|
Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus
The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature from the ipsilateral face. In addition to the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), and vagus nerves (CN X) also convey pain information from their areas to the spinal trigeminal nucleus. Thus the spinal trigeminal nucleus receives input from V, , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus (plural form: nuclei) is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons (nerve fibers) extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers. The term "nucleus" is in some cases used rather loosely, to mean simply an identifiably distinct group of neurons, even if they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
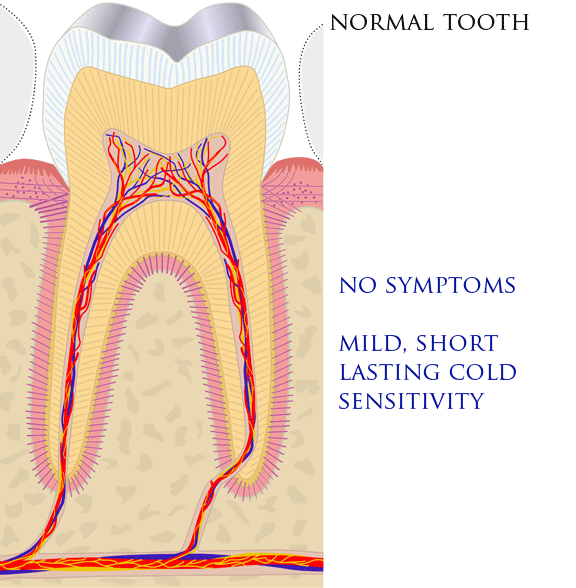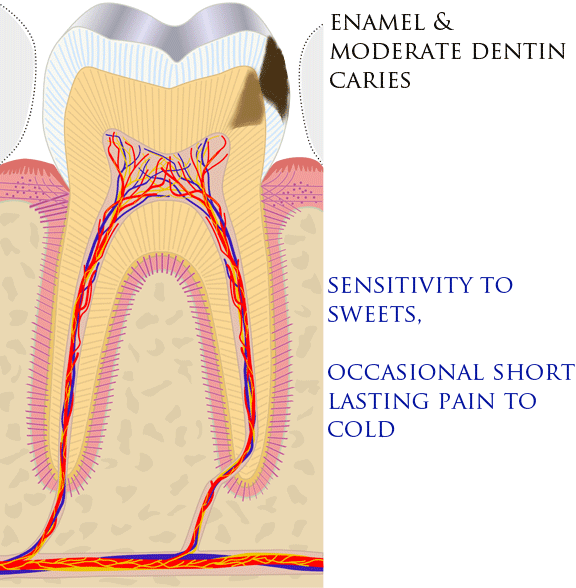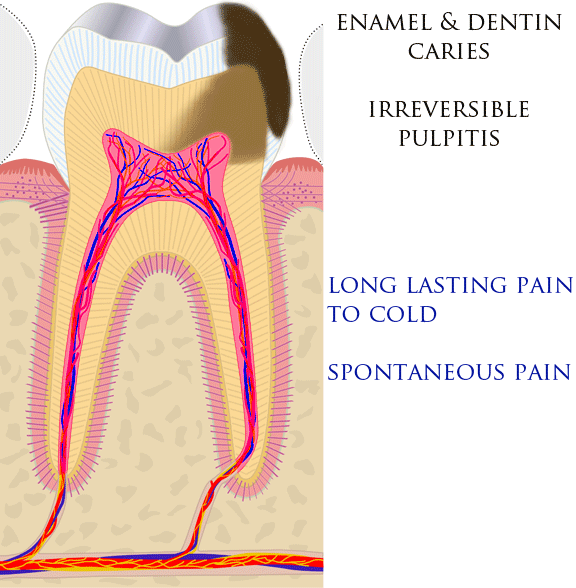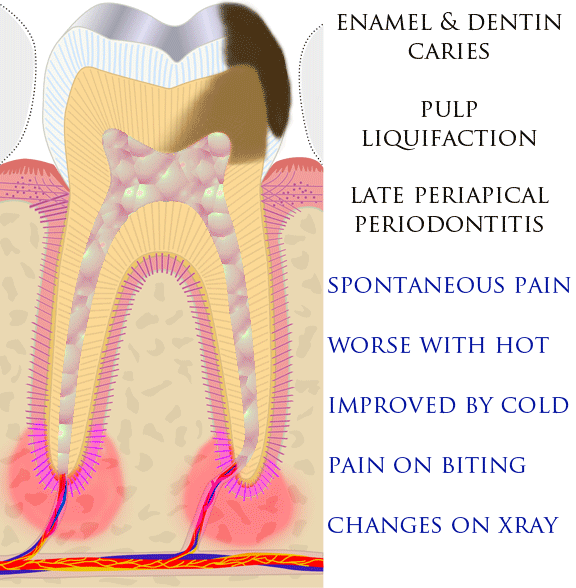
Dental Pain
Toothache, also known as dental pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities. Common causes include inflammation of the pulp, (usually in response to tooth decay, dental trauma, or other factors), dentin hypersensitivity, apical periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone around the root apex), dental abscesses (localized collections of pus), alveolar osteitis ("dry socket", a possible complication of tooth extraction), acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (a gum infection), and temporomandibular disorder. Pulpitis is reversible when the pain is mild to moderate and lasts for a short time after a stimulus (for instance cold); or irreversible when the pain is severe, spontaneous, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve) and anterior to cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). The facial nerve also supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to several head and neck ganglia. The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis. The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: # intracranial (cisternal) segment # meatal (canalicular) segment (within the internal auditory canal) # labyrinthine segment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerve Nuclei
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons (gray matter) in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve (CN IV) supply nerves of the same side of the body. Structure Motor and sensory In general, motor nuclei are closer to the front (ventral), and sensory nuclei and neurons are closer to the back (dorsal). This arrangement mirrors the arrangement of tracts in the spinal cord. * Close to the midline are the motor efferent nuclei, such as the oculomotor nucleus, which control skeletal muscle. Just lateral to this are the autonomic (or visceral) efferent nuclei. * There is a separation, called the sulcus limitans, and lateral to this are the sensory nuclei. Near the sulcus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Nerve Nuclei
The sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei, and extend through the whole of the midbrain, pons and medulla, and into the high cervical spinal cord. The nucleus is divided into three parts, from rostral to caudal (top to bottom in humans): * The mesencephalic nucleus * The chief sensory nucleus (or "pontine nucleus" or "main sensory nucleus" or "primary nucleus" or "principal nucleus") * The spinal trigeminal nucleus ::The spinal trigeminal nucleus is further subdivided into three parts, from rostral to caudal: :* Pars Oralis (from the Pons to the Hypoglossal nucleus) :* Pars Interpolaris (from the Hypoglossal nucleus to the obex) :* Pars Caudalis (from the obex to C2) There is also a distinct trigeminal motor nucleus that is medial to the chief sensory nucleus. See also * Photic sneeze reflex * Trigeminal nerve In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from the tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region. Alongside glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), GLP-1 is an incretin; thus, it has the ability to decrease blood sugar levels in a glucose-dependent manner by enhancing the secretion of insulin. Beside the insulinotropic effects, GLP-1 has been associated with numerous regulatory and protective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the mammalian central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate. In the autonomic system it is produced mainly by neurons of the sympathetic nervous system and serves as a strong vasoconstrictor and also causes growth of fat tissue. In the brain, it is produced in various locations including the hypothalamus, and is thought to have several functions, including: increasing food intake and storage of energy as fat, reducing anxiety and stress, reducing pain perception, affecting the circadian rhythm, reducing voluntary alcohol intake, lowering blood pressure, and controlling epileptic seizures. Function Neuropeptide Y has been identified as bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptin
Leptin (from Ancient Greek, Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate Energy homeostasis, energy balance by inhibiting Hunger (motivational state), hunger, which in turn diminishes fat storage in adipocytes. Leptin is coded for by the ''LEP'' gene. Leptin acts on cell receptors in the arcuate nucleus, arcuate and Ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus, ventromedial nuclei, as well as other parts of the hypothalamus and Dopamine, dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area, consequently mediating Eating, feeding. Although regulation of fat stores is deemed to be the primary function of leptin, it also plays a role in other physiological processes, as evidenced by its many sites of synthesis other than fat cells, and the many cell types beyond hypothalamic cells that have leptin receptors. Many of these additional functions are yet to be fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Trigeminal Tract
The ventral trigeminal tract, ventral trigeminothalamic tract, anterior trigeminal tract, or anterior trigeminothalamic tract, is a tract composed of second order neuronal axons. These fibers carry sensory information about discriminative and crude touch, conscious proprioception, pain, and temperature from the head, face, and oral cavity. The ventral trigeminal tract connects the two major components of the brainstem trigeminal complex – the principal, or main sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal nucleus, to the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus. The ventral trigeminal tract is also called the anterior trigeminal lemniscus. Structure The first order neurons (from the trigeminal ganglion) enter the pons and synapse in the principal (chief sensory) nucleus or spinal trigeminal nucleus. Axons of the second order neurons cross the midline and terminate in the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the contralateral thalamus (as opposed to the ventral posterolateral nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus
The ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) is a nucleus of the thalamus. Inputs and outputs The VPM contains synapses between second and third order neurons from the anterior (ventral) trigeminothalamic tract and posterior (dorsal) trigeminothalamic tract. These neurons convey sensory information from the face and oral cavity. Third order neurons in the trigeminothalamic systems project to the postcentral gyrus. The VPM also receives taste afferent information from the solitary tract The solitary tract (tractus solitarius, or fasciculus solitarius), is a compact fiber bundle that extends longitudinally through the posterolateral region of the medulla oblongata. The solitary tract is surrounded by the solitary nucleus, and des ... and projects to the cortical gustatory area. Subareas VPMpc The parvicellular part of the ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPMpc) is argued by some as not an actually part of the VPM, because it does not project to the somatosensory cortex as the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal in order to trigger an appropriate defense response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in Chili pepper or Cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers via the spinal cord to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are detected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |