|
Starting Vortex
In fluid dynamics, the starting vortex is a vortex which forms in the air adjacent to the trailing edge of an airfoil as it is accelerated from rest. It leaves the airfoil (which now has an equal but opposite "bound vortex" around it), and remains (nearly) stationary in the flow. It rapidly decays through the action of viscosity. The initial (and quite brief) presence of a starting vortex as an airfoil begins to move was predicted by early aerodynamicists, and eventually photographed. Whenever the speed or angle of attack of an airfoil changes there is a corresponding amount of vorticity deposited in the wake behind the airfoil, joining the two trailing vortices. This vorticity is a continuum of mini-starting-vortexes. The wake behind an aircraft is a continuous sheet of weak vorticity, between the two trailing vortices, and this accounts for the changes in strength of the trailing vortices as the airspeed of the aircraft and angle of attack on the wing change during fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
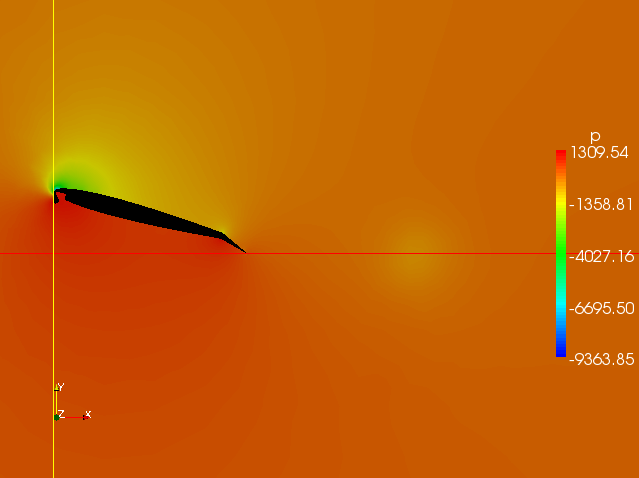
Pressure Distribution Around Flapped Profile With Starting Vortex
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various #Units, units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the International System of Units, SI unit of pressure, the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton (unit), newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the Pound (force), pound-force per square inch (Pounds per square inch, psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial units, imperial and United States customary units, U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulation (fluid Dynamics)
In physics, circulation is the line integral of a vector field around a closed curve. In fluid dynamics, the field is the fluid velocity field. In electrodynamics, it can be the electric or the magnetic field. Circulation was first used independently by Frederick Lanchester, Martin Kutta and Nikolay Zhukovsky. It is usually denoted Γ (Greek uppercase gamma). Definition and properties If V is a vector field and dl is a vector representing the differential length of a small element of a defined curve, the contribution of that differential length to circulation is dΓ: :\mathrm\Gamma=\mathbf\cdot \mathrm\mathbf=, \mathbf, , \mathrm\mathbf, \cos \theta. Here, ''θ'' is the angle between the vectors V and dl. The circulation Γ of a vector field V around a closed curve ''C'' is the line integral: :\Gamma=\oint_\mathbf\cdot \mathrm d \mathbf. In a conservative vector field this integral evaluates to zero for every closed curve. That means that a line integral between any two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wake Turbulence
Wake turbulence is a disturbance in the atmosphere that forms behind an aircraft as it passes through the air. It includes variety of elements, the most significant of which are wingtip vortices and jetwash. Jetwash refers to the rapidly moving gases expelled from a jet engine; it is extremely turbulent but of short duration. Wingtip vortices, however, are much more stable and can remain in the air for up to three minutes after the passage of an aircraft. It is therefore not true turbulence in the aerodynamic sense, as true turbulence would be chaotic. Instead, it refers to the similarity to atmospheric turbulence as experienced by an aircraft flying through this region of disturbed air. Wingtip vortices occur when a wing is generating lift. Air from below the wing is drawn around the wingtip into the region above the wing by the lesser amount of pressure above the wing, causing a vortex to trail from each wingtip. The strength of wingtip vortices is determined primarily by the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutta–Joukowski Theorem
The Kutta–Joukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil (and any two-dimensional body including circular cylinders) translating in a uniform fluid at a constant speed large enough so that the flow seen in the body-fixed frame is steady and unseparated. The theorem relates the lift generated by an airfoil to the speed of the airfoil through the fluid, the density of the fluid and the circulation around the airfoil. The circulation is defined as the line integral around a closed loop enclosing the airfoil of the component of the velocity of the fluid tangent to the loop. It is named after Martin Kutta and Nikolai Zhukovsky (or Joukowski) who first developed its key ideas in the early 20th century. Kutta–Joukowski theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications. Kutta–Joukowski theorem relates lift to circulation much like the Magnus effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz's Theorems
In fluid mechanics, Helmholtz's theorems, named after Hermann von Helmholtz, describe the three-dimensional motion of fluid in the vicinity of vortex lines. These theorems apply to inviscid flows and flows where the influence of viscous forces are small and can be ignored. Helmholtz's three theorems are as follows: ;Helmholtz's first theorem: :The strength of a vortex line is constant along its length. ;Helmholtz's second theorem: :A vortex line cannot end in a fluid; it must extend to the boundaries of the fluid or form a closed path. ;Helmholtz's third theorem: :A fluid element that is initially irrotational remains irrotational. Helmholtz's theorems apply to inviscid flows. In observations of vortices in real fluids the strength of the vortices always decays gradually due to the dissipative effect of viscous forces. Alternative expressions of the three theorems are as follows: # The strength of a vortex tube does not vary with time. # Fluid elements lying on a vortex line at so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence Clancy
Laurence Joseph Clancy (15 March 1929 - 16 October 2014) was an Education Officer in aerodynamics at Royal Air Force College Cranwell whose textbook ''Aerodynamics'' became standard. He was born in Egypt to Alfred Joseph Clancy and Agnes Hunter. In 1951 he gained a BsC (Hons) degree from the University of Liverpool.In Memoriam from Clancy studied aerodynamics at the College of Aeronautics at , where his teachers we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plume (hydrodynamics)
In hydrodynamics, a plume or a column is a vertical body of one fluid moving through another. Several effects control the motion of the fluid, including momentum (inertia), diffusion and buoyancy (density differences). Pure ''jets'' and pure ''plumes'' define flows that are driven entirely by momentum and buoyancy effects, respectively. Flows between these two limits are usually described as forced plumes or buoyant jets. "Buoyancy is defined as being positive" when, in the absence of other forces or initial motion, the entering fluid would tend to rise. Situations where the density of the plume fluid is greater than its surroundings (i.e. in still conditions, its natural tendency would be to sink), but the flow has sufficient initial momentum to carry it some distance vertically, are described as being negatively buoyant. Movement Usually, as a plume moves away from its source, it widens because of entrainment of the surrounding fluid at its edges. Plume shapes can be influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lift (force)
A fluid flowing around an object exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direction. Lift conventionally acts in an upward direction in order to counter the force of gravity, but it can act in any direction at right angles to the flow. If the surrounding fluid is air, the force is called an aerodynamic force. In water or any other liquid, it is called a hydrodynamic force. Dynamic lift is distinguished from other kinds of lift in fluids. Aerostatic lift or buoyancy, in which an internal fluid is lighter than the surrounding fluid, does not require movement and is used by balloons, blimps, dirigibles, boats, and submarines. Planing lift, in which only the lower portion of the body is immersed in a liquid flow, is used by motorboats, surfboards, windsurfers, sailboats, and water-skis. Overview A fluid flowing arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutta Condition
The Kutta condition is a principle in steady-flow fluid dynamics, especially aerodynamics, that is applicable to solid bodies with sharp corners, such as the trailing edges of airfoils. It is named for German mathematician and aerodynamicist Martin Kutta. Kuethe and Schetzer state the Kutta condition as follows:A body with a sharp trailing edge which is moving through a fluid will create about itself a circulation of sufficient strength to hold the rear stagnation point at the trailing edge. In fluid flow around a body with a sharp corner, the Kutta condition refers to the flow pattern in which fluid approaches the corner from above and below, meets at the corner, and then flows away from the body. None of the fluid flows around the sharp corner. The Kutta condition is significant when using the Kutta–Joukowski theorem to calculate the lift created by an airfoil with a sharp trailing edge. The value of circulation of the flow around the airfoil must be that value which woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wingtip Vortices
Wingtip vortices are circular patterns of rotating air left behind a wing as it generates lift.Clancy, L.J., ''Aerodynamics'', section 5.14 One wingtip vortex trails from the tip of each wing. Wingtip vortices are sometimes named ''trailing'' or ''lift-induced vortices'' because they also occur at points other than at the wing tips. Indeed, vorticity is trailed at any point on the wing where the lift varies span-wise (a fact described and quantified by the lifting-line theory); it eventually rolls up into large vortices near the wingtip, at the edge of flap devices, or at other abrupt changes in wing planform. Wingtip vortices are associated with induced drag, the imparting of downwash, and are a fundamental consequence of three-dimensional lift generation. Careful selection of wing geometry (in particular, wingspan), as well as of cruise conditions, are design and operational methods to minimize induced drag. Wingtip vortices form the primary component of wake turbulence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |