|
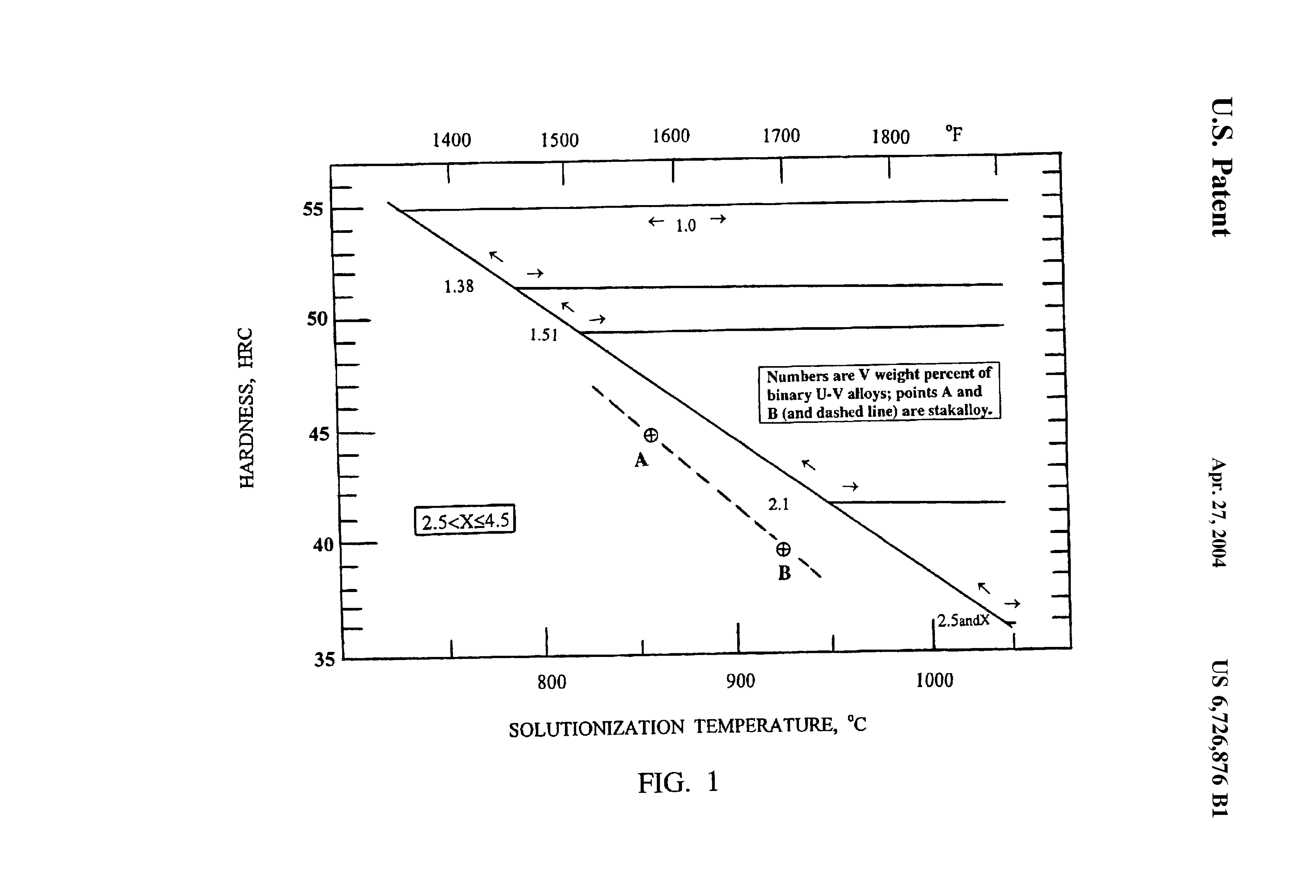
Stakalloy
Stakalloy is a ternary alloy of uranium composed of vanadium, niobium, and depleted uranium. The alloy was developed in 2002 by Michael R. Staker of Loyola University Maryland under grant from the United States Army. Composition The niobium content of stakalloy is between 0.01 to 0.95 percent by weight and the balance being uranium. The vanadium content of the alloy is between the gamma eutectoid and the eutectic compositions, 1.0 percent and 4.5 percent by weight respectively. Properties Stakalloy has improved metallurgical properties over other depleted uranium alloys, such as staballoy, being more viable as a structural alloy where a combination between Strength of materials, high strength and high density is required. Changes include that of density, hardness, ballistic properties, and machinability. Production Staker's invention of stakalloy involved reducing excessive carbon levels while adding together uranium with trace amounts of niobium and vanadium. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stakalloy
Stakalloy is a ternary alloy of uranium composed of vanadium, niobium, and depleted uranium. The alloy was developed in 2002 by Michael R. Staker of Loyola University Maryland under grant from the United States Army. Composition The niobium content of stakalloy is between 0.01 to 0.95 percent by weight and the balance being uranium. The vanadium content of the alloy is between the gamma eutectoid and the eutectic compositions, 1.0 percent and 4.5 percent by weight respectively. Properties Stakalloy has improved metallurgical properties over other depleted uranium alloys, such as staballoy, being more viable as a structural alloy where a combination between Strength of materials, high strength and high density is required. Changes include that of density, hardness, ballistic properties, and machinability. Production Staker's invention of stakalloy involved reducing excessive carbon levels while adding together uranium with trace amounts of niobium and vanadium. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staballoy
] Staballoy is the name of two different classes of metal alloys, one class typically used for munitions and a different class developed for drilling rods. Kinetic penetrators In a military context, staballoys are metal alloys of a high proportion of depleted uranium with other metals, usually titanium or molybdenum, designed for use in kinetic energy penetrator armor-piercing munitions. One formulation has a composition of 99.25% of depleted uranium and 0.75% of titanium. Other variants can have 3.5% of titanium. They are about 65% more dense than lead. An alternative to staballoys in kinetic penetrator munition is tungsten, but it is more expensive, more difficult to machine and is not pyrophoric, so the munition lacks the incendiary effect enhancing its impact. Tungsten penetrators also tend to form a mushroom shaped tip during armor penetration, while uranium ones tend to be self-sharpening. An emerging alternative alloy of depleted uranium is stakalloy, formed of niobium (0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30mm DU Slug
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter. Measuring hardness There are three main types of hardness measurements: ''scratch' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy Penetrator
A kinetic energy penetrator (KEP), also known as long-rod penetrator (LRP), is a type of ammunition designed to penetrate vehicle armour using a flechette-like, high-sectional density projectile. Like a bullet or kinetic energy weapon, this type of ammunition does not contain explosive payloads and uses purely kinetic energy to penetrate the target. Modern KEP munitions are typically of the armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) type. History Early cannons fired kinetic energy ammunition, initially consisting of heavy balls of worked stone and later of dense metals. From the beginning, combining high muzzle energy with projectile weight and hardness have been the foremost factors in the design of such weapons. Similarly, the foremost purpose of such weapons has generally been to defeat protective shells of armored vehicles or other defensive structures, whether it is stone walls, sailship timbers, or modern tank armour. Kinetic energy ammunition, in its vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789). See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabot Separating , a mansion in Senneville, Quebec, Canada
