|
Spin–statistics Theorem
In quantum mechanics, the spin–statistics theorem relates the intrinsic spin of a particle (angular momentum not due to the orbital motion) to the particle statistics it obeys. In units of the reduced Planck constant ''ħ'', all particles that move in 3 dimensions have either integer spin or half-integer spin. Background Quantum states and indistinguishable particles In a quantum system, a physical state is described by a state vector. A pair of distinct state vectors are physically equivalent if they differ only by an overall phase factor, ignoring other interactions. A pair of indistinguishable particles such as this have only one state. This means that if the positions of the particles are exchanged (i.e., they undergo a permutation), this does not identify a new physical state, but rather one matching the original physical state. In fact, one cannot tell which particle is in which position. While the physical state does not change under the exchange of the particles' pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Statistics
Particle statistics is a particular description of multiple particles in statistical mechanics. A key prerequisite concept is that of a statistical ensemble (an idealization comprising the state space of possible states of a system, each labeled with a probability) that emphasizes properties of a large system as a whole at the expense of knowledge about parameters of separate particles. When an ensemble describes a system of particles with similar properties, their number is called the particle number and usually denoted by ''N''. Classical statistics In classical mechanics, all particles ( fundamental and composite particles, atoms, molecules, electrons, etc.) in the system are considered distinguishable. This means that individual particles in a system can be tracked. As a consequence, switching the positions of any pair of particles in the system leads to a different configuration of the system. Furthermore, there is no restriction on placing more than one particle in any giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
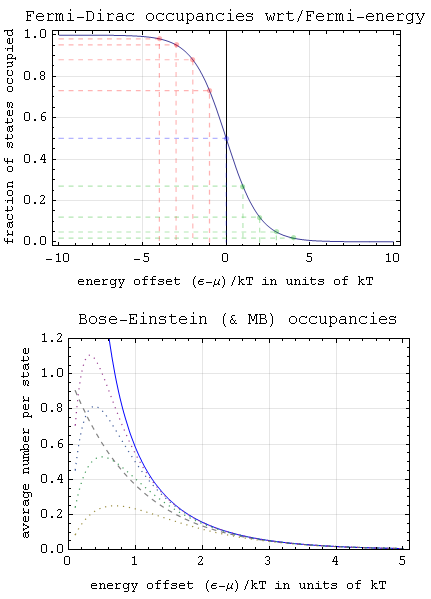
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spin (,, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Bosons are named after physicist Satyendra Nath Bose. Some bosons are elementary particles and occupy a special role in particle physics unlike that of fermions, which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter". Some elementary bosons (for example, gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) gives rise to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, superfluidity arises because composite bosons (bose particles), such as low temperature helium-4 atoms, follow Bose� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress Of Theoretical Physics
''Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics'' (PTEP) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Physical Society of Japan. It was established as ''Progress of Theoretical Physics'' in July 1946 by Hideki Yukawa was a Japanese theoretical physicist and the first Japanese Nobel laureate for his prediction of the pi meson, or pion. Biography He was born as Hideki Ogawa in Tokyo and grew up in Kyoto with two older brothers, two older sisters, and two ... and obtained its current name in January 2013. ''Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics'' is part of the SCOAP3 initiative. References External links * Physics journals English-language journals Publications established in 1946 Theoretical physics Monthly journals Oxford University Press academic journals Open access journals Particle physics journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Books
Basic Books is a book publisher founded in 1950 and located in New York, now an imprint of Hachette Book Group. It publishes books in the fields of psychology, philosophy, economics, science, politics, sociology, current affairs, and history. History Basic Books originated as a small Greenwich Village-based book club marketed to psychoanalysts. Arthur Rosenthal took over the book club in 1950, and under his ownership it soon began producing original books, mostly in the behavioral sciences. Early successes included Ernest Jones's ''The Life and Work of Sigmund Freud'', as well as works by Claude Lévi-Strauss, Jean Piaget and Erik Erikson. Irving Kristol joined Basic Books in 1960, and helped Basic to expand into the social sciences. Harper & Row purchased the company in 1969. In 1997, HarperCollins announced that it would merge Basic Books into its trade publishing program, effectively closing the imprint and ending its publishing of serious academic books. That same year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitarity
In quantum physics, unitarity is the condition that the time evolution of a quantum state according to the Schrödinger equation is mathematically represented by a unitary operator. This is typically taken as an axiom or basic postulate of quantum mechanics, while generalizations of or departures from unitarity are part of speculations about theories that may go beyond quantum mechanics. A unitarity bound is any inequality that follows from the unitarity of the evolution operator, i.e. from the statement that time evolution preserves inner products in Hilbert space. Hamiltonian evolution Time evolution described by a time-independent Hamiltonian is represented by a one-parameter family of unitary operators, for which the Hamiltonian is a generator: U(t) = e^. In the Schrödinger picture, the unitary operators are taken to act upon the system's quantum state, whereas in the Heisenberg picture, the time dependence is incorporated into the observables instead. Implications of un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, as well as his work in particle physics for which he proposed the parton model. For contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga. Feynman developed a widely used pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles, which later became known as Feynman diagrams. During his lifetime, Feynman became one of the best-known scientists in the world. In a 1999 poll of 130 leading physicists worldwide by the British journal '' Physics World'', he was ranked the seventh-greatest physicist of all time. He assisted in the develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Schwinger
Julian Seymour Schwinger (; February 12, 1918 – July 16, 1994) was a Nobel Prize winning American theoretical physicist. He is best known for his work on quantum electrodynamics (QED), in particular for developing a relativistically invariant perturbation theory, and for renormalizing QED to one loop order. Schwinger was a physics professor at several universities. Schwinger is recognized as one of the greatest physicists of the twentieth century, responsible for much of modern quantum field theory, including a variational approach, and the equations of motion for quantum fields. He developed the first electroweak model, and the first example of confinement in 1+1 dimensions. He is responsible for the theory of multiple neutrinos, Schwinger terms, and the theory of the spin-3/2 field. Biography Early life and career Julian Seymour Schwinger was born in New York City, to Ashkenazi Jewish parents, Belle (née Rosenfeld) and Benjamin Schwinger, a garment manufacturer, who had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, ''Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publication in 1913 and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle". The discovery involved spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the structure of matter. Early years Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, Wolfgang Joseph Pauli (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent families of Prague; his great-grandfather was the publisher Wolf Pascheles. Pauli's mother, Bertha Schütz, was raised in her mother's Roman Catholic religion; Pauli was raised as a Roman Catholic, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markus Fierz
Markus Eduard Fierz (20 June 1912 – 20 June 2006) was a Swiss physicist, particularly remembered for his formulation of spin–statistics theorem, and for his contributions to the development of quantum theory, particle physics, and statistical mechanics. He was awarded the Max Planck Medal in 1979 and the Albert Einstein Medal in 1989 for all his work. Biography Fierz's father Hans Eduard Fierz was a chemist with Geigy and later a professor at ETH Zurich, his mother was Linda Fierz-David. Fierz studied at the Realgymnasium in Zurich. In 1931 he began his studies in Göttingen, where he listened to the lectures of prolific academics including Hermann Weyl. In 1933 he returned to Zurich and studied physics at ETH under Wolfgang Pauli and Gregor Wentzel. In 1936 he earned a doctoral degree with his thesis on the infrared catastrophe in quantum electrodynamics. Afterward he went to Werner Heisenberg in Leipzig and in 1936 became an assistant to Wolfgang Pauli in Zurich. For his ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacelike
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum State
In quantum field theory, the quantum vacuum state (also called the quantum vacuum or vacuum state) is the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. Generally, it contains no physical particles. The word zero-point field is sometimes used as a synonym for the vacuum state of a quantized field which is completely individual. According to present-day understanding of what is called the vacuum state or the quantum vacuum, it is "by no means a simple empty space". According to quantum mechanics, the vacuum state is not truly empty but instead contains fleeting electromagnetic waves and particles that pop into and out of the quantum field. The QED vacuum of quantum electrodynamics (or QED) was the first vacuum of quantum field theory to be developed. QED originated in the 1930s, and in the late 1940s and early 1950s it was reformulated by Feynman, Tomonaga, and Schwinger, who jointly received the Nobel prize for this work in 1965. For a historical discussion, see fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |