|
Sparkling Enope Squid
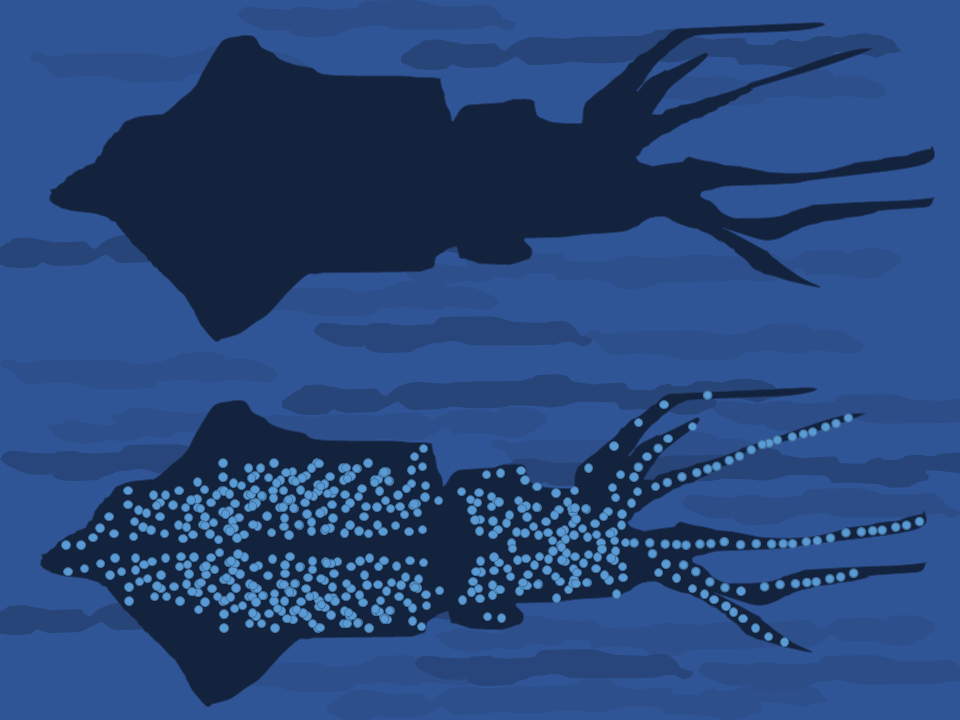
The firefly squid (''Watasenia scintillans''), also commonly known as the sparkling enope squid or hotaru-ika in Japan, is a species of squid in the family Enoploteuthidae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus ''Watasenia''. These tiny squid are found on the shores of Japan in springtime during spawning season, but spend most of their lives in deeper waters between . They are bioluminescent organisms and emit blue light from photophores, which some scientists have hypothesized could be used for communication, camouflage, or attracting food, but it is still unclear in the scientific community exactly how this species uses their bioluminescence. The firefly squid is a predator and actively hunts its food, which includes copepods, small fish, and other squids. The lifespan of a firefly squid is about one year. At the end of their lives females return close to shore to release their eggs, and then die shortly thereafter. This mass migration of firefly squid to the shore is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiyomatsu Ishikawa
was a Japanese biologist, zoologist, evolutionary theorist, and ichthyologist at the Naples Zoological Station starting 1887. He was responsible for disseminating Darwin's ideas on evolution in Japan. Biography Ishikawa Chiyomatsu was born in Edo as a son of a high-ranking samurai, a Hatamoto. But the Meiji Restoration occurred and when the Tokugawa shogunate collapsed, he moved to Sunpu (Shizuoka prefecture) in 1867. In 1972, he returned to Tokyo and studied English. He entered the Tokyo Kaisei Gakko, which was a high education college belonging Ministry of Education in 1876. His was taught by Montague Arthur Fenton, which influenced Chiyomatsu to start a collection of butterflies. Chiyomatsu entered the Tokyo Imperial University in 1978, and studied under Edward S. Morse. After Morse left Japan, his teachers were Charles Otis Whitman and Kakichi Mitsukuri. After graduating from the Tokyo Imperial University, he studied in Germany under eminent evolutionary theorist August Weis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diel Vertical Migration
Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The word ''diel'' comes from the Latin ''dies'' day, and means a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the sea at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. It is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically driven sequestration of carbon. In terms of biomass, it is the largest synchronous migration in the world. It is not restricted to any one taxon as examples are known from crustaceans (copepods), molluscs ( squid), and ray-finned fishes (trout). The phenomenon may be advantageous for a number of reasons, most typically to access food and avoid predators. It is triggered by various stimuli, the most prominent being response to changes in ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescent Molluscs
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Special Places Of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites And Special Natural Monuments
To protect Japan's cultural heritage, the country's government selects through the Agency for Cultural Affairs important items and designates them as Cultural Properties under the Law for the Protection of Cultural Properties. Designated items are classified in a number of categories, one of which is . This category includes historic locations such as shell mounds, ancient tombs, sites of palaces, sites of forts or castles, monumental dwelling houses and other sites of high historical or scientific value; gardens, bridges, gorges, mountains, and other places of great scenic beauty; and natural features such as animals, plants, and geological or mineral formations of high scientific value. The government further designates "significant" monuments classifying them in three categories: , , and . Items of particularly high significance receive higher classifications: , , and respectively. As of December 17, 2022 there are 1,038 Natural Monuments, 1881 Historic Sites, 427 Places of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiled Firefly Squids (2014
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. There are two main types of boiling: nucleate boiling where small bubbles of vapour form at discrete points, and critical heat flux boiling where the boiling surface is heated above a certain critical temperature and a film of vapor forms on the surface. Transition boiling is an intermediate, unstable form of boiling with elements of both types. The boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F but is lower with the decreased atmospheric pressure found at higher altitudes. Boiling water is used as a method of making it potable by killing microbes and viruses that may be present. The sensitivity of different micro-organisms to heat varies, but if water is held at for one minute, most micro-organisms and viruses are inactivated. Ten m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefly Squid
The firefly squid (''Watasenia scintillans''), also commonly known as the sparkling enope squid or hotaru-ika in Japan, is a species of squid in the family Enoploteuthidae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus ''Watasenia''. These tiny squid are found on the shores of Japan in springtime during spawning season, but spend most of their lives in deeper waters between . They are bioluminescent organisms and emit blue light from photophores, which some scientists have hypothesized could be used for communication, camouflage, or attracting food, but it is still unclear in the scientific community exactly how this species uses their bioluminescence. The firefly squid is a predator and actively hunts its food, which includes copepods, small fish, and other squids. The lifespan of a firefly squid is about one year. At the end of their lives females return close to shore to release their eggs, and then die shortly thereafter. This mass migration of firefly squid to the shore is a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Aberration
In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. Lenses and curved mirrors are prime examples, because this shape is easier to manufacture. Light rays that strike a spherical surface off-centre are refracted or reflected more or less than those that strike close to the centre. This deviation reduces the quality of images produced by optical systems. Overview A spherical lens has an aplanatic point (i.e., no spherical aberration) only at a radius that equals the radius of the sphere divided by the index of refraction of the lens material. A typical value of refractive index for crown glass is 1.5 (see list), which indicates that only about 43% of the area (67% of diameter) of a spherical lens is useful. It is often considered to be an imperfection of telescopes and other instruments which makes their focusing less than ideal due to the spherical shape of lenses and mirrors. This is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision). Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. In fact, a recent study suggests most living organisms on our planet ~3 billion years ago used retinal to convert sunlight into energy rather than chlorophyll. Since retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the Purple Earth Hypothesis. There are many forms of vitamin A — all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. Retinal itself is considered to be a form of vitamin A when eaten by an animal. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called retinene, and was renamed after it was discovered to be vitamin A aldehyde. Vertebrate animals ingest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm ( near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. '' Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or purple variations like magenta, for example, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid Counterillumination
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, Symmetry (biology)#Bilateral symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle (mollusc), mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the bioluminescence, ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chamel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)