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Sabot may refer to: * Sabot (firearms), disposable supportive device used in gunpowder ammunitions to fit/patch around a sub-caliber projectile * Sabot (shoe), a type of wooden shoe People * Dick Sabot (1944–2005), American economist and businessman * Hamilton Sabot (born 1987), French gymnast Vessels * Sabot (dinghy), a type of leeboard dinghy * Naples Sabot, a type of centerboard dinghy * US Sabot, an American sailing dinghy * , a motorboat acquired by but never commissioned into the United States Navy Other uses * Sabot (newspaper), a former US newspaper * Le Sabot Le Sabot is a mansion built in 1912, in the town of Senneville, Quebec, for F. Cleveland Morgan. Morgan was a cultural philanthropist and department store owner and the great-nephew of the founder of the Henry Morgan & Co department stores. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucible
A crucible is a ceramic or metal container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. While crucibles were historically usually made from clay, they can be made from any material that withstands temperatures high enough to melt or otherwise alter its contents. History Typology and chronology The form of the crucible has varied through time, with designs reflecting the process for which they are used, as well as regional variation. The earliest crucible forms derive from the sixth/fifth millennium B.C. in Eastern Europe and Iran. Chalcolithic Crucibles used for copper smelting were generally wide shallow vessels made from clay that lacks refractory properties which is similar to the types of clay used in other ceramics of the time. During the Chalcolithic period, crucibles were heated from the top by using blowpipes.Hauptmann A., 2003, ''Developments in copper Metallurgy During the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C. at Feinan'', Jorda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Arc Furnace
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc. Industrial arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one-tonne capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to about 400-tonne units used for secondary steelmaking. Arc furnaces used in research laboratories and by dentists may have a capacity of only a few dozen grams. Industrial electric arc furnace temperatures can reach , while laboratory units can exceed . In electric arc furnaces, the charged material (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with electric charge) is directly exposed to an electric arc, and the current from the furnace terminals passes through the charged material. Arc furnaces differ from induction furnaces, in which the charge is heated instead by eddy currents. History In the 19th century, a number of people had employed an electric arc to melt iron. Sir Humphry Davy conducted an experimental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machinability
Machinability is the ease with which a metal can be cut (machined) permitting the removal of the material with a satisfactory finish at low cost.Degarmo, p. 542. Materials with good machinability (free machining materials) require little power to cut, can be cut quickly, easily obtain a good finish, and do not cause significant wear on the tooling. Factors that typically improve a material's performance often degrade its machinability, presenting a significant engineering challenge. Machinability can be difficult to predict due to the large number of variables involved in the machining process. Two sets of factors are the condition of work materials and the physical properties of work materials. The condition of the work material includes at least eight factors: microstructure, grain size, heat treatment, chemical composition, fabrication, hardness, yield strength, and tensile strength.Schneider, "Machinability." Physical properties are those of the individual material groups, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strength Of Materials
The field of strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials, typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes takes into account the properties of the materials such as its yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio. In addition, the mechanical element's macroscopic properties (geometric properties) such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered. The theory began with the consideration of the behavior of one and two dimensional members of structures, whose states of stress can be approximated as two dimensional, and was then generalized to three dimensions to develop a more complete theory of the elastic and plastic behavior of materials. An important founding pion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |