|
Spar (aeronautics)
In a fixed-wing aircraft, the spar is often the main structural member of the wing, running spanwise at right angles (or thereabouts depending on wing sweep) to the fuselage. The spar carries flight loads and the weight of the wings while on the ground. Other structural and forming members such as ribs may be attached to the spar or spars, with stressed skin construction also sharing the loads where it is used. There may be more than one spar in a wing or none at all. Where a single spar carries most of the force, it is known as the main spar. Spars are also used in other aircraft aerofoil surfaces such as the tailplane and fin and serve a similar function, although the loads transmitted may be different from those of a wing spar. Spar loads The wing spar provides the majority of the weight support and dynamic load integrity of cantilever monoplanes, often coupled with the strength of the wing 'D' box itself. Together, these two structural components collectively provide t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Interplane Strut
In aeronautics, bracing comprises additional structural members which stiffen the functional airframe to give it rigidity and strength under load. Bracing may be applied both internally and externally, and may take the form of strut, which act in compression or tension as the need arises, and/or wires, which act only in tension. In general, bracing allows a stronger, lighter structure than one which is unbraced, but external bracing in particular adds drag which slows down the aircraft and raises considerably more design issues than internal bracing. Another disadvantage of bracing wires is that they require routine checking and adjustment, or rigging, even when located internally. During the early years of aviation, bracing was a universal feature of all forms of aeroplane, including the monoplanes and biplanes which were then equally common. Today, bracing in the form of lift struts is still used for some light commercial designs where a high wing and light weight are more im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a p ... described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal vector, normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newton (unit), newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 Metre per second squared, meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Control Reversal
Control reversal is an adverse effect on the controllability of aircraft. The flight controls reverse themselves in a way that is not intuitive, so pilots may not be aware of the situation and therefore provide the wrong inputs; in order to roll to the left, for instance, they have to push the control stick to the right, the opposite of the normal direction. Causes There are several causes for this problem: pilot error, effects of high-speed flight, incorrectly connected controls, and various coupling forces on the aircraft. Equipment malfunction Equipment failure may cause flight controls to behave unexpectedly, for example the possible rudder reversal experienced onboard United Airlines Flight 585. Pilot error Pilot error is the most common cause of control reversal. In unusual attitudes it is not uncommon for the pilot to become disoriented and start feeding in incorrect control movements in order to regain level flight. This is particularly common when using helmet-mounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.png) |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
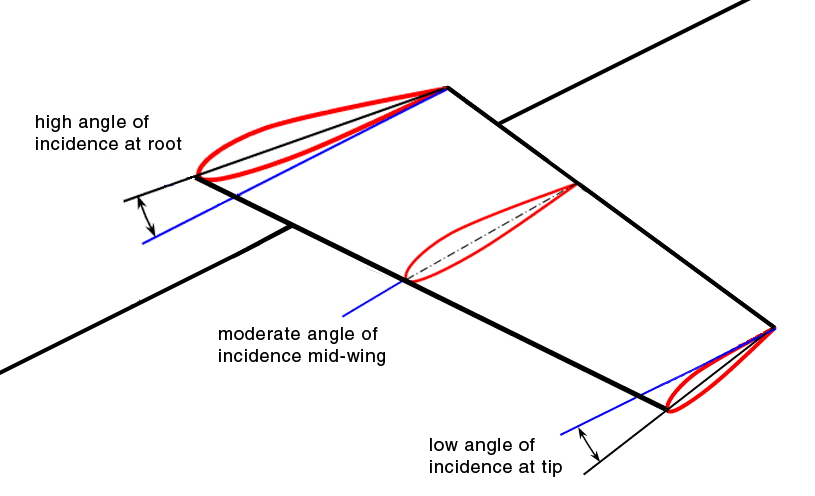 |
Washout (aviation)
Washout is a characteristic of aircraft wing design which deliberately reduces the lift distribution across the span of an aircraft’s wing. The wing is designed so that the angle of incidence is greater at the wing roots and decreases across the span, becoming lowest at the wing tip. This is usually to ensure that at stall speed the wing root stalls before the wing tips, providing the aircraft with continued aileron control and some resistance to spinning. Washout may also be used to modify the spanwise lift distribution to reduce lift-induced drag. Design considerations Washout is commonly achieved by designing the wing with a slight twist, reducing the angle of incidence from root to tip, and therefore causing a lower angle of attack at the tips than at the roots. This feature is sometimes referred to as structural washout, to distinguish it from aerodynamic washout. Wingtip stall is unlikely to occur symmetrically, especially if the aircraft is maneuvering. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Chord (aircraft)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the point where the chord intersects the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direction of the airflow. (If a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Moment Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law of motion. After some other definitions, Newton states in his first law of motion: The word "perseveres" is a direct translation from Newton's Latin. Other, less forceful terms such as "to continue" or "to remain" are commonly found in modern textbooks. The modern use follows from some changes in Newton's original mechanics (as stated in the ''Principia'') made by Euler, d'Alembert, and other Cartesians. The term inertia comes from the Latin word ''iners'', meaning idle, sluggish. The term inertia may also refer to the resistance of any physical object to a change in its velocity. This includes changes to the object's speed or direction of motion. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: * Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system; * Calibrated airspeed ("CAS"), indicated airspeed adjusted for pitot system position and installation error; * Equivalent airspeed ("EAS"), calibrated airspeed adjusted for compressibility effects; * True airspeed ("TAS"), equivalent airspeed adjusted for air density, and is also the speed of the aircraft through the air in which it is flying. Calibrated airspeed is typically within a few knots of indicated airspeed, while equivalent airspeed decreases slightly from CAS as aircraft altitude increases or at high speeds. With EAS constant, true airspeed increases as aircraft altitude increases. This is because air density decreases with higher altitude. The measurement and indication of airspeed is ordinarily accomplished on board an aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cessna 310
The Cessna 310 is an American four-to-six-seat, low-wing, twin-engine monoplane produced by Cessna between 1954 and 1980. It was the first twin-engine aircraft that Cessna put into production after World War II. Development The 310 first flew on January 3, 1953, with deliveries starting in late 1954. The sleek modern lines of the new twin were backed up by innovative features such as engine exhaust thrust augmenter tubes and the storage of all fuel in tip tanks in early models. In 1964, the engine exhaust was changed to flow under the wing instead of the augmenter tubes, which were considered to be noisy. Typical of Cessna model naming conventions, a letter was added after the model number to identify changes to the original design over the years. The first significant upgrade to the 310 series was the 310C in 1959, which introduced more powerful Continental IO-470-D engines. In 1960 the 310D featured swept-back vertical tail surfaces. An extra cabin window was added with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |