|
Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen. Function Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its formation from putrescine. It is a precursor to other polyamines, such as spermine and its structural isomer thermospermine. Spermidine synchronizes an array of biological processes, (such as Ca2+, Na+, K+ -ATPase) thus maintaining membrane potential and controlling intracellular pH and volume. Spermidine regulates biological processes, such as Ca2+ influx by glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor), which has been associated with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cGMP/PKG pathway activation and a decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex synaptosomes. Spermidine is a longevity agent in mammals due to various mechanisms of action, which are just beginning to be understood. Autophagy is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norspermidine
Norspermidine is a polyamine of similar structure to the more common spermidine Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen. Function Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS .... While norspermidine has been found to occur naturally in some species of plants, bacteria, and algae, it is not known to exist in humans. Norspermidine is being researched for use as a cancer medication. References {{reflist Polyamines Secondary amines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermidine Synthase
Spermidine synthase is an enzyme () that catalyzes the transfer of the propylamine group from ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine to putrescine in the biosynthesis of spermidine. The systematic name is S-adenosyl 3-(methylthio)propylamine:putrescine 3-aminopropyltransferase and it belongs to the group of aminopropyl transferases. It does not need any cofactors. Most spermidine synthases exist in solution as dimers. Specificity With exception of the spermidine synthases from ''Thermotoga maritimum'' and from ''Escherichia coli'', which accept different kinds of polyamines, all enzymes are highly specific for putrescine. No known spermidine synthase can use ''S''-adenosyl methionine. This is prevented by a conserved aspartatyl residue in the active site, which is thought to repel the carboxyl moiety of ''S''-adenosyl methionine. The putrescine-N-methyl transferase whose substrates are putrescine and ''S''-adenosyl methionine and which is evolutionary related to the spermidine synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyamine Synthesis
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature. Natural polyamines Low-molecular-weight linear polyamines are found in all forms of life. The principal examples are the triamine spermidine and the tetraamine spermine. They are structurally and biosynthetically related to the diamines putrescine and cadaverine. Polyamine metabolism is regulated by the activity of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Polyamines are found in high concentrations in the mammalian brain. File:Spermidine-2D-skeletal.svg, spermidine File:Spermine.svg, spermine Synthetic polyamines Several synthetic polyamines are used in chemical industry and the research laboratory. They are mainly of interest as additives to motor oil and as co-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contributes to other unpleasant odors. Production Putrescine is produced on an industrial scale by the hydrogenation of succinonitrile. Biotechnological production of putrescine from renewable feedstock has been investigated. A metabolically engineered strain of ''Escherichia coli'' that produces putrescine at high concentrations in glucose mineral salts medium has been described. Biochemistry Spermidine synthase uses putrescine and ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine (decarboxylated ''S''-adenosyl methionine) to produce spermidine. Spermidine in turn is combined with another ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine and gets converted to spermine. Putrescine is synthesized in small quantities by healthy living cells by the action of ornithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermine
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described crystals of spermine phosphate in human semen in 1678. The name ''spermin'' was first used by the German chemists Ladenburg and Abel in 1888, and the correct structure of spermine was not finally established until 1926, simultaneously in England (by Dudley, Rosenheim, and Starling) and Germany (by Wrede et al.). Spermine is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen. Derivative A derivative of spermine, N1, N12-bis(ethyl)spermine (also known as BESm) was investigated in the late 1980s along with similar polyamine analogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl-n-amylnitrosamine
Methyl-''n''-amylnitrosamine (MNAN) is a potential carcinogen It is metabolized in the liver by the enzyme CYP2A6 Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and .... References Carcinogens Nitrosamines {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipropylamine
It occurs naturally in tobacco leaves and artificially in industrial wastes. Exposure can cause excitement followed by depression, internal bleeding, dystrophy Dystrophy is the degeneration of tissue, due to disease or malnutrition, most likely due to heredity. Types * Muscular dystrophy ** Duchenne muscular dystrophy ** Becker's muscular dystrophy ** Myotonic dystrophy * Reflex neurovascular dyst ..., and severe irritation. References Alkylamines Secondary amines Propyl compounds {{amine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Semen is produced and originates from the seminal vesicle, which is located in the pelvis. The process that results in the discharge of semen from the urethral orifice is called ejaculation. In humans, seminal fluid contains several components besides spermatozoa: proteolytic and other enzymes as well as fructose are elements of seminal fluid which promote the survival of spermatozoa, and provide a medium through which they can move or "swim". The fluid is designed to be discharged deep into the vagina, so the spermatozoa can pass into the uterus and form a zygote with an egg. Semen is also a form of genetic material. In animals, semen has been collected for cryoconservation. Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is a practice th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
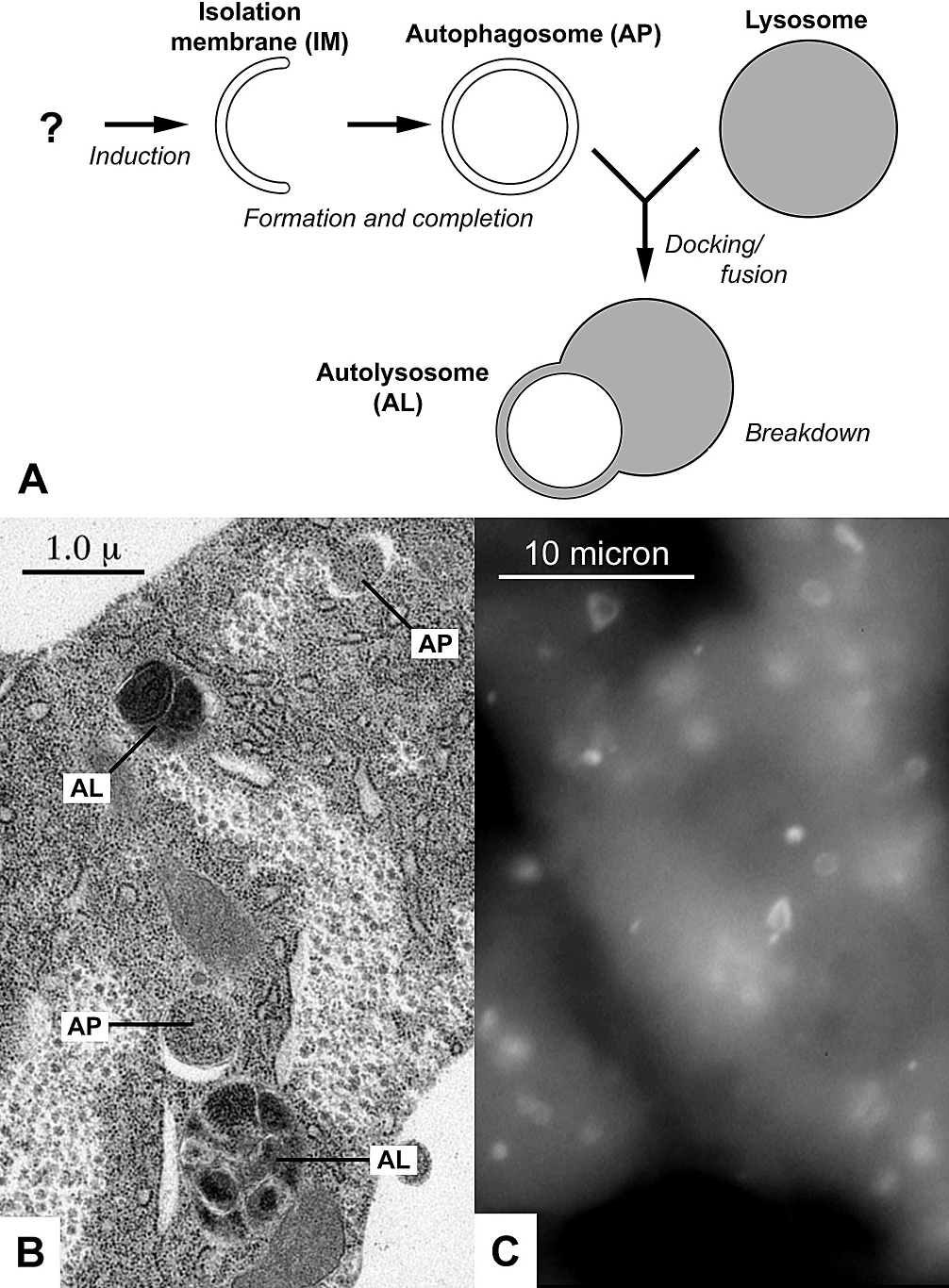
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |