is the step between the Formal specification, formalization and the evaluation of an idea. A prototype can also mean a typical example of something such as in the use of the derivation 'prototypical'. This is a useful term in identifying objects, behaviours and concepts which are considered the accepted norm and is analogous with terms such as stereotypes and archetypes. The word ''wikt:prototype, prototype'' derives from the Greek language, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic Representation Of Stereolithography
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Systems
3-D, 3D, or 3d may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Relating to three-dimensionality * Three-dimensional space ** 3D computer graphics, computer graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data ** 3D film, a motion picture that gives the illusion of three-dimensional perception ** 3D modeling, developing a representation of any three-dimensional surface or object ** 3D printing, making a three-dimensional solid object of a shape from a digital model ** 3D display, a type of information display that conveys depth to the viewer ** 3D television, television that conveys depth perception to the viewer ** Stereoscopy, any technique capable of recording three-dimensional visual information or creating the illusion of depth in an image Other uses in science and technology or commercial products * 3D projection * 3D rendering * 3D scanning, making a digital representation of three-dimensional objects * 3D video game (other) * 3-D Secure, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Overmars
Markus Hendrik Overmars (; born 29 September 1958 in Zeist, Netherlands) is a Dutch computer scientist and teacher of game programming known for his game development application GameMaker. GameMaker lets people create computer games using a drag-and-drop interface. He is the former head of the ''Center for Geometry, Imaging, and Virtual Environments'' at Utrecht University, in the Netherlands. This research center concentrates on computational geometry and its application in areas like computer graphics, robotics, geographic information systems, imaging, multimedia, virtual environments, and games. Overmars received his Ph.D. in 1983 from Utrecht University under the supervision of Jan van Leeuwen, and continued to be a member of the faculty of the same university until September 2013. Overmars has published over 100 journal papers, largely on computational geometry, and is the co-author of several books including a widely used computational geometry text. Overmars has also wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jit Bose
Prosenjit K. "Jit" Bose is a Canadian mathematician and computer scientist who works at Carleton University as a professor in the School of Computer Science and associate dean of research and graduate studies for the Faculty of Science.Curriculum vitae retrieved 2015-03-18. His research concerns s and , including work on s and |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146 Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 11 Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Originally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat limestone plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)