|
Statnamic Load Test
The Statnamic load test is a type of test for assessing the load-carrying capacity of deep foundations which is faster and less expensive than the static load test. The Statnamic test was conceived in 1985, with the first prototype tests carried out in 1988 through collaboration between Berminghammer Foundation Equipment of Canada and TNO Building Research of the Netherlands.Middendorp, P. (2000) Statnamic the engineering of art. Proc.6th Int. Conf. on the Application of Stress Wave Theory to Piles, Balkema, Rotterdam, 551–562Middendorp, P., Bermingham, P. & Kuiper, B. (1992) Statnamic load testing of foundation piles. 4th Int. Conf. on the Application of Stresswave Theory to Piles, The Hague 21–24 September 1992, pp. 265–272 Guidance on rapid load pile testing can be found in: Methods for Axial Compressive Force Pulse (Rapid) Testing of Deep Foundations. Sanken D7383 - 08 Standard Test. How it works Statnamic testing works by accelerating a mass Mass is an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Foundations
A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site. There are many reasons that a geotechnical engineer would recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, such as for a skyscraper. Some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints like property lines. There are different terms used to describe different types of deep foundations including the pile (which is analogous to a pole), the pier (which is analogous to a column), drilled shafts, and caissons. Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep foundations are typically put in place using excavation and drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Load Test
Static may refer to: Places *Static Nunatak, a nunatak in Antarctica United States * Static, Kentucky and Tennessee * Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming **Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak Science and technology Physics *Static electricity, a net charge of an object **Triboelectric effect, due to frictional contact between different materials *Static spacetime, a spacetime having a global, non-vanishing, timelike Killing vector field which is irrotational *Statics, a branch of physics concerned with physical systems in equilibrium **Fluid statics, the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at rest Engineering * Static pressure, in aircraft instrumentation and fluid dynamics ** Static port, a proprietary sensor used on aircraft to measure static pressure * White noise or static noise, a random signal with a flat power spectral density ** Noise (radio), in radio reception ** Noise (video), the random black-and-white image produced by televisions attempting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands Organisation For Applied Scientific Research
Nederlandse Organisatie voor Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek (TNO; en, Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research) is an independent research organisation in the Netherlands that focuses on applied science. The organisation also conducts contract research, offers specialist consulting services, and grants licences for patents and specialist software. TNO tests and certifies products and services, and issues an independent evaluation of quality. Moreover, TNO sets up new companies to market innovations. Background TNO was established by law in 1932 to support companies and governments with innovative, practicable knowledge. As a statutory organisation, TNO has an independent position that allows to give objective, scientifically founded judgments. It is similar to the following: * CSIR in Ghana * CSIR in India * CSIR in South Africa * CSIRO in Australia * Fraunhofer Society in Germany * SINTEF in Norway Furthermore, TNO also held 10% of the Austria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Wave
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model of how solid objects deform and become internally stressed due to prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics. The fundamental "linearizing" assumptions of linear elasticity are: infinitesimal strains or "small" deformations (or strains) and linear relationships between the components of stress and strain. In addition linear elasticity is valid only for stress states that do not produce yielding. These assumptions are reasonable for many engineering materials and engineering design scenarios. Linear elasticity is therefore used extensively in structural analysis and engineering design, often with the aid of finite element analysis. Mathematical formulation Equations governing a linear elastic boundary value problem are based on three tensor partial differential equations for the balance of linear momentum and six infinitesimal strain-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
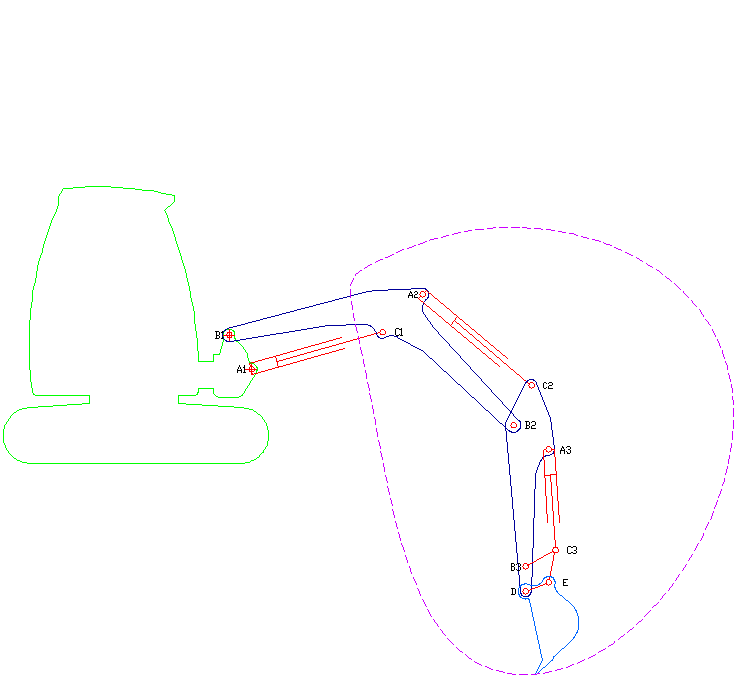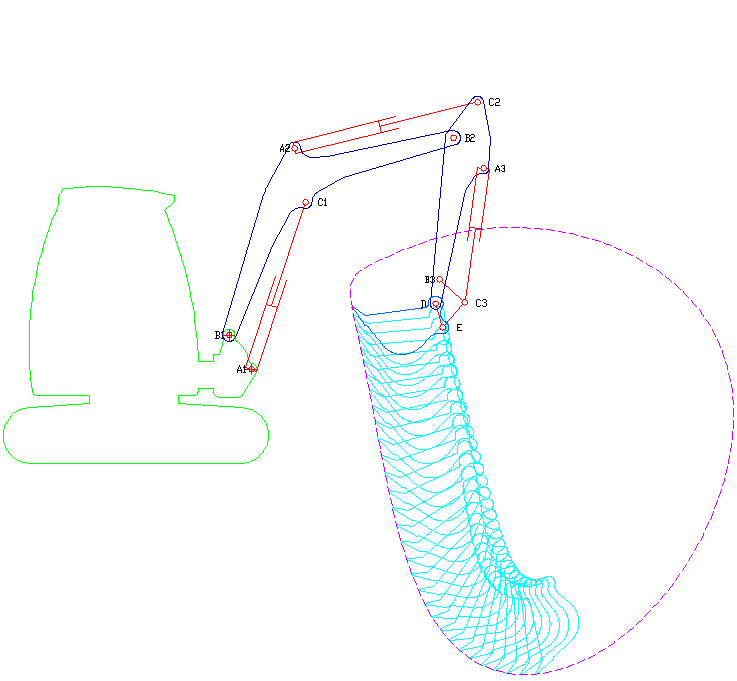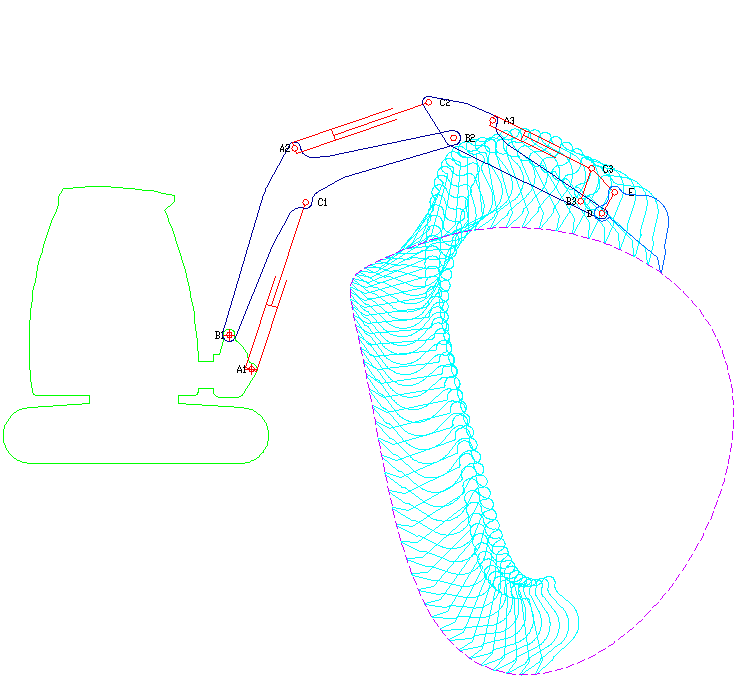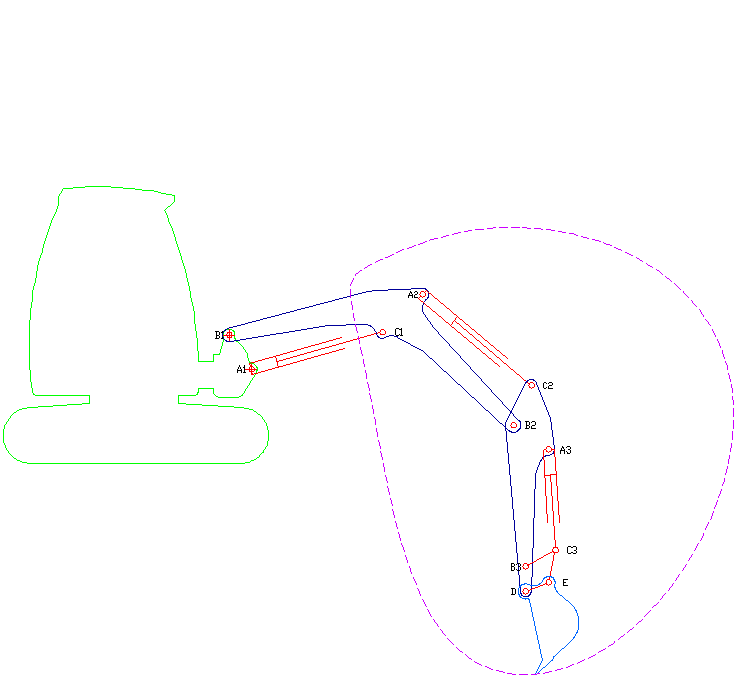
Excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression from the steam shovels and often mistakenly called power shovels. All movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors. Due to the linear actuation of hydraulic cylinders, their mode of operation is fundamentally different from cable-operated excavators which use winches and steel ropes to accomplish the movements. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, JCBs (a proprietary name, in an example of a generic trademark), mechanical shovels, or 360-degree excavators (sometimes abbreviated simply to "360"). Tracked excavators are sometimes called "trackhoes" by analogy to the backhoe. In the UK and Ireland, wheeled excavators are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Load Testing
Dynamic load testing (or dynamic loading) is a method to assess a pile's bearing capacity In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce s ... by applying a dynamic load to the pile head (a falling mass) while recording acceleration and strain on the pile head. Dynamic load testing is a '' high strain dynamic test'' which can be applied ''after ''pile installation for concrete piles. For steel or timber piles, dynamic load testing can be done during installation or after installation. The procedure is standardized by ASTM D4945-00 Standard Test Method for High Strain Dynamic Testing of Piles. It may be performed on all piles, regardless of their installation method. In addition to bearing capacity, Dynamic Load Testing gives information on resistance distribution (shaft resistance an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ Foundation Tests
IN, In or in may refer to: Places * India (country code IN) * Indiana, United States (postal code IN) * Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN) * In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast Businesses and organizations * Independent Network, a UK-based political association * Indiana Northeastern Railroad (Association of American Railroads reporting mark) * Indian Navy, a part of the India military * Infantry, the branch of a military force that fights on foot * IN Groupe , the producer of French official documents * MAT Macedonian Airlines (IATA designator IN) * Nam Air (IATA designator IN) Science and technology * .in, the internet top-level domain of India * Inch (in), a unit of length * Indium, symbol In, a chemical element * Intelligent Network, a telecommunication network standard * Intra-nasal (insufflation), a method of administrating some medications and vaccines * Integrase, a retroviral enzyme Other uses * ''In'' (album), by the Outsiders, 1967 * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |